Lecture 19
... Electrical conductivity detectors should be well suited for the detection of inorganic ions. However, in ion-exchange chromatography, mobile phases with high electrolyte concentration are needed to elute many analytes, and the conductivity of the mobile phase interferes with the detection of the ana ...
... Electrical conductivity detectors should be well suited for the detection of inorganic ions. However, in ion-exchange chromatography, mobile phases with high electrolyte concentration are needed to elute many analytes, and the conductivity of the mobile phase interferes with the detection of the ana ...
writing chemical equations
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
9182747 Chemistry Ja02
... circle with pencil the number of the choice that you have selected. The sample below is an example of the first step in recording your answers. ...
... circle with pencil the number of the choice that you have selected. The sample below is an example of the first step in recording your answers. ...
Cold encounters: Electrons and molecules
... collision energy, in atomic units. This rate of change may be obtained by suitable fitting of the data in figure 2, resulting in a lifetime of CO 2- at 10 meV impact energy of 8.48±0.lxlO- IS seconds. But how can this be? An s-wave is attempting to attach to CO 2• The LUMO of CO 2 is however of p-li ...
... collision energy, in atomic units. This rate of change may be obtained by suitable fitting of the data in figure 2, resulting in a lifetime of CO 2- at 10 meV impact energy of 8.48±0.lxlO- IS seconds. But how can this be? An s-wave is attempting to attach to CO 2• The LUMO of CO 2 is however of p-li ...
Request reprint © - Research at the Department of Chemistry
... modiÐed version of the Chait design26 and the Knapp and Schey design.27 The ESI/SID instrument used for these experiments has previously been used for studies involving large biological molecules28,29 and cis-DDP bound to guanosine.30 The potential di†erence between the capillary and skimmer was hel ...
... modiÐed version of the Chait design26 and the Knapp and Schey design.27 The ESI/SID instrument used for these experiments has previously been used for studies involving large biological molecules28,29 and cis-DDP bound to guanosine.30 The potential di†erence between the capillary and skimmer was hel ...
C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a different number of hydrogen bonds. c. T ...
... 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a different number of hydrogen bonds. c. T ...
Crystal Field Theory, gemstones and color
... metal ions in crystals using a purely electrostatic bonding model. We will use this theory to explain the color of the gemstones ruby and emerald, and will see the limitations of the theory ...
... metal ions in crystals using a purely electrostatic bonding model. We will use this theory to explain the color of the gemstones ruby and emerald, and will see the limitations of the theory ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
... If a metal is more reactive than hydrogen its ions stay in solution and hydrogen bubbles off ...
An Overview of Computational Chemistry
... Electron-electron repulsion is included as an average effect. The electron repulsion felt by one electron is an average potential field of all the others, assuming that their spatial distribution is represented by orbitals. This is sometimes referred to as the Mean Field Approximation. ...
... Electron-electron repulsion is included as an average effect. The electron repulsion felt by one electron is an average potential field of all the others, assuming that their spatial distribution is represented by orbitals. This is sometimes referred to as the Mean Field Approximation. ...
MATTER-Ch. 3-homogeneous vs. heterogeneous, elements
... a. Atoms cannot be divided, created, or destroyed. b. The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number. c. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. d. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. ____ 20. Which of the following statements is true ...
... a. Atoms cannot be divided, created, or destroyed. b. The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number. c. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. d. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. ____ 20. Which of the following statements is true ...
2 day in-class guided inquiry exercise
... e) given the structures of Beryl and Corundum, explain using a physical model why the two materials have such different harndesses. Breakdown of CFT - covalency One of the useful things about crystal field theory is its predictive nature. Once we know a crystal field splitting pattern and what atoms ...
... e) given the structures of Beryl and Corundum, explain using a physical model why the two materials have such different harndesses. Breakdown of CFT - covalency One of the useful things about crystal field theory is its predictive nature. Once we know a crystal field splitting pattern and what atoms ...
Crystal Field Theory, gemstones and color
... e) given the structures of Beryl and Corundum, explain using a physical model why the two materials have such different harndesses. Breakdown of CFT - covalency One of the useful things about crystal field theory is its predictive nature. Once we know a crystal field splitting pattern and what atoms ...
... e) given the structures of Beryl and Corundum, explain using a physical model why the two materials have such different harndesses. Breakdown of CFT - covalency One of the useful things about crystal field theory is its predictive nature. Once we know a crystal field splitting pattern and what atoms ...
A Student want to prepare 250mL of .10 M NaCl solution
... The Number of atoms in 9.0g of Aluminum is equal to the Number of atoms in A) 8.1g Mg B) 12.1g Mg The Long way: C) 9.0g Mg Calculate # of atoms in 9.0 g Al D) 18.0g Mg Then calculate mass of that # of Mg atoms Look for ratios: Al has a molar mass of 27 This is 1/3 of a mole Al Which one is 1/3 mole ...
... The Number of atoms in 9.0g of Aluminum is equal to the Number of atoms in A) 8.1g Mg B) 12.1g Mg The Long way: C) 9.0g Mg Calculate # of atoms in 9.0 g Al D) 18.0g Mg Then calculate mass of that # of Mg atoms Look for ratios: Al has a molar mass of 27 This is 1/3 of a mole Al Which one is 1/3 mole ...
Chemistry S1 Unit 5 – Chemistry At Work Check for Understanding
... A. The reactant that has the atom that gets oxidized B. The reactant that has the atom that gets reduced C. The product that has the atom that was reduced D. The product that has the atom that was oxidized Correct Answer My Answer ...
... A. The reactant that has the atom that gets oxidized B. The reactant that has the atom that gets reduced C. The product that has the atom that was reduced D. The product that has the atom that was oxidized Correct Answer My Answer ...
Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory
... Once we have developed an understanding of the relationship between molecular structure and chemical bonding, we can attempt an understanding of the relationship of he structure and bonding in a polyatomic molecule to the physical and chemical properties we observe for those molecules. ...
... Once we have developed an understanding of the relationship between molecular structure and chemical bonding, we can attempt an understanding of the relationship of he structure and bonding in a polyatomic molecule to the physical and chemical properties we observe for those molecules. ...
Equivalent weight
... •Equivalent weight (also known as gram equivalent) is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. •In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will: •supply or react with one mole of hydrogen ions(H+) in an acid–base react ...
... •Equivalent weight (also known as gram equivalent) is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. •In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will: •supply or react with one mole of hydrogen ions(H+) in an acid–base react ...
Lecture 4
... The oxidation number of an atom in a substance is the actual charge of the atom if it is a monatomic ion. 1. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. 2. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on the ion. 3. Nonmetals usually have negative oxidati ...
... The oxidation number of an atom in a substance is the actual charge of the atom if it is a monatomic ion. 1. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. 2. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on the ion. 3. Nonmetals usually have negative oxidati ...
... of conventional quantum mechanics, as it applies in atoms and molecules, in solids, the associated distance has marginal consequence. This is because except within the immediate vicinity of each surface or interface, the substrate effectively “behaves” as if it is neutral. For this reason, electrost ...
Final Exam Study Guide Word document
... How many molecules are in 237 grams (about a cup) of water? 18. What are the coefficients when the following chemical equation is balanced? AlCl 3 + H2SO4 ----> ...
... How many molecules are in 237 grams (about a cup) of water? 18. What are the coefficients when the following chemical equation is balanced? AlCl 3 + H2SO4 ----> ...
Students know
... A. Because the gas molecules are too small to be affected by the increase in heat. B. Because the gas molecules are too hard to stir and heating is just like stirring on the molecular level. C. Gas molecules move faster when heated and this causes them to move out of the solution so they don’t disso ...
... A. Because the gas molecules are too small to be affected by the increase in heat. B. Because the gas molecules are too hard to stir and heating is just like stirring on the molecular level. C. Gas molecules move faster when heated and this causes them to move out of the solution so they don’t disso ...
Test No. 108: Complex Formation Ability in Water - Books
... This method is based on the fact that the reduction potentials of metal ions are shifted, usually to more negative values, as a result of complex formation. A positive shift can also occur, but only if another metal ion is present in the solution that is capable of binding to excess complex-forming ...
... This method is based on the fact that the reduction potentials of metal ions are shifted, usually to more negative values, as a result of complex formation. A positive shift can also occur, but only if another metal ion is present in the solution that is capable of binding to excess complex-forming ...
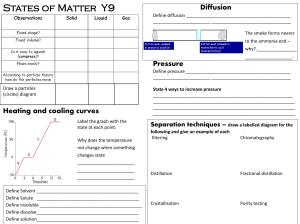
Matter Unit Study Guide Phases of Matter
... Define Matter: Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Fill in the chart below about the three phases of matter: ...
... Define Matter: Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Fill in the chart below about the three phases of matter: ...