Document
... (called spectator ions) Ag1+ + Cl1- AgCl (s) This is the net ionic equation Let’s talk about precipitates before we do some other examples ...
... (called spectator ions) Ag1+ + Cl1- AgCl (s) This is the net ionic equation Let’s talk about precipitates before we do some other examples ...
1)A neutral atom has no overall charge, and ion is a
... b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attraction due to i)the increased distance of the elect ...
... b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attraction due to i)the increased distance of the elect ...
- Catalyst
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
... Question 7: Fill in the blanks of the statements below with the words in the box. Note, you will only use each word once. A. atom ...
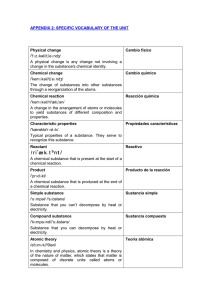
specific vocabulary of the unit
... The order of an element in Mendeleyev's table of the elements; equal to the number of protons in the nucleus or electrons in the neutral state of an atom of an element. Mass number Número másico /mæs//'nʌmbər / The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus. Atomic mass ...
... The order of an element in Mendeleyev's table of the elements; equal to the number of protons in the nucleus or electrons in the neutral state of an atom of an element. Mass number Número másico /mæs//'nʌmbər / The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus. Atomic mass ...
Chapter 22 REDOX
... Explain why AgNO3 is a better choice than AgCl for use in this electrolytic process. [1] Explain the purpose of the battery in this cell. [1] ...
... Explain why AgNO3 is a better choice than AgCl for use in this electrolytic process. [1] Explain the purpose of the battery in this cell. [1] ...
1 - Study Hungary
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
... 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 19 electrons 19 protons, 20 neutrons, 18 electrons 39 protons, 19 neutrons, 38 electrons 20 protons, 19 neutrons, 20 electrons 40 protons, 20 neutrons, 19 electrons ...
File
... D) D only 11. In which molecule are the bond angles closest to 90̊ ? A) A B) B C) C D)D 12. In which molecule does the central atom contain non-bonding electron pairs (lone pairs)? A) A B) B C) C D) D 13. Which molecule contains both sigma and pi bonds? A) A B) B C) C D) D 14. A yellow solid melts a ...
... D) D only 11. In which molecule are the bond angles closest to 90̊ ? A) A B) B C) C D)D 12. In which molecule does the central atom contain non-bonding electron pairs (lone pairs)? A) A B) B C) C D) D 13. Which molecule contains both sigma and pi bonds? A) A B) B C) C D) D 14. A yellow solid melts a ...
Appendix I.
... inelastically scattered light from molecules. Like FTIR, this technique is used to determine molecular structures, but it utilizes a different wavelength of radiation (a laser source), and it is concerned with the scattering of radiation by the sample, rather than the absorption process. Light there ...
... inelastically scattered light from molecules. Like FTIR, this technique is used to determine molecular structures, but it utilizes a different wavelength of radiation (a laser source), and it is concerned with the scattering of radiation by the sample, rather than the absorption process. Light there ...
Electric Field Perturbation Caused by an Increase in
... where A is the index of radioactivity growth in the nearEarth layer and B is the index of the relative efficiency of gamma radiation and alpha particle ionization sources. This index is within the range 0 < B < ∞. If B = 0, ionization occurs under the action of gamma radiation only, and, if B ∞, the ...
... where A is the index of radioactivity growth in the nearEarth layer and B is the index of the relative efficiency of gamma radiation and alpha particle ionization sources. This index is within the range 0 < B < ∞. If B = 0, ionization occurs under the action of gamma radiation only, and, if B ∞, the ...
materials: metals and non—metals
... Brittle - if a solid. Nonductile. Do not possess metallic luster. Transparent as a thin sheet. Solids, liquids or gases at room temperature ...
... Brittle - if a solid. Nonductile. Do not possess metallic luster. Transparent as a thin sheet. Solids, liquids or gases at room temperature ...
Chemical Reaction and Matter Review
... typical type of ionic compound, called a binary compound because it is made up of two elements, will be composed of metallic positive ions (cations) and nonmetal negative ions (anions). When dealing with ionic formulas it is very important to remember that the formula does not show how the compound ...
... typical type of ionic compound, called a binary compound because it is made up of two elements, will be composed of metallic positive ions (cations) and nonmetal negative ions (anions). When dealing with ionic formulas it is very important to remember that the formula does not show how the compound ...
ACID AND BASES
... An acid is traditionally considered any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a pH less than 7 Properties of acids: generally taste sour, are corrosive to metals, turns blue litmus paper red and reacts with a base to produce a salt and water ...
... An acid is traditionally considered any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a pH less than 7 Properties of acids: generally taste sour, are corrosive to metals, turns blue litmus paper red and reacts with a base to produce a salt and water ...
ACID AND BASES
... An acid is traditionally considered any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a pH less than 7 Properties of acids: generally taste sour, are corrosive to metals, turns blue litmus paper red and reacts with a base to produce a salt and water ...
... An acid is traditionally considered any chemical compound that, when dissolved in water, gives a solution with a pH less than 7 Properties of acids: generally taste sour, are corrosive to metals, turns blue litmus paper red and reacts with a base to produce a salt and water ...
Molecules & Condensed Matter
... • The energy band concept, introduced in 1928, looks at how the outer energy levels of states in an atom vary with distance. When atoms are close enough together, the bands from one atom can join with another to permit lots of states in a closely spaced band of energy. • Some bands are filled, some ...
... • The energy band concept, introduced in 1928, looks at how the outer energy levels of states in an atom vary with distance. When atoms are close enough together, the bands from one atom can join with another to permit lots of states in a closely spaced band of energy. • Some bands are filled, some ...
semester two final review key units 5 and 6 only
... Monomer: a molecule of any class of compounds, mostly organic that can react with other molecules that can form larger molecules Polymer: any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called mon ...
... Monomer: a molecule of any class of compounds, mostly organic that can react with other molecules that can form larger molecules Polymer: any of a class of natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules, called macromolecules, that are multiples of simpler chemical units called mon ...
Spectra
... The Mass Spectrometer • The mass spectrometer contains a vacuum chamber into which a small amount of a compound is vaporized. The molecules are then bombarded by high energy electrons which cause the molecule to fragment into molecular ions ...
... The Mass Spectrometer • The mass spectrometer contains a vacuum chamber into which a small amount of a compound is vaporized. The molecules are then bombarded by high energy electrons which cause the molecule to fragment into molecular ions ...
Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... In the present work thermochemistry of intermolecular interactions of organic compounds in solutions of imidazolium based ionic liquids (ILs) has been studied using solution calorimetry method. Enthalpies of solution at infinite dilution of non-polar (alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons) and polar (alcoho ...
... In the present work thermochemistry of intermolecular interactions of organic compounds in solutions of imidazolium based ionic liquids (ILs) has been studied using solution calorimetry method. Enthalpies of solution at infinite dilution of non-polar (alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons) and polar (alcoho ...
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... WHICH OXIDATION NUMBER ? • elements can exist in more than one oxidation state • certain elements can be used as benchmarks ...
... WHICH OXIDATION NUMBER ? • elements can exist in more than one oxidation state • certain elements can be used as benchmarks ...
The Complete Notes - Joliet Junior College
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don’t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don’t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
Specification
... These show the arrangement of valence electrons in molecules. Bonding electrons may be represented using ...
... These show the arrangement of valence electrons in molecules. Bonding electrons may be represented using ...
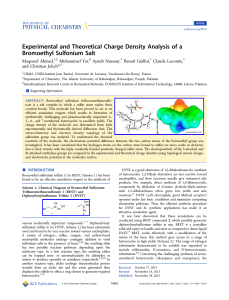
Experimental and Theoretical Charge Density Analysis of a
... due to their vicinity with the triply covalently bonded positively charged sulfur atom. The electropositivity of the S-attached and Br-attached methylene groups are compared in the experimental and theoretical charge densities using topological atomic charges and electrostatic potential at the molec ...
... due to their vicinity with the triply covalently bonded positively charged sulfur atom. The electropositivity of the S-attached and Br-attached methylene groups are compared in the experimental and theoretical charge densities using topological atomic charges and electrostatic potential at the molec ...
Chemistry 101: The Complete Notes
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don‟t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
... remembering. An analogy would be this: you read all the books out there on the subject of golf, but don‟t get round to swinging a club – what do you think happens when you tee off for the first time? ...
Atoms and Molecules
... 4. A molecule’s biological function is related to its shape • The three-dimensional shape of a molecule is an important determinant of its function in a cell. • The shape of a molecule is determined by the arrangement of electron orbitals that are shared by the atoms involved in the bond. • When co ...
... 4. A molecule’s biological function is related to its shape • The three-dimensional shape of a molecule is an important determinant of its function in a cell. • The shape of a molecule is determined by the arrangement of electron orbitals that are shared by the atoms involved in the bond. • When co ...