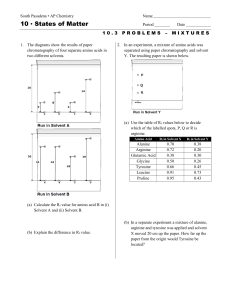
Chapter 19 - public.asu.edu
... Second Law of Thermodynamics 2nd Law: In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases. ∆Suniv = ∆Ssys + ∆Ssurr: the change in entropy of the universe is the sum of the change in entropy of the system and the change in entropy of the surroundings. Entropy is not conserved: ∆Suniv is ...
... Second Law of Thermodynamics 2nd Law: In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases. ∆Suniv = ∆Ssys + ∆Ssurr: the change in entropy of the universe is the sum of the change in entropy of the system and the change in entropy of the surroundings. Entropy is not conserved: ∆Suniv is ...
Notes #2 Chem 341
... _____________ _______ _______________ and from the enthalpy of reaction at some other temp. For an individual reactant or product: ......................................................... H = ..... For the entire reaction then: ...
... _____________ _______ _______________ and from the enthalpy of reaction at some other temp. For an individual reactant or product: ......................................................... H = ..... For the entire reaction then: ...
5. Physical and Chemical Change
... place. Gases are produced, but the gases are not water. They are oxygen and hydrogen, the substances that make up water. In the space shuttle’s main engines, liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen are mixed and burned as a fuel. Water—a new substance—is produced. Changes in which one or more new substanc ...
... place. Gases are produced, but the gases are not water. They are oxygen and hydrogen, the substances that make up water. In the space shuttle’s main engines, liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen are mixed and burned as a fuel. Water—a new substance—is produced. Changes in which one or more new substanc ...
Chemical Equations
... • To represent chemical equations correctly, equations must be balanced. • The number of atoms on both sides of the equation must be the same • Law of conservation of mass – the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products. • Atoms are not created or ...
... • To represent chemical equations correctly, equations must be balanced. • The number of atoms on both sides of the equation must be the same • Law of conservation of mass – the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products. • Atoms are not created or ...
Acid Base Equilibrium
... The stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base will be. We can categorize acids and bases according to their behavior in water. • 1. Strong acids completely transfer their protons to water. • No undissociated molecules remain in solution. • Their conjugate bases have negligible tendencies to ...
... The stronger an acid is, the weaker its conjugate base will be. We can categorize acids and bases according to their behavior in water. • 1. Strong acids completely transfer their protons to water. • No undissociated molecules remain in solution. • Their conjugate bases have negligible tendencies to ...
50 Forgotten Facts
... b) Adding a catalyst will _________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps from the reaction pathway (mechanism). c) Adding an inhibitor will __________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps to the reaction pathway. ...
... b) Adding a catalyst will _________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps from the reaction pathway (mechanism). c) Adding an inhibitor will __________________________ the activation energy by ___________________ steps to the reaction pathway. ...
Solutions!
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...
The Relation between Salt and Ionic Transport Coefficients
... in (c) largely cancel each other. Thus, for example, if the solutions contain NaC1 at 0.1 and 0.01 M, respectively, the values for ~ according to the two definitions agree within 2 %. If, however, the lower concentration is decreased to a very small value, the last term in (e) vanishes while the oth ...
... in (c) largely cancel each other. Thus, for example, if the solutions contain NaC1 at 0.1 and 0.01 M, respectively, the values for ~ according to the two definitions agree within 2 %. If, however, the lower concentration is decreased to a very small value, the last term in (e) vanishes while the oth ...
Aqueous chemistry is a very important component to laboratory
... The partially negative oxygen atom in water will surround the positive cations, while the partially positive hydrogen atoms will surround the negative anions. If two electrodes (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solut ...
... The partially negative oxygen atom in water will surround the positive cations, while the partially positive hydrogen atoms will surround the negative anions. If two electrodes (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solut ...
Problems - Department of Chemistry HKU
... 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high pressures of hydrogen chloride (up to 25 atm) and propene (up to 5 atm) were exami ...
... 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high pressures of hydrogen chloride (up to 25 atm) and propene (up to 5 atm) were exami ...
Test Objectives for Unit 11: Oxidation/Reduction
... Write correct equations for the oxidation half-reaction and the reduction half-reaction in a redox reaction. Balance a redox equation, by balancing electrons lost with electrons gained. Use Table J to predict whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Use a table of standard electrode po ...
... Write correct equations for the oxidation half-reaction and the reduction half-reaction in a redox reaction. Balance a redox equation, by balancing electrons lost with electrons gained. Use Table J to predict whether a particular redox reaction will occur or not. Use a table of standard electrode po ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.