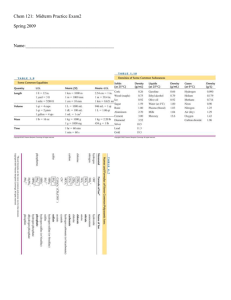
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Hess’s Law Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps ...
... Hess’s Law Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps ...
Unit 6 – Chemical Reactions: Particles and Energy
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
practice test2
... A) aluminum(III) sulfate. B) dialuminum trisulfate. C) dialuminum sulfate. D) dialuminum trisulfide. E) aluminum sulfate. ...
... A) aluminum(III) sulfate. B) dialuminum trisulfate. C) dialuminum sulfate. D) dialuminum trisulfide. E) aluminum sulfate. ...
Chemistry - Solutions
... Higher temperatures = faster dissolving due to greater kinetic energy of water molecules ...
... Higher temperatures = faster dissolving due to greater kinetic energy of water molecules ...
CH30S Chemical Reactions Part 2 Unit Review
... 19. A student placed 8.25g of aluminum metal into excess hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution. All of the aluminum reacted to form solid aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. a. Write the balanced equation for the above reaction. Include states for the reactants and products. b. Calculate the moles of alu ...
... 19. A student placed 8.25g of aluminum metal into excess hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution. All of the aluminum reacted to form solid aluminum chloride and hydrogen gas. a. Write the balanced equation for the above reaction. Include states for the reactants and products. b. Calculate the moles of alu ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... 15. A binary compound of zinc and sulfur contains 67.1% zinc by mass. What is the ratio of zinc and sulfur atoms in the compound? 16. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, 10B (19.9%), with an atomic mass of 10.0129, and 11B (80.1%) with an atomic mass of 11.00931. What is the atomic w ...
... 15. A binary compound of zinc and sulfur contains 67.1% zinc by mass. What is the ratio of zinc and sulfur atoms in the compound? 16. Naturally occurring boron consists of two isotopes, 10B (19.9%), with an atomic mass of 10.0129, and 11B (80.1%) with an atomic mass of 11.00931. What is the atomic w ...
Worksheet 9b - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... The decomposition of 18F follows first order kinetics (i.e. Rate = k[18F]) and has a halflife of 1.83 days. The initial amount of a fluorine-18 is 20.0 g. How much time must pass for 1.00 g to remain? ...
... The decomposition of 18F follows first order kinetics (i.e. Rate = k[18F]) and has a halflife of 1.83 days. The initial amount of a fluorine-18 is 20.0 g. How much time must pass for 1.00 g to remain? ...
Practice Test Packet
... [D] 0.10 [E] none of these 18. The correct mathematical expression for finding the molar solubility (S) of Sn(OH) 2 is: [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will rea ...
... [D] 0.10 [E] none of these 18. The correct mathematical expression for finding the molar solubility (S) of Sn(OH) 2 is: [A] 2S3 = Ksp [B] 108S5 = Ksp [C] 2S2 = Ksp [D] 4S3 = Ksp [E] 8S3 = Ksp 19. A weak acid, HF, is in solution with dissolved sodium fluoride, NaF. If HCl is added, which ion will rea ...
quant6stoichiom
... - if you know the amount of one substance in a chemical reaction (in particles, moles, or mass), you can calculate the amount of any other substance in the ...
... - if you know the amount of one substance in a chemical reaction (in particles, moles, or mass), you can calculate the amount of any other substance in the ...
Energy and Reactions
... and endothermic reaction in a graph Could (Grade B/A): Explain the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions. ...
... and endothermic reaction in a graph Could (Grade B/A): Explain the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions. ...
Name: 1) In a chemical reaction, the difference between the
... A catalyst is added as an additional reactant and is consumed but not regenerated. A catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway that requires less activation energy. A catalyst changes the kinds of products produced. A catalyst limits the amount of reactants used. ...
... A catalyst is added as an additional reactant and is consumed but not regenerated. A catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway that requires less activation energy. A catalyst changes the kinds of products produced. A catalyst limits the amount of reactants used. ...
Iodine Clock Reaction and Photochemical Reduction
... the beaker in diffuse light (inside locker or cupboard ). Add 50 mL of ferric chloride solution to the solution of oxalic acid and diammonium phosphate under stirring in diffuse light. A small precipitate initially formed dissolves on further stirring. Close your locker and open it only when needed. ...
... the beaker in diffuse light (inside locker or cupboard ). Add 50 mL of ferric chloride solution to the solution of oxalic acid and diammonium phosphate under stirring in diffuse light. A small precipitate initially formed dissolves on further stirring. Close your locker and open it only when needed. ...
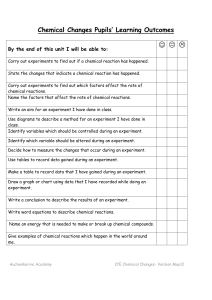
Chemical Reactions Unit Pupils` Learning Outcomes
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
... Chemical Changes Pupils’ Learning Outcomes ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 16 - A
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.