Chemical Reactions
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
File
... is evidently true? A) The precision is poor, but the accuracy is excellent B) The precision is good, but the accuracy cannot be evaluated from the given information. C) The accuracy would be better if a more concentrated NaOH solution were used D) All three titrations have the same amount of error E ...
... is evidently true? A) The precision is poor, but the accuracy is excellent B) The precision is good, but the accuracy cannot be evaluated from the given information. C) The accuracy would be better if a more concentrated NaOH solution were used D) All three titrations have the same amount of error E ...
Ch 13 kinetics
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
... More than a balanced chemical equation, a reaction mechanism ________________________________________ . Provides a detailed picture of how a reaction occurs. Elementary step: Any process that occurs ____________________________________________________________________ Makes either ___________________ ...
Time
... - explain reaction rates in terms of the collision theory - effect of changes in temperature, concentrations, nature of the reactants, etc. - identify reaction mechanisms: catalysis, reaction intermediates, net overall equations, ratedetermining steps - explain how catalysts speed up reaction rates ...
... - explain reaction rates in terms of the collision theory - effect of changes in temperature, concentrations, nature of the reactants, etc. - identify reaction mechanisms: catalysis, reaction intermediates, net overall equations, ratedetermining steps - explain how catalysts speed up reaction rates ...
Slide 1
... Dynamic equilibrium will be established when the rate at which ions are leaving the surface is exactly equal to the rate at which they are joining it again. At that point there will be a constant negative charge on the magnesium, and a constant number of magnesium ions present in the solution around ...
... Dynamic equilibrium will be established when the rate at which ions are leaving the surface is exactly equal to the rate at which they are joining it again. At that point there will be a constant negative charge on the magnesium, and a constant number of magnesium ions present in the solution around ...
Chem 12 UNIT TWO CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM 7.1 REVERSIBLE
... value for entropy means very random. If entropy increases during a chemical reaction, it means the system is becoming more random or disordered. These two variables are related in the Gibb's free energy equation which says: ΔGo = ΔH - TΔSo o indicates standard state conditions. where ΔG is a measure ...
... value for entropy means very random. If entropy increases during a chemical reaction, it means the system is becoming more random or disordered. These two variables are related in the Gibb's free energy equation which says: ΔGo = ΔH - TΔSo o indicates standard state conditions. where ΔG is a measure ...
- Deans Community High School
... c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction E A using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the graph. ii) which is the better catalyst for the reaction? Explain your choice. d) The gold and platinum cat ...
... c) Gold and platinum both catalyse the reaction. For the forward reaction E A using gold is 30 kJ, while EA using platinum is 40 kJ. i) using different dotted lines add this information to the graph. ii) which is the better catalyst for the reaction? Explain your choice. d) The gold and platinum cat ...
02_Lecture_Presentation
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or ...
... • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or ...
Objective: The objective of the lab is to study the types of reactions
... soluble. It is dissolved in water and that is called aqueous. The material hasn’t yet formed, it is ions floating around. Think of salt water, when you put salt in water it dissolves in. You can’t see the salt, but if you let the water evaporate you would get a salt residue in the beaker. The (s) me ...
... soluble. It is dissolved in water and that is called aqueous. The material hasn’t yet formed, it is ions floating around. Think of salt water, when you put salt in water it dissolves in. You can’t see the salt, but if you let the water evaporate you would get a salt residue in the beaker. The (s) me ...
decomposition - Chemical Minds
... 6) A group of students carried out an investigation into whether or not various solid carbonates undergo thermal decomposition. The students found that copper (II) carbonate did decompose when heated. Discuss the thermal decomposition of copper (II) carbonate. In your answer, you should: name the ...
... 6) A group of students carried out an investigation into whether or not various solid carbonates undergo thermal decomposition. The students found that copper (II) carbonate did decompose when heated. Discuss the thermal decomposition of copper (II) carbonate. In your answer, you should: name the ...
AP Semestar Exam REVIEW
... ____ 22. Which of the following are strong bases: NH3, NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF? a. NH3 and HF b. NaOH and Ba(OH)2 c. NH3 and NaOH d. NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF e. NH3, NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF ____ 23. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction of lithium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid? a. H+ + I- HCl( ...
... ____ 22. Which of the following are strong bases: NH3, NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF? a. NH3 and HF b. NaOH and Ba(OH)2 c. NH3 and NaOH d. NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF e. NH3, NaOH, Ba(OH)2, and HF ____ 23. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction of lithium hydroxide with hydroiodic acid? a. H+ + I- HCl( ...
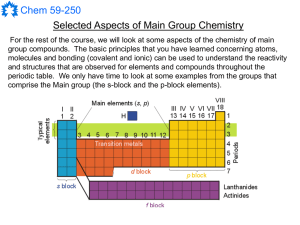
Main Group Notes 1
... up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state from -2 to +6 electrons (with a complete octet) around the group 16 atom so such compounds are also “electron-rich” but the high electronegativities of O and S make them good oxidizing agents. ...
... up to six bonds. This provides for common oxidation state from -2 to +6 electrons (with a complete octet) around the group 16 atom so such compounds are also “electron-rich” but the high electronegativities of O and S make them good oxidizing agents. ...
Second exam 2014 with answers
... Last Name: ____________________________________________ First Name: _____________________________________________ Note: There are 10 questions in this exam (check both sides of the sheet). Fill in your answer in the blank space provided immediately following each question. 1/2 point will be subtract ...
... Last Name: ____________________________________________ First Name: _____________________________________________ Note: There are 10 questions in this exam (check both sides of the sheet). Fill in your answer in the blank space provided immediately following each question. 1/2 point will be subtract ...
Please do not remove this page. The periodic table, constants, and
... In one trial 10.0 mL of 1.00 x 10 M Fe3+ (aq) is combined with 50.0 mL of 0.0200 M SCN– (aq) and diluted to a total volume of 100.0 mL. The concentration of FeSCN2+ (aq) at equilibrium is determined via an absorbance measurement to be 5.75 x 10–5 M. What is [Fe3+] at equilibrium? a. 5.75 x 10–5 M ...
... In one trial 10.0 mL of 1.00 x 10 M Fe3+ (aq) is combined with 50.0 mL of 0.0200 M SCN– (aq) and diluted to a total volume of 100.0 mL. The concentration of FeSCN2+ (aq) at equilibrium is determined via an absorbance measurement to be 5.75 x 10–5 M. What is [Fe3+] at equilibrium? a. 5.75 x 10–5 M ...
Aqueous Reactions
... became ions. This is the result of a transfer of electrons. In the above reaction, an electron is transferred from a sodium atom to a chlorine atom. The sodium atoms now have ten electrons, instead of eleven. This means that the sodium has one more proton than electron and has a charge of +1. The c ...
... became ions. This is the result of a transfer of electrons. In the above reaction, an electron is transferred from a sodium atom to a chlorine atom. The sodium atoms now have ten electrons, instead of eleven. This means that the sodium has one more proton than electron and has a charge of +1. The c ...
ACP Chemistry Semester 1 Final Exam - Doc-U-Ment
... D) AgC2H3O2 + Cu(NO3)2 E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate. 12) Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed. A) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2CO3(s) B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3( ...
... D) AgC2H3O2 + Cu(NO3)2 E) None of the above solution pairs will produce a precipitate. 12) Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed. A) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2CO3(s) B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3( ...
chapter 4 review_package
... 9. Given the following balanced equations, solve the stoichiometric problems (PLO-D5) a. Ammonia combines with oxygen gas in the following reaction: 4 NH3 + 5O2 → 6H2O + 4NO i. How many moles of NH3 are needed to combine with 3.57 moles of O2 gas? ...
... 9. Given the following balanced equations, solve the stoichiometric problems (PLO-D5) a. Ammonia combines with oxygen gas in the following reaction: 4 NH3 + 5O2 → 6H2O + 4NO i. How many moles of NH3 are needed to combine with 3.57 moles of O2 gas? ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
Chemical reaction model:
... irrespective of the crystal morphology [7]. The initial radicals formed are essentially alkyl radicals that react with oxygen to degrade to allyl and peroxy radicals. O’Neill et al. [30] evaluated the nature of these free radicals in shelf aging using Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. They ...
... irrespective of the crystal morphology [7]. The initial radicals formed are essentially alkyl radicals that react with oxygen to degrade to allyl and peroxy radicals. O’Neill et al. [30] evaluated the nature of these free radicals in shelf aging using Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. They ...
do reactions of hydroxyl radicals with metal ion go via outer sphere
... Possible explanations for the behaviour displayed on the graph can be given from a consideration of theoretical and literature data. Considering first the ions which show no correlation between log k and E°, Ag (1), TI (I) and Au (I) (having a completed d shell) and Cu e} undergo very rapid exchange ...
... Possible explanations for the behaviour displayed on the graph can be given from a consideration of theoretical and literature data. Considering first the ions which show no correlation between log k and E°, Ag (1), TI (I) and Au (I) (having a completed d shell) and Cu e} undergo very rapid exchange ...
Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution 4.1 Aqueous Solutions
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
... 22.5 mL of 0.383 M H2SO4 are required to neutralize 20.0 mL of a KOH solution. Calculate the molarity of the KOH solution. H2SO4 + 2 KOH d K2SO4 + 2 H2O M KOH = (0.0225 L H2SO4)(0.383 mol H2SO4/L H2SO4)(2 mol KOH/ 1 mol H2SO4)/ (0.0200 mL KOH) = ...
practice unit #2 exam
... A. The higher the activation energy barrier, the faster the reaction. B. Increasing the concentration of a reactant may increase the rate of a reaction. C. Adding a catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction for both the forward and reverse reactions. D. Increasing the concentration increases the rate ...
... A. The higher the activation energy barrier, the faster the reaction. B. Increasing the concentration of a reactant may increase the rate of a reaction. C. Adding a catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction for both the forward and reverse reactions. D. Increasing the concentration increases the rate ...
11-1 SECTION 11 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry: Study of
... Most chemical reactions are accompanied by the release of energy to the surroundings or absorption of energy from the surroundings, or put more simply the reacting system gets hotter or cooler as the reaction proceeds. The most common form of energy transferred is heat. This section introduces the l ...
... Most chemical reactions are accompanied by the release of energy to the surroundings or absorption of energy from the surroundings, or put more simply the reacting system gets hotter or cooler as the reaction proceeds. The most common form of energy transferred is heat. This section introduces the l ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
... double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2H3O2– b) Na+, OH– ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.