Lecture 18. Chemical Equilibrium (Ch. 5)
... always taken to the power of their stoichiometric factors, equals a constant K which has a numerical value that depends on the temperature and pressure. In particular, - the exponential temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant K is due to the Boltzmann factor: ...
... always taken to the power of their stoichiometric factors, equals a constant K which has a numerical value that depends on the temperature and pressure. In particular, - the exponential temperature dependence of the equilibrium constant K is due to the Boltzmann factor: ...
File
... A) electron and neutron B) electron and proton C) proton and neutron D) proton and positron 11. Atoms of different isotopes of the same element differ in their total number of A) electrons B) neutrons C) protons D) valence electrons 12. The stability of an isotope is based on its A) number of neutro ...
... A) electron and neutron B) electron and proton C) proton and neutron D) proton and positron 11. Atoms of different isotopes of the same element differ in their total number of A) electrons B) neutrons C) protons D) valence electrons 12. The stability of an isotope is based on its A) number of neutro ...
Cl -1
... 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compound is always -1. 5. Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 unless it is combined with F (when it is +2), or it is in a per ...
... 3. The more-electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compound is always -1. 5. Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 unless it is combined with F (when it is +2), or it is in a per ...
Code: I1 Title: Heterogeneous Catalysis Lecturer: Prof S D Jackson
... Evaluate the formal oxidation states and d-electron counts of transition metal organometallic compounds, and be able to relate these to the types of ligand in the complex. Explain synergic bonding using simple molecular orbital theory and hence explain why certain ligands such as CO are able to stab ...
... Evaluate the formal oxidation states and d-electron counts of transition metal organometallic compounds, and be able to relate these to the types of ligand in the complex. Explain synergic bonding using simple molecular orbital theory and hence explain why certain ligands such as CO are able to stab ...
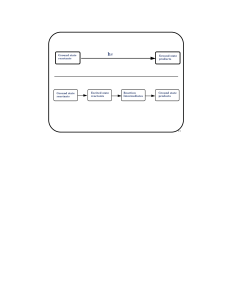
Ground state reactants Ground state products Ground state
... Singlet oxygen is a better oxidant than ground state oxygen. When the excitation energy of singlet oxygen is taken into consideration the values of E˚ (1O2/ O2• ) are 0.34 V in dimethylformamide and 0.79 V in water. Singlet oxygen oxidizes molecules such as N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-pphenylenediamine to ...
... Singlet oxygen is a better oxidant than ground state oxygen. When the excitation energy of singlet oxygen is taken into consideration the values of E˚ (1O2/ O2• ) are 0.34 V in dimethylformamide and 0.79 V in water. Singlet oxygen oxidizes molecules such as N,N,N',N'-tetramethyl-pphenylenediamine to ...
13.0 Redox Reactions PowerPoint
... transferred between entities • The total number of electrons gained in the reduction equals the total number of electrons lost in the oxidation • Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by an entity • Oxidation is a process in which electrons are lost by an entity • Both reduction and o ...
... transferred between entities • The total number of electrons gained in the reduction equals the total number of electrons lost in the oxidation • Reduction is a process in which electrons are gained by an entity • Oxidation is a process in which electrons are lost by an entity • Both reduction and o ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group ...
... about a double bond and the requirement for two different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the C=C group ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... for each bag of brownie mix, how many bags of brownie mix do you need if you want to use up a total of 3 eggs and 1 cup of oil? In a reaction between copper metal and silver nitrate, 12.7 g Cu produced 38.1 g Ag. What is the percent yield of silver in this reaction? ...
... for each bag of brownie mix, how many bags of brownie mix do you need if you want to use up a total of 3 eggs and 1 cup of oil? In a reaction between copper metal and silver nitrate, 12.7 g Cu produced 38.1 g Ag. What is the percent yield of silver in this reaction? ...
File
... How catalysts work: “to avoid a hill, build a tunnel.” A Catalyst- is an introduced substance which has an alternate mechanism with a lower activation energy…and - a catalyst NEVER changes the PE of reactants or of products - only the route between them. - also there is no change in H of the reacti ...
... How catalysts work: “to avoid a hill, build a tunnel.” A Catalyst- is an introduced substance which has an alternate mechanism with a lower activation energy…and - a catalyst NEVER changes the PE of reactants or of products - only the route between them. - also there is no change in H of the reacti ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... of the following is true for: C5H12(l) + 8O2(g) → 5CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) a) 9 moles of reactants chemically change into 11 moles of product, or b) 9 atoms of reactants chemically change into 11 atoms of product? How many moles of aluminum react with 1.2 mol of FeO: ...
... of the following is true for: C5H12(l) + 8O2(g) → 5CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) a) 9 moles of reactants chemically change into 11 moles of product, or b) 9 atoms of reactants chemically change into 11 atoms of product? How many moles of aluminum react with 1.2 mol of FeO: ...
Chapter 12 Review “Stoichiometry”
... of the following is true for: C5H12(l) + 8O2(g) → 5CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) a) 9 moles of reactants chemically change into 11 moles of product, or b) 9 atoms of reactants chemically change into 11 atoms of product? How many moles of aluminum react with 1.2 mol of FeO: ...
... of the following is true for: C5H12(l) + 8O2(g) → 5CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) a) 9 moles of reactants chemically change into 11 moles of product, or b) 9 atoms of reactants chemically change into 11 atoms of product? How many moles of aluminum react with 1.2 mol of FeO: ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... In this reaction there is an increase in the entropy because there are more moles of products than reactants (from 2 to 7), creating more disorder. The enthalpy change is small as there are similar numbers of bonds in both complexes. Free energy ΔG will be negative as ΔS is positive and ΔH is small. ...
... In this reaction there is an increase in the entropy because there are more moles of products than reactants (from 2 to 7), creating more disorder. The enthalpy change is small as there are similar numbers of bonds in both complexes. Free energy ΔG will be negative as ΔS is positive and ΔH is small. ...
Problem Set: Empirical and Molecular Formulas
... b) When 100.0 g of P4O10 are reacted with 200.0 g of H2O, what is the theoretical yield of phosphoric acid? c) If the actual yield is 126.24 g of H3PO4, what is the percent yield for this reaction? ...
... b) When 100.0 g of P4O10 are reacted with 200.0 g of H2O, what is the theoretical yield of phosphoric acid? c) If the actual yield is 126.24 g of H3PO4, what is the percent yield for this reaction? ...
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... In moving across the transition series, however, the nuclear charge is also increasing, but electrons are being added to an INNER d sub-shell. The outer 4s electrons, which determine the atomic radii, are more effectively shielded from the increasing nuclear charge (1° shielding effect). Consequentl ...
... In moving across the transition series, however, the nuclear charge is also increasing, but electrons are being added to an INNER d sub-shell. The outer 4s electrons, which determine the atomic radii, are more effectively shielded from the increasing nuclear charge (1° shielding effect). Consequentl ...
Chapter 17: Thermodynamics
... heat and other forms of energy. Internal energy (U): the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles making up a system. State Function: a property of a system that depends only on its present state which is determined by variables such as temperature and pressure. ...
... heat and other forms of energy. Internal energy (U): the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles making up a system. State Function: a property of a system that depends only on its present state which is determined by variables such as temperature and pressure. ...
CO Oxidation on Palladium. 2. A Combined
... reaction cell in the batch mode. Since in the CO + l / 2 0 2 C02 reaction three molecules of reactants produce two molecules of products, and no product other than C02 is formed, the kinetics of C O oxidation can be followed conveniently by monitoring the total pressure change during the course of r ...
... reaction cell in the batch mode. Since in the CO + l / 2 0 2 C02 reaction three molecules of reactants produce two molecules of products, and no product other than C02 is formed, the kinetics of C O oxidation can be followed conveniently by monitoring the total pressure change during the course of r ...
chemical reaction
... Chemical reactions are described by chemical equations. A chemical equation represents, with symbols and formulas, the identities and relative molecular or molar amounts of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. For example, the following chemical equation shows that the reactant ammoni ...
... Chemical reactions are described by chemical equations. A chemical equation represents, with symbols and formulas, the identities and relative molecular or molar amounts of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. For example, the following chemical equation shows that the reactant ammoni ...
Dec. 15 , 2012, 9:00 am – noon - Dr. K. Brown
... (b) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the following molecules and indicate whether they are polar or non-polar. (3 marks) The central atom has been underlined in each molecule. i) CF4 ...
... (b) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the following molecules and indicate whether they are polar or non-polar. (3 marks) The central atom has been underlined in each molecule. i) CF4 ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... • In the 1930’s Linus Pauling introduced the concept of hybridization to explain chemical bond formation. Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom to generate a set of new atomic orbitals called hybrid orbitals. • Mixing an s orbital with one of the p orbitals generates two equivale ...
... • In the 1930’s Linus Pauling introduced the concept of hybridization to explain chemical bond formation. Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom to generate a set of new atomic orbitals called hybrid orbitals. • Mixing an s orbital with one of the p orbitals generates two equivale ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS XII (2013-14)
... (a) (i)Hinsberg test positive for primary amines and correct reactions (ii) NaHCO3 teast is given by carboxylic acids and correct reactions (b) : (a) CH3OH + CO → CH3COOH ...
... (a) (i)Hinsberg test positive for primary amines and correct reactions (ii) NaHCO3 teast is given by carboxylic acids and correct reactions (b) : (a) CH3OH + CO → CH3COOH ...
Pages from PS 11 Textbook for Lab
... change for a given reaction, called the enthalpy of reaction, ΔHR, can be readily calculated. The convention is to define the standard enthalpy of formation, ΔH°f , to specific molecular species, and then tabulate those values of ΔH°f . Because enthalpy is a state function, we are concerned only wit ...
... change for a given reaction, called the enthalpy of reaction, ΔHR, can be readily calculated. The convention is to define the standard enthalpy of formation, ΔH°f , to specific molecular species, and then tabulate those values of ΔH°f . Because enthalpy is a state function, we are concerned only wit ...
GCSE_C2_Revision_+_Exam_Questions
... Substances that consist of simple molecules have only weak forces between the molecules (intermolecular forces). It is these intermolecular forces that are overcome, not the covalent bonds, when the substance melts or boils. Substances that consist of simple molecules do not conduct electricity beca ...
... Substances that consist of simple molecules have only weak forces between the molecules (intermolecular forces). It is these intermolecular forces that are overcome, not the covalent bonds, when the substance melts or boils. Substances that consist of simple molecules do not conduct electricity beca ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... questions or answers prior to the examination and that you have neither given nor received assistance in answering any of the questions during the examination. Your answer sheet and answer booklet cannot be accepted if you fail to sign this ...
... questions or answers prior to the examination and that you have neither given nor received assistance in answering any of the questions during the examination. Your answer sheet and answer booklet cannot be accepted if you fail to sign this ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.