Regents Exam In Chemistry Review Homework #1
... 4) Draw a PE Diagram sketch of what this reaction would look like. Label the Hreactants, Hproducts, Hactivated complex, H and activation energy. ...
... 4) Draw a PE Diagram sketch of what this reaction would look like. Label the Hreactants, Hproducts, Hactivated complex, H and activation energy. ...
Gen Chem Final--review problems Fall 2006
... For the precipitation reaction/s above in problem 1, please add the appropriate ‘state’ (i.e. solid or aq) to each species. For the oxidation/reduction reaction/s above, please identify the species that is being oxidized and the species being reduced and assign oxidation numbers to each atom. For th ...
... For the precipitation reaction/s above in problem 1, please add the appropriate ‘state’ (i.e. solid or aq) to each species. For the oxidation/reduction reaction/s above, please identify the species that is being oxidized and the species being reduced and assign oxidation numbers to each atom. For th ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Across the periodic table, sizes of atoms show the following trends, with many irregularities: Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one ...
... Across the periodic table, sizes of atoms show the following trends, with many irregularities: Size increases down a group. The outermost electrons are in successively more extensive orbitals as n increases. Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one ...
200 ways to pass the regents
... 108. Molarity is a way to measure the concentration of a solution. Molarity is equal to the number of moles of solute divided by the number of liters of solution. The formula is on the back of the reference tables. 109. Percent by mass = mass of the part / mass of the whole x 100% 110. Parts per mil ...
... 108. Molarity is a way to measure the concentration of a solution. Molarity is equal to the number of moles of solute divided by the number of liters of solution. The formula is on the back of the reference tables. 109. Percent by mass = mass of the part / mass of the whole x 100% 110. Parts per mil ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... 11. Draw an orbital diagram, complete electron configuration and noble gas notation for: a. Na b. C c. Mo d. Se 12. How does an electron become excited? What does it do when it returns to the ground state? 13. What is a photon? Quantum? 14. Describe the relationship between wavelength and frequency. ...
... 11. Draw an orbital diagram, complete electron configuration and noble gas notation for: a. Na b. C c. Mo d. Se 12. How does an electron become excited? What does it do when it returns to the ground state? 13. What is a photon? Quantum? 14. Describe the relationship between wavelength and frequency. ...
Fall Exam 4 - Chemistry - University of Kentucky
... Which of the following describes the bond formed between oxygen and fluorine in the OF2 molecule? Please note that in this structure oxygen is the central atom. ...
... Which of the following describes the bond formed between oxygen and fluorine in the OF2 molecule? Please note that in this structure oxygen is the central atom. ...
6.1 Organizing the Periodic Table
... • The attraction between the metal cation and the shared electrons around it • In a metal the valence electrons are free to move among the atoms- this accounts for many of the properties of metals ...
... • The attraction between the metal cation and the shared electrons around it • In a metal the valence electrons are free to move among the atoms- this accounts for many of the properties of metals ...
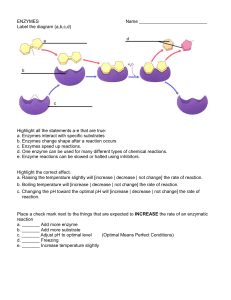
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Exam 3 Review Sheet
... 9. Give the complete mechanism for the electrophilic bromination of benzene using Br2 and FeBr3. Include the formation of the electrophile. 10. NMR. Phenol undergoes a Friedel-Crafts reaction with t-butyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride. Only one product is formed, and NMR data for the ...
... 9. Give the complete mechanism for the electrophilic bromination of benzene using Br2 and FeBr3. Include the formation of the electrophile. 10. NMR. Phenol undergoes a Friedel-Crafts reaction with t-butyl chloride in the presence of aluminum chloride. Only one product is formed, and NMR data for the ...
Nuclear Astrophysics (1)
... a noninteracting gas can be represented by a 3D box in which it is contained (with ...
... a noninteracting gas can be represented by a 3D box in which it is contained (with ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... reactants to one another, so more collisions, and more reactions 3. Stirring: ^ exposure of reactants to each other ...
... reactants to one another, so more collisions, and more reactions 3. Stirring: ^ exposure of reactants to each other ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... The correct sequence of the increasing order of the number of unpaired electrons in these ions is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4 (b) 4, 2, 3, 1 (c) 1, 3, 2, 4 (d) 3, 4, 2, 1 If Auf - bau rule is not followed, 19th electron in Fe (Z = 21) will have (a) n = 3, l = 0 (b) n = 3, l = 1 (c) n = 3, l = 2 (d) n = 4, l = 0 ...
... The correct sequence of the increasing order of the number of unpaired electrons in these ions is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4 (b) 4, 2, 3, 1 (c) 1, 3, 2, 4 (d) 3, 4, 2, 1 If Auf - bau rule is not followed, 19th electron in Fe (Z = 21) will have (a) n = 3, l = 0 (b) n = 3, l = 1 (c) n = 3, l = 2 (d) n = 4, l = 0 ...
"Introduction" Kinetics in Process Chemistry: Case Studies Baran Group Meeting Mike DeMartino
... N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole is commonly used as an acid activator for coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for ...
... N,N'-carbonyldiimidazole is commonly used as an acid activator for coupling reactions. There are advantages to using CDI: price -$8/mol (large-scale purchase), and the byproducts are the innocuous CO2 and imidazole. It is not without its problems though. The acyl imidazole is less reactive than, for ...
Exam 2-f06 - Clayton State University
... 2.) Which one of the following statements is false? a.) In order for a reaction to occur, reactant molecules must collide with each other. b.) A catalyst alters the rate of a reaction and is neither a product nor a reactant in the overall equation. c.) According to collision theory a three body coll ...
... 2.) Which one of the following statements is false? a.) In order for a reaction to occur, reactant molecules must collide with each other. b.) A catalyst alters the rate of a reaction and is neither a product nor a reactant in the overall equation. c.) According to collision theory a three body coll ...
Chapter 3 – part I Sections 1-3
... ions) are these. You will learn later that strong acids and bases are strong electrolytes. • Weak electrolytes are weak conductors, ionic compounds that are insoluble are these. Insoluble = only a few dissolve into ions. You will learn later that weak acids and bases are weak electrolytes. • Non-ele ...
... ions) are these. You will learn later that strong acids and bases are strong electrolytes. • Weak electrolytes are weak conductors, ionic compounds that are insoluble are these. Insoluble = only a few dissolve into ions. You will learn later that weak acids and bases are weak electrolytes. • Non-ele ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH sol ...
... 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH sol ...
82KB - NZQA
... Zinc, copper and lead do not react with magnesium nitrate because magnesium is higher on the activity series, so is more reactive than the other metals. Therefore none of zinc, copper, or lead can displace magnesium ions from solution, so no reaction will occur. ...
... Zinc, copper and lead do not react with magnesium nitrate because magnesium is higher on the activity series, so is more reactive than the other metals. Therefore none of zinc, copper, or lead can displace magnesium ions from solution, so no reaction will occur. ...
C2 Knowledge PowerPoint
... forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. •Graphite conducts electricity – the only nonmetal to do so. The free electron from each carbon atom means that each layer has delocalized electrons, which can carry charge. It is often used as an electrode for this ...
... forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. •Graphite conducts electricity – the only nonmetal to do so. The free electron from each carbon atom means that each layer has delocalized electrons, which can carry charge. It is often used as an electrode for this ...
Document
... forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. •Graphite conducts electricity – the only nonmetal to do so. The free electron from each carbon atom means that each layer has delocalized electrons, which can carry charge. It is often used as an electrode for this ...
... forces of attraction are easily broken. This is why graphite is used as a lubricant. •Graphite conducts electricity – the only nonmetal to do so. The free electron from each carbon atom means that each layer has delocalized electrons, which can carry charge. It is often used as an electrode for this ...
Reaction Rate Reading Packet
... 3. Surface area is the measure of how much area of an object is exposed. For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collid ...
... 3. Surface area is the measure of how much area of an object is exposed. For the same mass, many small particles have a greater total surface area than one large particle. For example, steel wool has a larger surface area than a block of steel of the same mass. This allows oxygen molecules to collid ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
chemistry 102 fall 2001 part 1
... keep the multiple choice part - the answers will be given to you as you leave. (6) There are a total of 28 questions (16 actual questions). ...
... keep the multiple choice part - the answers will be given to you as you leave. (6) There are a total of 28 questions (16 actual questions). ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.