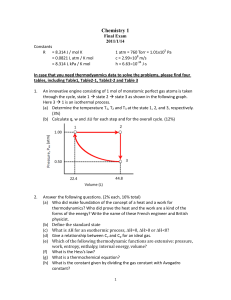
Analytical Chemistry
... Since molarity involves a basis of solution volume, it is apparent that the molarity of a solution will change as volume changes which is associated with changes in temperature. Formal Concentration: Some substances do not exist in molecular form, whether in solid or solution form, they remain in io ...
... Since molarity involves a basis of solution volume, it is apparent that the molarity of a solution will change as volume changes which is associated with changes in temperature. Formal Concentration: Some substances do not exist in molecular form, whether in solid or solution form, they remain in io ...
General Chemistry
... • Solutes and solvent are components of the solution. • In the process of making solutions with condensed phases, intermolecular forces become rearranged. • Consider NaCl (solute) dissolving in water (solvent): – the water H-bonds have to be interrupted, – NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl-, – ion-di ...
... • Solutes and solvent are components of the solution. • In the process of making solutions with condensed phases, intermolecular forces become rearranged. • Consider NaCl (solute) dissolving in water (solvent): – the water H-bonds have to be interrupted, – NaCl dissociates into Na+ and Cl-, – ion-di ...
03.Thermodynamics in Corrosion Engineering
... By altering the pH and potential to the regions of immunity and passivation, corrosion can be controlled. For example, on increasing the pH of environment in moving to slightly alkaline regions, the corrosion of iron can be controlled Changing the potential of iron to more negative values elimin ...
... By altering the pH and potential to the regions of immunity and passivation, corrosion can be controlled. For example, on increasing the pH of environment in moving to slightly alkaline regions, the corrosion of iron can be controlled Changing the potential of iron to more negative values elimin ...
Unit F335/01
... organise information clearly and coherently, using specialist vocabulary when appropriate. ...
... organise information clearly and coherently, using specialist vocabulary when appropriate. ...
Ksp - ChemConnections
... Qsp = Ksp : When a solution becomes saturated, no more solute will dissolve, and the solution is called “saturated.” There will be no changes that will occur. Qsp > Ksp : Precipitates will form until the solution becomes saturated. Qsp< Ksp : Solution is unsaturated, and no precipitate will fo ...
... Qsp = Ksp : When a solution becomes saturated, no more solute will dissolve, and the solution is called “saturated.” There will be no changes that will occur. Qsp > Ksp : Precipitates will form until the solution becomes saturated. Qsp< Ksp : Solution is unsaturated, and no precipitate will fo ...
Paired with Lecture
... • We just studied Phase Diagrams which are thermodynamic maps which tell us the equilibrium phases present at any specific combination of temperature, pressure, and composition • These phase diagrams are based on the concept of Gibbs Free Energy, DG, which we have briefly introduced before: DG is ...
... • We just studied Phase Diagrams which are thermodynamic maps which tell us the equilibrium phases present at any specific combination of temperature, pressure, and composition • These phase diagrams are based on the concept of Gibbs Free Energy, DG, which we have briefly introduced before: DG is ...
Chapter 4
... K2CrO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) Complete Ionic equation show dissolved electrolytes as the ions. 2K+ + CrO4-2 + Ba+2 + 2 NO3- BaCrO4(s) + 2K+ + 2 NO3 Spectator ions are those that don’t react. ...
... K2CrO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) Complete Ionic equation show dissolved electrolytes as the ions. 2K+ + CrO4-2 + Ba+2 + 2 NO3- BaCrO4(s) + 2K+ + 2 NO3 Spectator ions are those that don’t react. ...
Course: Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry
... legible. Any errors will be crossed out with ONE line. Errors are not to be scribbled out. Formal lab reports will not need to be done for each lab. However, they will be done from time to time and will be awarded points instead of the lab notebook. Lab is an essential part of your AP experience. Th ...
... legible. Any errors will be crossed out with ONE line. Errors are not to be scribbled out. Formal lab reports will not need to be done for each lab. However, they will be done from time to time and will be awarded points instead of the lab notebook. Lab is an essential part of your AP experience. Th ...
lecture slides of chap19_FU
... Changing the stoichiometric coefficients of a half-cell reaction does not change the value of E0 Zn2+ (1 M) + 2eE0= -0.76V 2Zn2+ (1 M) + 4eE0= -0.76V ...
... Changing the stoichiometric coefficients of a half-cell reaction does not change the value of E0 Zn2+ (1 M) + 2eE0= -0.76V 2Zn2+ (1 M) + 4eE0= -0.76V ...
Chapter 15
... formula units dissolved. Thus, one mole of NaCl dissolved in water produces more than one mole (actually about 2 moles) of solute particles. For electrolytes, we expect i to be equal to the number of ions into which a substance dissociates into in solution. Note: for nonelectrolyte solutes, i = 1. T ...
... formula units dissolved. Thus, one mole of NaCl dissolved in water produces more than one mole (actually about 2 moles) of solute particles. For electrolytes, we expect i to be equal to the number of ions into which a substance dissociates into in solution. Note: for nonelectrolyte solutes, i = 1. T ...
Concentration of solutions
... • Vapor pressure lowering. Boiling point is higher and freezing point of a solution is lower than that of a pure solvent. This is due to the presence of nonvolatile solutes. These are substances that have little tendency to become a gas under existing conditions. ...
... • Vapor pressure lowering. Boiling point is higher and freezing point of a solution is lower than that of a pure solvent. This is due to the presence of nonvolatile solutes. These are substances that have little tendency to become a gas under existing conditions. ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.