Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... An element is in group 14 and period 3 of the periodic table. How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of an atom of this element? 51. Which group on the periodic table has the lowest first ionization energies? 52. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are present in each atom ...
... An element is in group 14 and period 3 of the periodic table. How many electrons are in the highest occupied energy level of an atom of this element? 51. Which group on the periodic table has the lowest first ionization energies? 52. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are present in each atom ...
Chemistry exam review
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
2005/6 - SAASTA
... The top left number (56) represents the total number of nucleons (protons plus neutrons). The bottom left number (26) is the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons. The number of neutrons is 56-26 = 30. The top right number (3+) is the oxidation number. That it is positive means thre ...
... The top left number (56) represents the total number of nucleons (protons plus neutrons). The bottom left number (26) is the atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons. The number of neutrons is 56-26 = 30. The top right number (3+) is the oxidation number. That it is positive means thre ...
6.1 Coulomb interaction energy among charged particles in an atom
... Thus the problem of solving eq 6.20 is reduced to that of determining the “radial” functions R(r). In order to find them, one substitutes of eq 6.23 into eq 6.20, and simplifies. You should verify that the resultant equation for R(r) is eq 6.24 The purpose up to this point has been to demonstrate ho ...
... Thus the problem of solving eq 6.20 is reduced to that of determining the “radial” functions R(r). In order to find them, one substitutes of eq 6.23 into eq 6.20, and simplifies. You should verify that the resultant equation for R(r) is eq 6.24 The purpose up to this point has been to demonstrate ho ...
AP Chem -‐ Unit 1 Part 1 AP Chemistry 2016
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
111 Exam II Outline
... A. Bond Energy - The average energy required for the dissociation of a bond B. Bond Length - The average distance between the two nuclei of covalently bonded atoms. C. Drawing electron dot structures ...
... A. Bond Energy - The average energy required for the dissociation of a bond B. Bond Length - The average distance between the two nuclei of covalently bonded atoms. C. Drawing electron dot structures ...
Test - Regents
... 15 Which formula is correct for ammonium sulfate? (3) NH4(SO4)2 (1) NH4SO4 (2) (NH4)2SO4 (4) (NH4)2(SO4)2 16 An example of an empirical formula is (3) C2H4(OH)2 (1) CH4 (2) C2H4 (4) C6H12O6 ...
... 15 Which formula is correct for ammonium sulfate? (3) NH4(SO4)2 (1) NH4SO4 (2) (NH4)2SO4 (4) (NH4)2(SO4)2 16 An example of an empirical formula is (3) C2H4(OH)2 (1) CH4 (2) C2H4 (4) C6H12O6 ...
im11
... 23. Weak acids are typically found in foods and provide a sour or tart flavor. 24. Both strong acids (HCl in gastric juice) and weak acids (bicarbonate in the blood and the amino acids in proteins) are found in the human body. The bicarbonate anion and the amino acids in proteins also serve as weak ...
... 23. Weak acids are typically found in foods and provide a sour or tart flavor. 24. Both strong acids (HCl in gastric juice) and weak acids (bicarbonate in the blood and the amino acids in proteins) are found in the human body. The bicarbonate anion and the amino acids in proteins also serve as weak ...
Chemistry exam review
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
Chemistry exam review
... 2. The gases helium, neon, and argon are in separate containers at 55°C. Which is true about the kinetic energy of the gases? a. Helium has the lowest mass and therefore the greatest kinetic energy. b. They each have a different kinetic energy. c. Argon has greatest mass and therefore the greatest ...
... 2. The gases helium, neon, and argon are in separate containers at 55°C. Which is true about the kinetic energy of the gases? a. Helium has the lowest mass and therefore the greatest kinetic energy. b. They each have a different kinetic energy. c. Argon has greatest mass and therefore the greatest ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion of alkanes in a limited supply of oxygen and outline the potential dangers arising from production of CO in the home and from car use. Descri ...
... Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion of alkanes in a limited supply of oxygen and outline the potential dangers arising from production of CO in the home and from car use. Descri ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... Explain how to determine whether a molecule needs single, double, or triple bonds. Draw Lewis dot and Lewis structure diagrams of molecules including resonance structures Understand the concept of the co-ordinate bond related to Lewis structures Understand that ionic solids are held together in a la ...
... Explain how to determine whether a molecule needs single, double, or triple bonds. Draw Lewis dot and Lewis structure diagrams of molecules including resonance structures Understand the concept of the co-ordinate bond related to Lewis structures Understand that ionic solids are held together in a la ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • As a group, look at the food labels on the items at your table. Make a list of the items in the left hand side column and in the right hand side column make a list of any elements found in that substance. • You may use your periodic table to help you identify the elements. ...
... • As a group, look at the food labels on the items at your table. Make a list of the items in the left hand side column and in the right hand side column make a list of any elements found in that substance. • You may use your periodic table to help you identify the elements. ...
Chemistry I Exam
... A student performed a laboratory procedure to determine the relative reactivity of elements bromine, chlorine, and iodine. To do this, she prepared a water solution of each element, as well as a solution of sodium salt (bromide, chloride, iodide) of each of these elements. In separate test tubes, sh ...
... A student performed a laboratory procedure to determine the relative reactivity of elements bromine, chlorine, and iodine. To do this, she prepared a water solution of each element, as well as a solution of sodium salt (bromide, chloride, iodide) of each of these elements. In separate test tubes, sh ...
as a PDF
... are many important chemical changes to which thermodynamics is rather insensitive. Structure is often a good example. The smooth energy variation in Fig. 1.2 refers to a complexing reaction in aqueous solution. It is generally accepted that, as we move across the lanthanide series, the coordination ...
... are many important chemical changes to which thermodynamics is rather insensitive. Structure is often a good example. The smooth energy variation in Fig. 1.2 refers to a complexing reaction in aqueous solution. It is generally accepted that, as we move across the lanthanide series, the coordination ...
Lecture 2 - MyCourses
... of experimental and computational data Similar to ionic radii, the covalent radii can be used for example: – To check whether a new crystal structure shows covalent bonding – To check whether an bond that is expected to be covalent has a reasonable length (even pointing out possible problems with th ...
... of experimental and computational data Similar to ionic radii, the covalent radii can be used for example: – To check whether a new crystal structure shows covalent bonding – To check whether an bond that is expected to be covalent has a reasonable length (even pointing out possible problems with th ...
Unit 1 Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Nuclear Chemistry
... 3. Thomson observed that the production of cathode rays did not depend on the kind of gas in the tube or the type of metal used for the electrodes. What conclusion did he draw from these observations? _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
... 3. Thomson observed that the production of cathode rays did not depend on the kind of gas in the tube or the type of metal used for the electrodes. What conclusion did he draw from these observations? _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
Unit 1 Student Booklet
... of valence electrons in its valence shell. For example, atoms with one valence electron in its valence shell will have a tendency to lose that electron and become positively charged. Positively charged ions are called cations, and negatively charged ions are called anions. Atoms gain or lose electro ...
... of valence electrons in its valence shell. For example, atoms with one valence electron in its valence shell will have a tendency to lose that electron and become positively charged. Positively charged ions are called cations, and negatively charged ions are called anions. Atoms gain or lose electro ...
g moles molarity
... Example: When aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and iron(III) nitrate are mixed, a red gelatinous precipitate forms. Calculate the mass of precipitate formed when 50.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH and 30.00 mL of 0.125 M Fe(NO3)3 are mixed 1. Check for charge dense ions that can precipitate 2. Write a ne ...
... Example: When aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and iron(III) nitrate are mixed, a red gelatinous precipitate forms. Calculate the mass of precipitate formed when 50.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH and 30.00 mL of 0.125 M Fe(NO3)3 are mixed 1. Check for charge dense ions that can precipitate 2. Write a ne ...
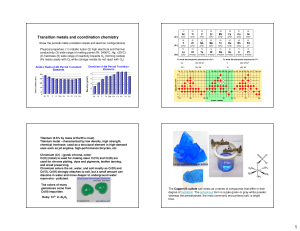
Transition metals and coordination chemistry
... molecule of the chemical formula [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] were connected. The theories at the time predicted such molecules to be connected as linear chains: [Pt-NH3-NH3-Cl]Cl or Cl-NH3-Pt-NH3-Cl ...
... molecule of the chemical formula [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] were connected. The theories at the time predicted such molecules to be connected as linear chains: [Pt-NH3-NH3-Cl]Cl or Cl-NH3-Pt-NH3-Cl ...
Reaction of potassium atoms with oriented bromotrifluoromethane
... = 2) than “edge-on attack”, suggesting a bent minumum energy configuration. Similarly, polarized light has been used4 to produce atoms in which excited p- or d-orbitals are directed parallel or perpendicular to the relative velocity. In the case of Ca + HC1, the direction of the Ca* p-orbital strong ...
... = 2) than “edge-on attack”, suggesting a bent minumum energy configuration. Similarly, polarized light has been used4 to produce atoms in which excited p- or d-orbitals are directed parallel or perpendicular to the relative velocity. In the case of Ca + HC1, the direction of the Ca* p-orbital strong ...
2007 - SAASTA
... the container. Solids retain both their shape and volume when moved from one container ...
... the container. Solids retain both their shape and volume when moved from one container ...
Practice Questions Section 2
... hydrogen chloride gas is produced from hydrogen gas and chlorine gas. nitrogen gas and oxygen gas combine to produce gaseous dinitrogen oxide. solid hydrogen cyanide dissolves to produce hydrogen ions and cyanide ions in solution. solid silver chloride dissolves to produce silver ions and chloride i ...
... hydrogen chloride gas is produced from hydrogen gas and chlorine gas. nitrogen gas and oxygen gas combine to produce gaseous dinitrogen oxide. solid hydrogen cyanide dissolves to produce hydrogen ions and cyanide ions in solution. solid silver chloride dissolves to produce silver ions and chloride i ...
2 (aq)
... Designates a reactant or product in the solid state; placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the liquid state: placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the gaseous state; placed after the formula Designates an aqueous solution; the substance is dissolved in w ...
... Designates a reactant or product in the solid state; placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the liquid state: placed after the formula Designates a reactant or product in the gaseous state; placed after the formula Designates an aqueous solution; the substance is dissolved in w ...