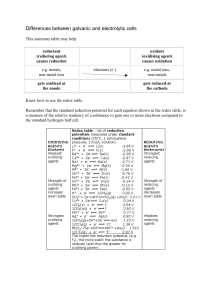
Differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells
... Remember that the standard reduction potential for each equation shown in the redox table, is a measure of the relative tendency of a substance to gain one or more electrons compared to the standard hydrogen half cell. ...
... Remember that the standard reduction potential for each equation shown in the redox table, is a measure of the relative tendency of a substance to gain one or more electrons compared to the standard hydrogen half cell. ...
LECTURE 6 - GENESIS OF MINERAL1
... Equilibrium: - The condition of minimum energy for a system. Phase: A physically and chemically homogeneous, mechanically separable part of a physicalchemical system. Degree of freedom (also known as variance): A variable, which if changed, does not result in a change in the equilibrium assemblage o ...
... Equilibrium: - The condition of minimum energy for a system. Phase: A physically and chemically homogeneous, mechanically separable part of a physicalchemical system. Degree of freedom (also known as variance): A variable, which if changed, does not result in a change in the equilibrium assemblage o ...
document
... • Sometimes we can’t always use our judgement and we need to calculate the entropy • In order to do this, we need the standard molar entropies of the products and the reactants as well as the number of moles of each S = ...
... • Sometimes we can’t always use our judgement and we need to calculate the entropy • In order to do this, we need the standard molar entropies of the products and the reactants as well as the number of moles of each S = ...
Determination of K of Weak Acids
... The ionization constant of a weak acid can be determined experimentally by measuring the H3O concentration in a dilute aqueous solution of the weak acid. This procedure is most accurate when the solution contains equal molar amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate base. Consider acetic acid as an ...
... The ionization constant of a weak acid can be determined experimentally by measuring the H3O concentration in a dilute aqueous solution of the weak acid. This procedure is most accurate when the solution contains equal molar amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate base. Consider acetic acid as an ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... Would not be spontaneous because it is endothermic (+enthalpy) and reactants are smaller and in greater quantity (more disordered than the products (more orderly) 8. Balance the following using the half-reaction method. Identify the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the atom oxidized and the atom ...
... Would not be spontaneous because it is endothermic (+enthalpy) and reactants are smaller and in greater quantity (more disordered than the products (more orderly) 8. Balance the following using the half-reaction method. Identify the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the atom oxidized and the atom ...
Physical chemistry 1
... • Joule-Thomson effect, adiabates and isotherms of an ideal gas, the second law of thermodynamics, entropy. • Entropy, entropy changes in the environment, entropy of the irreversible processes, Clausius inequality, the entropy dependence on temperature. • The third law of thermodynamics, Helmholtz a ...
... • Joule-Thomson effect, adiabates and isotherms of an ideal gas, the second law of thermodynamics, entropy. • Entropy, entropy changes in the environment, entropy of the irreversible processes, Clausius inequality, the entropy dependence on temperature. • The third law of thermodynamics, Helmholtz a ...
A simple calorimeter was used as a vessel to measure the heat
... g) A student combines Ammonium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate to perform a reaction. The solution vessel felt cold to the touch. This reaction produces +126kJ of energy. i. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction (double replacement with energy ...
... g) A student combines Ammonium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate to perform a reaction. The solution vessel felt cold to the touch. This reaction produces +126kJ of energy. i. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction (double replacement with energy ...
unit 4 review sheet
... When “a” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coeff ...
... When “a” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the sum of these coefficients? g. When “c” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coefficients, what is the coefficient for HCl? h. When “d” is correctly balanced using the smallest whole number coeff ...
fied molal concentration. The molality, or molal concentration, is the
... In scenarios where the activity does not equal the molar concentration, the activity is necessary. In these cases, the concentration alone is not enough to accurately solve the Nernst equation due to effects like ionic strength and ion size. While the molar concentration is easier to calculate when ...
... In scenarios where the activity does not equal the molar concentration, the activity is necessary. In these cases, the concentration alone is not enough to accurately solve the Nernst equation due to effects like ionic strength and ion size. While the molar concentration is easier to calculate when ...
File
... can usually be separated physically composition is not uniform has no chemical formula ...
... can usually be separated physically composition is not uniform has no chemical formula ...
Chemistry Standards Review
... 23. An aerosol can contains gas at 150 kPa. Using the formula below, what will the pressure be if the can is heated from 20oC to 85oC? P1 = P2 T1 T2 (A) 123 kPa (B) 183 kPa (C) 240 kPa (D) 699 kPa 24. How many moles of gas fill a volume of 18.1 L at 85.4 kPa and 10oC? (R = 8.314) (A) 0.657 mol (B) 1 ...
... 23. An aerosol can contains gas at 150 kPa. Using the formula below, what will the pressure be if the can is heated from 20oC to 85oC? P1 = P2 T1 T2 (A) 123 kPa (B) 183 kPa (C) 240 kPa (D) 699 kPa 24. How many moles of gas fill a volume of 18.1 L at 85.4 kPa and 10oC? (R = 8.314) (A) 0.657 mol (B) 1 ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.























