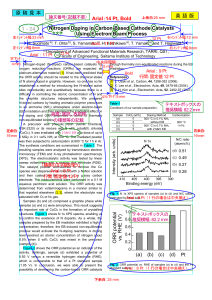
Year 9 Chemical Sciences Program Term 3 Course 2 2017
... describing in simple terms how alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation are released from unstable atoms ...
... describing in simple terms how alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation are released from unstable atoms ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... illustrate and explain the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds determine the distribution of electrons in the major energy levels for the first thirtyeighth elements and for ions in groups 1, 2, 3, 15, 16, and 17 state the octet rule predict the ionic charge for ions in the main ...
... illustrate and explain the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds determine the distribution of electrons in the major energy levels for the first thirtyeighth elements and for ions in groups 1, 2, 3, 15, 16, and 17 state the octet rule predict the ionic charge for ions in the main ...
Modeling the Rate of Heterogeneous Reactions
... point of view one distinguishes between hard sphere and soft interactions. Hard sphere interactions are very strong lateral interactions, in which the adsorbed species behave as hard spheres and exclude neighboring places from being occupied. This can be incorporated into the reactant pattern (Fig. ...
... point of view one distinguishes between hard sphere and soft interactions. Hard sphere interactions are very strong lateral interactions, in which the adsorbed species behave as hard spheres and exclude neighboring places from being occupied. This can be incorporated into the reactant pattern (Fig. ...
Document
... It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multiply the first reaction by 2. Note that we also multiply DH by 2. ...
... It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multiply the first reaction by 2. Note that we also multiply DH by 2. ...
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
... Chemical Equation: we represent a chemical reaction in the form of a chemical equation, using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical eq ...
... Chemical Equation: we represent a chemical reaction in the form of a chemical equation, using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical eq ...
Week of Sept. 20
... · 9 Valence Orbitals: upper limit of 9 bonds may be formed. In most cases a maximum of 6 σ bonds are formed and the remaining d orbitals are non-bonding. It's these non-bonding d orbitals that give TM complexes many of their unique properties. · 18 electron rule: upper limit of 18 e- can be accomoda ...
... · 9 Valence Orbitals: upper limit of 9 bonds may be formed. In most cases a maximum of 6 σ bonds are formed and the remaining d orbitals are non-bonding. It's these non-bonding d orbitals that give TM complexes many of their unique properties. · 18 electron rule: upper limit of 18 e- can be accomoda ...
① Name AP CHEM __/__/__ Chapter 12 Outline
... The kinetic molecular theory of gases predicts that an increase in temperature raises molecular velocities and so increases the frequency of collisions between molecules. This agrees with the observation that reaction rates are greater at higher temperatures qualitatively. However, it is found tha ...
... The kinetic molecular theory of gases predicts that an increase in temperature raises molecular velocities and so increases the frequency of collisions between molecules. This agrees with the observation that reaction rates are greater at higher temperatures qualitatively. However, it is found tha ...
Effects of antioxidants for the degradation of flame
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
Questions 1-2
... (A) are made up of atoms that are intrinsically hard because of their electronic structures (B) consist of positive and negative ions that are strongly attracted to each other (C) are giant molecules in which each atom forms strong covalent bonds with all of its neighboring atoms (D) are formed unde ...
... (A) are made up of atoms that are intrinsically hard because of their electronic structures (B) consist of positive and negative ions that are strongly attracted to each other (C) are giant molecules in which each atom forms strong covalent bonds with all of its neighboring atoms (D) are formed unde ...
Semester 1 exam review
... exothermic or endothermic process? 24. .I have .84g of carbon dioxide in a 50 ml container at 105 kPa. If I release pressure (by making my volume bigger) until the gas is 25 kPa what is the density of my gas? 25. Why does sweating cool you down? Chapter 4 Review Questions 1. What were the two theori ...
... exothermic or endothermic process? 24. .I have .84g of carbon dioxide in a 50 ml container at 105 kPa. If I release pressure (by making my volume bigger) until the gas is 25 kPa what is the density of my gas? 25. Why does sweating cool you down? Chapter 4 Review Questions 1. What were the two theori ...
File
... What is the electron structure of the halogens? All halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell. This means that: They can easily obtain a full outer shell by gaining one electron. They all gain an electron in reactions to form negative ions with a -1 charge. ...
... What is the electron structure of the halogens? All halogens have seven electrons in their outer shell. This means that: They can easily obtain a full outer shell by gaining one electron. They all gain an electron in reactions to form negative ions with a -1 charge. ...
Document
... New developments can enable an isothermal shift one-step conversion to take place, applying an internal cooling of the process gas with cooling tubes running through the catalyst layers. Process condensates. The gas exiting the low temperature shift reactor is cooled and after most of the excess ste ...
... New developments can enable an isothermal shift one-step conversion to take place, applying an internal cooling of the process gas with cooling tubes running through the catalyst layers. Process condensates. The gas exiting the low temperature shift reactor is cooled and after most of the excess ste ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, it is conserved. ...
... of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, it is conserved. ...
Computational Study of protonation of ozone
... Optimization of geometrical parameters of molecular structures was carried out using a threeparameter exchange-correlation functional B3LYP and the basis set 6-311 ++ G (d, p). To confirm that the structures are minima on the potential energy surface, and to determine the zeropoint energy at the sam ...
... Optimization of geometrical parameters of molecular structures was carried out using a threeparameter exchange-correlation functional B3LYP and the basis set 6-311 ++ G (d, p). To confirm that the structures are minima on the potential energy surface, and to determine the zeropoint energy at the sam ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... discovering materials and exploiting their properties, the aim is instead to understand materials so that new materials with the desired properties can be created 1.2 Intercalation Materials with layer structures, for which the bonding between the layers is of the weak vander Waals type, offer a uni ...
... discovering materials and exploiting their properties, the aim is instead to understand materials so that new materials with the desired properties can be created 1.2 Intercalation Materials with layer structures, for which the bonding between the layers is of the weak vander Waals type, offer a uni ...
First Semester complete review with answers
... o Noble gases are nonreactive (inert) because their valence energy level is full o Elements are generally reactive when the valence energy level is not full o Highly reactive = valence energy level is almost full, or the valence energy level is almost empty Understand how to read chemical formulas ...
... o Noble gases are nonreactive (inert) because their valence energy level is full o Elements are generally reactive when the valence energy level is not full o Highly reactive = valence energy level is almost full, or the valence energy level is almost empty Understand how to read chemical formulas ...
ouble Replacement or (Metathesis) Reactions
... hydroxides will form, but no gases will be released. Example: K2O(s) + H2O ...
... hydroxides will form, but no gases will be released. Example: K2O(s) + H2O ...
www.studyguide.pk
... Structural formulae do not show all of the isomers that may exist for a given molecular formula. Which two compounds each show different types of isomerism and what type of isomerism does each compound show? Identify each compound ...
... Structural formulae do not show all of the isomers that may exist for a given molecular formula. Which two compounds each show different types of isomerism and what type of isomerism does each compound show? Identify each compound ...
Chemistry 12 is an intensive course, covering a great deal of
... A5 apply collision theory to explain how reaction rates can be changed use collision theory to explain the effect of the following factors on reaction rate: – nature of reactants – concentration – temperature – surface area A6 analyse the reaction mechanism for a reacting system 1. explain why most ...
... A5 apply collision theory to explain how reaction rates can be changed use collision theory to explain the effect of the following factors on reaction rate: – nature of reactants – concentration – temperature – surface area A6 analyse the reaction mechanism for a reacting system 1. explain why most ...
Document
... NOW: Read pages 630-633 & p. 635 of your textbook (skip page 634). Take notes. You should use those notes to help the questions, on the next page. While reading the text, read for the following goals. Read to: grasp / identify / list / comprehend / apply the ....various definitions of what is mean ...
... NOW: Read pages 630-633 & p. 635 of your textbook (skip page 634). Take notes. You should use those notes to help the questions, on the next page. While reading the text, read for the following goals. Read to: grasp / identify / list / comprehend / apply the ....various definitions of what is mean ...
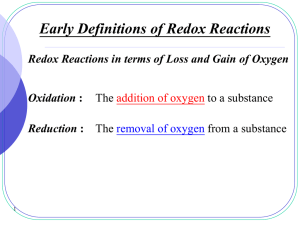
Redox reactions - SALEM-Immanuel Lutheran College
... Total in O.N. = 1(-3) = -3 Total in O.N. = +3 = 1.5(+2) 1.5 oxygen atoms are needed 0.75 O2 is needed ...
... Total in O.N. = 1(-3) = -3 Total in O.N. = +3 = 1.5(+2) 1.5 oxygen atoms are needed 0.75 O2 is needed ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... Note: Your Scantrons will not be returned to you, therefore, for your records, you may want to mark your answers on this sheet. On the Scantron you need to fill in your perm number, test version, and name. Failure to do any of these things will result in the loss of 1 point. Your perm number is plac ...
... Note: Your Scantrons will not be returned to you, therefore, for your records, you may want to mark your answers on this sheet. On the Scantron you need to fill in your perm number, test version, and name. Failure to do any of these things will result in the loss of 1 point. Your perm number is plac ...
Key - GCC
... Reactions in Aqueous Solutions 1. List the three general classes of chemical reactions: precipitation, acid-base neutralization, and redox reactions 2. How can you identify each of the three reaction types above (e.g., what characteristic defines each one?)? Precipitation reactions have solid produc ...
... Reactions in Aqueous Solutions 1. List the three general classes of chemical reactions: precipitation, acid-base neutralization, and redox reactions 2. How can you identify each of the three reaction types above (e.g., what characteristic defines each one?)? Precipitation reactions have solid produc ...
General Chemistry Questions
... 6. Two solutions (the system), each of 25.0 mL volume and at 25.0 °C, are mixed in a beaker. A reaction occurs between them, causing the temperature to drop to 20.0 °C. After the products have equilibrated with the surroundings, the temperature is again 25.0 °C and the total volume is 50.0 mL. No ga ...
... 6. Two solutions (the system), each of 25.0 mL volume and at 25.0 °C, are mixed in a beaker. A reaction occurs between them, causing the temperature to drop to 20.0 °C. After the products have equilibrated with the surroundings, the temperature is again 25.0 °C and the total volume is 50.0 mL. No ga ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.