Final Exam Review
... b. Kinetic energy of water molecules increases when the heated metal is immersed. c. Kinetic energy of water molecules decreases when the heated metal is immersed. d. Kinetic energy of metal atoms increases when immersed in the cooler water. 2. The gases helium, neon, and argon are in separate conta ...
... b. Kinetic energy of water molecules increases when the heated metal is immersed. c. Kinetic energy of water molecules decreases when the heated metal is immersed. d. Kinetic energy of metal atoms increases when immersed in the cooler water. 2. The gases helium, neon, and argon are in separate conta ...
Chapter 2 Lecture notes
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Unit 1: Sig. Figs, Compounds, Elements, Homo/Hetero mixtures
... 1. Which of the following gases does not exist in nature as a diatomic molecule? a. Nitrogen b. Helium c. Hydrogen d. oxygen 2. Ionic compounds generally form: a. Liquids b. Gases c. Crystals d. molecules 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all atoms are shared in: a. A nonpolar covalen ...
... 1. Which of the following gases does not exist in nature as a diatomic molecule? a. Nitrogen b. Helium c. Hydrogen d. oxygen 2. Ionic compounds generally form: a. Liquids b. Gases c. Crystals d. molecules 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all atoms are shared in: a. A nonpolar covalen ...
physical setting chemistry
... and identical properties. (2) They have identical molecular and different properties. (3) They have different molecular and identical properties. (4) They have different molecular and different properties. ...
... and identical properties. (2) They have identical molecular and different properties. (3) They have different molecular and identical properties. (4) They have different molecular and different properties. ...
Wet Corrosion Conditions for Wet Corrosion Just as we live in an
... To predict the anode or cathode for different chemistries, two reference tables are available: the Standard Electrode Potential and the Galvanic Series in Sea Water. Each should be used with caution. They summarize controlled, standardized experiments, which may not closely match actual environments ...
... To predict the anode or cathode for different chemistries, two reference tables are available: the Standard Electrode Potential and the Galvanic Series in Sea Water. Each should be used with caution. They summarize controlled, standardized experiments, which may not closely match actual environments ...
Chapter 6. Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Be able to calculation various Energy transitions between two energy levels. Be able to write electronic structure both long & short-cut forms, Energy level diagram, and identifications by structures including atoms and ions Be able to recognize valence electrons, those mostly involved in gain & los ...
... Be able to calculation various Energy transitions between two energy levels. Be able to write electronic structure both long & short-cut forms, Energy level diagram, and identifications by structures including atoms and ions Be able to recognize valence electrons, those mostly involved in gain & los ...
Are you ready for S279?
... those of the noble gases (e.g. helium, neon and argon), which take part in few chemical reactions. Atoms chemically bond with other atoms in order to achieve the stable electronic configuration of a noble gas. This can be achieved by either: (i) transferring electrons (ionic bonding) to form positi ...
... those of the noble gases (e.g. helium, neon and argon), which take part in few chemical reactions. Atoms chemically bond with other atoms in order to achieve the stable electronic configuration of a noble gas. This can be achieved by either: (i) transferring electrons (ionic bonding) to form positi ...
ChemChapter_7sec1_and_section2[1]FORMULA
... nonmetals can have more than one oxidation number. • These numbers can sometimes be used in the same manner as ionic charges to determine formulas. – example: What is the formula of a binary compound formed between sulfur and oxygen? From the common +4 and +6 oxidation states of sulfur, you could pr ...
... nonmetals can have more than one oxidation number. • These numbers can sometimes be used in the same manner as ionic charges to determine formulas. – example: What is the formula of a binary compound formed between sulfur and oxygen? From the common +4 and +6 oxidation states of sulfur, you could pr ...
50 frequently forgotten facts answer key
... 21) At STP, the liquids on the Periodic Table are Br and Hg. The gases are N, Cl, H, O, F and the Noble Gases. All other elements are solids. [Periodic Table] a) Which element on the Periodic Table is a nonmetallic liquid at STP?___bromine (Br)___ b) Which element at STP is a liquid that conducts e ...
... 21) At STP, the liquids on the Periodic Table are Br and Hg. The gases are N, Cl, H, O, F and the Noble Gases. All other elements are solids. [Periodic Table] a) Which element on the Periodic Table is a nonmetallic liquid at STP?___bromine (Br)___ b) Which element at STP is a liquid that conducts e ...
Energy Level Models - Middle School Chemistry
... electrons is intended to suggest information about the substructure within energy levels. This substructure is made up of regions called orbitals which comprise each energy level. The shape and size of the orbital is defined by the space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of findin ...
... electrons is intended to suggest information about the substructure within energy levels. This substructure is made up of regions called orbitals which comprise each energy level. The shape and size of the orbital is defined by the space around the nucleus where there is a high probability of findin ...
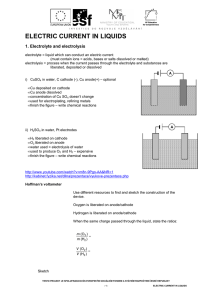
ELECTRIC CURRENT IN LIQUIDS
... 3. Compare the masses of hydrogen and copper that would be deposited when the same charge passed through the solutions of H2SO4 and CuSO4. 4. A current passed through a solution of H2SO4 for 15 minutes and 10 mg of oxygen were liberated. Calculate a) the electrochemical equivalent of oxygen b) the v ...
... 3. Compare the masses of hydrogen and copper that would be deposited when the same charge passed through the solutions of H2SO4 and CuSO4. 4. A current passed through a solution of H2SO4 for 15 minutes and 10 mg of oxygen were liberated. Calculate a) the electrochemical equivalent of oxygen b) the v ...
Syracuse University
... Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (See Table 2.1 Comparing the proton, neutron, and electron ) Isotopes, Atomic Numbers, and Mass Numbers 2.4 The Periodic Table (Study figure showing the division of eleme ...
... Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (See Table 2.1 Comparing the proton, neutron, and electron ) Isotopes, Atomic Numbers, and Mass Numbers 2.4 The Periodic Table (Study figure showing the division of eleme ...
50 Frequently Forgotten Facts Answer Key
... 21) At STP, the liquids on the Periodic Table are Br and Hg. The gases are N, Cl, H, O, F and the Noble Gases. All other elements are solids. [Periodic Table] a) Which element on the Periodic Table is a nonmetallic liquid at STP?___bromine (Br)___ b) Which element at STP is a liquid that conducts e ...
... 21) At STP, the liquids on the Periodic Table are Br and Hg. The gases are N, Cl, H, O, F and the Noble Gases. All other elements are solids. [Periodic Table] a) Which element on the Periodic Table is a nonmetallic liquid at STP?___bromine (Br)___ b) Which element at STP is a liquid that conducts e ...
Average Atomic Mass
... 25. water Classify the following as A/F. mixture or B/G. pure substance. 26. a multivitamin tablet 27. distilled water 28. tap water Classify the following as A/F. homogeneous mixture or B/G. heterogeneous mixture. 29. chunky peanut butter 30. a solution of copper (II) sulfate 31. a bag of trail mix ...
... 25. water Classify the following as A/F. mixture or B/G. pure substance. 26. a multivitamin tablet 27. distilled water 28. tap water Classify the following as A/F. homogeneous mixture or B/G. heterogeneous mixture. 29. chunky peanut butter 30. a solution of copper (II) sulfate 31. a bag of trail mix ...
Regents Exam In Chemistry Review Homework #1
... 11) Explain how a photon of light is formed:____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 11) Explain how a photon of light is formed:____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Final Exam Practice Questions for General Chemistry NOTICE TO
... These exact questions will not appear on your exam. These example questions are provided to you help you review the material and become familiar with the TYPES of questions that are generally presented on the final exam. This is not a complete list of the ideas, concepts, principles, or questions co ...
... These exact questions will not appear on your exam. These example questions are provided to you help you review the material and become familiar with the TYPES of questions that are generally presented on the final exam. This is not a complete list of the ideas, concepts, principles, or questions co ...
Document
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
... anions and cations are separated from each other. This is called dissociation. Na2S(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + S2–(aq) When compounds containing polyatomic ions dissociate, the polyatomic group stays together as one ion. Na2SO4(aq) 2 Na+(aq) + SO42−(aq) When strong acids dissolve in water, the molecule ion ...
Old EXAM I - gozips.uakron.edu
... Two objects have the same density, but one has more mass than (is heavier than) the other. Which object has the smaller volume? (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
... Two objects have the same density, but one has more mass than (is heavier than) the other. Which object has the smaller volume? (a) (b) (c) (d) ...
File
... Sample Problem 21.2: The pH of a Base Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. Find the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of NaOH into enough water to make 1.0 L of solution. Step 1: List the known values and plan the problem. Known mass of NaOH = 1.0 g molar mass of NaOH = 40.00 g/mol volume ...
... Sample Problem 21.2: The pH of a Base Sodium hydroxide is a strong base. Find the pH of a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of NaOH into enough water to make 1.0 L of solution. Step 1: List the known values and plan the problem. Known mass of NaOH = 1.0 g molar mass of NaOH = 40.00 g/mol volume ...
Wizard Test Maker
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
... (2) propanal (4) water 6856 Which Group 14 element is classified as a metal? (1) carbon (3) silicon (2) germanium (4) tin 6763 An element that has a low first ionization energy and good conductivity of heat and electricity is classified as a (3) nonmetal (1) metal (2) metalloid (4) noble gas 6709 A ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Homework Booklet Unit 1 Feb14
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Lesson 9 Review Teacher`s Copy
... 3. Matter is made up of particles whose properties determine the observable characteristics of matter and its reactivity. (22) 3.2. Use atomic and molecular models to explain common chemical reactions. (22) 3.2.d. An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons (e-). (4) 3 ...
... 3. Matter is made up of particles whose properties determine the observable characteristics of matter and its reactivity. (22) 3.2. Use atomic and molecular models to explain common chemical reactions. (22) 3.2.d. An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction involves the transfer of electrons (e-). (4) 3 ...
Paper - Revision Science
... D it cannot be poisoned. (Total for Question 12 = 1 mark) 13 In the reaction of benzene with chloromethane, aluminium chloride is added because it reacts with A benzene to produce an electrophile. B benzene to produce a nucleophile. C chloromethane to produce a nucleophile. D chloromethane to produc ...
... D it cannot be poisoned. (Total for Question 12 = 1 mark) 13 In the reaction of benzene with chloromethane, aluminium chloride is added because it reacts with A benzene to produce an electrophile. B benzene to produce a nucleophile. C chloromethane to produce a nucleophile. D chloromethane to produc ...







![ChemChapter_7sec1_and_section2[1]FORMULA](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000546743_1-278f96ccbbfd49e292510ec017e27124-300x300.png)