380 KB / 39 pages
... That is, the straight lines intersect where the mole fractions of the reactants are in the same ratio as the stoichiometry of their reaction with one another. (d) For an unknown precipitation stoichiometry, you could perform a similar series of reactions in which you measure the mass of precipitate ...
... That is, the straight lines intersect where the mole fractions of the reactants are in the same ratio as the stoichiometry of their reaction with one another. (d) For an unknown precipitation stoichiometry, you could perform a similar series of reactions in which you measure the mass of precipitate ...
Writing Chemical Formulas - Owen
... You want the positive side of the compound to balance the negative side of the compound. You can do this by crisscrossing the numbers, making superscripts into subscripts, and dropping the charge signs. Example: ...
... You want the positive side of the compound to balance the negative side of the compound. You can do this by crisscrossing the numbers, making superscripts into subscripts, and dropping the charge signs. Example: ...
N5 Chemistry Course Specification 2017-18 session
... The purpose of the course is to develop candidates’ curiosity, interest and enthusiasm for chemistry in a range of contexts. The skills of scientific inquiry are integrated and developed throughout the course. The relevance of chemistry is highlighted by the study of the applications of chemistry in ...
... The purpose of the course is to develop candidates’ curiosity, interest and enthusiasm for chemistry in a range of contexts. The skills of scientific inquiry are integrated and developed throughout the course. The relevance of chemistry is highlighted by the study of the applications of chemistry in ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... 1. The energy required to convert a groundstate atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion 2. The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely separated gaseous ions 3. The energy in a chemical or physical change that is available to do useful work 4. The energy requi ...
... 1. The energy required to convert a groundstate atom in the gas phase to a gaseous positive ion 2. The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely separated gaseous ions 3. The energy in a chemical or physical change that is available to do useful work 4. The energy requi ...
2014 Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... electron configurations, Coulomb’s Law, electrostatic potential energy, ionization energy, atomic and ionic radius, electronegativity, ionic charges, etc… THE ATOM – How Attractive! The atom is composed of negatively charged electrons, which can leave the atom, and a positively charged nucleus that ...
... electron configurations, Coulomb’s Law, electrostatic potential energy, ionization energy, atomic and ionic radius, electronegativity, ionic charges, etc… THE ATOM – How Attractive! The atom is composed of negatively charged electrons, which can leave the atom, and a positively charged nucleus that ...
physical setting chemistry
... 60 Explain, in terms of bonding, why compound A is saturated. [1] 61 Explain, in terms of molecular structure, why the chemical properties of compound A are different from the chemical properties of compound B. [1] ...
... 60 Explain, in terms of bonding, why compound A is saturated. [1] 61 Explain, in terms of molecular structure, why the chemical properties of compound A are different from the chemical properties of compound B. [1] ...
Chapter 24. Organic Chemistry
... An ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electron cloud in a chemical bond Electronegativity is a relative concept, meaning that an electronegativilty of one atom can be measured relative to another atom Generally electronegativity increases from left to right acros a period in the periodi ...
... An ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electron cloud in a chemical bond Electronegativity is a relative concept, meaning that an electronegativilty of one atom can be measured relative to another atom Generally electronegativity increases from left to right acros a period in the periodi ...
Inorganic and organic chemistry 2
... The coordination number is the number of coordinate bonds between the ligand(s) and the central metal atom or ion. EDTA4− is a hexadentate ligand, so one ion forms six coordinate bonds. The other ligands are monodentate so each forms a single coordinate bond with the central metal atom or ion. ...
... The coordination number is the number of coordinate bonds between the ligand(s) and the central metal atom or ion. EDTA4− is a hexadentate ligand, so one ion forms six coordinate bonds. The other ligands are monodentate so each forms a single coordinate bond with the central metal atom or ion. ...
Saturday Study Session 1 1st Class Reactions
... • SOLUTION – if it says a solution, then it CAN be broken into ions if it is soluble in water. • Only ionic compounds can become separate ions in a solution. • The 6 strong acids (HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4) and the strong bases (group 1 + OH-and Ba, Sr, Ca + OH-) are always written as separat ...
... • SOLUTION – if it says a solution, then it CAN be broken into ions if it is soluble in water. • Only ionic compounds can become separate ions in a solution. • The 6 strong acids (HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4) and the strong bases (group 1 + OH-and Ba, Sr, Ca + OH-) are always written as separat ...
The d block:
... Chromium and Copper • Cr and Cu don’t fit the pattern of building up the 3d sub-shell, why? – In the ground state electrons are always arranged to give lowest total energy – Electrons are negatively charged and repel each other – Lower total energy is obtained with e- singly in orbitals rather than ...
... Chromium and Copper • Cr and Cu don’t fit the pattern of building up the 3d sub-shell, why? – In the ground state electrons are always arranged to give lowest total energy – Electrons are negatively charged and repel each other – Lower total energy is obtained with e- singly in orbitals rather than ...
Physical Setting/Chemistry Examination
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
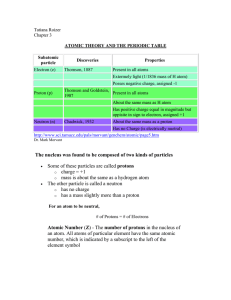
atomic theory and the periodic table
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
Answers
... a) What is the empirical formula for the substance? b) What is the molecular formula for the substance? 8) How many liters of ammonia gas would be produced by 3.00 grams of magnesium nitride, according to the reaction Mg3N2 + 6 H2O --> 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 NH3? 9) Solid iron (II) sulfide reacts with aqueou ...
... a) What is the empirical formula for the substance? b) What is the molecular formula for the substance? 8) How many liters of ammonia gas would be produced by 3.00 grams of magnesium nitride, according to the reaction Mg3N2 + 6 H2O --> 3 Mg(OH)2 + 2 NH3? 9) Solid iron (II) sulfide reacts with aqueou ...
pp. 18-21
... To answer this, use knowledge of: ¾ Molecular shape ¾ Bond Polarity To determine the polarity of a molecule that has more than 2 atoms: a) find molecular shape (3D) b) find "bond" dipoles (using electronegativity differences) c) use vector "analysis" to find net molecular dipole ...
... To answer this, use knowledge of: ¾ Molecular shape ¾ Bond Polarity To determine the polarity of a molecule that has more than 2 atoms: a) find molecular shape (3D) b) find "bond" dipoles (using electronegativity differences) c) use vector "analysis" to find net molecular dipole ...
Introduction to Qualitative Analysis
... qualitative analysis often involves the identification of ions present in a sample. This is the type of analysis you will be involved with for your unknown; you will be given an aqueous solution containing a mixture of several metal cations that you must identify. The techniques you will learn can b ...
... qualitative analysis often involves the identification of ions present in a sample. This is the type of analysis you will be involved with for your unknown; you will be given an aqueous solution containing a mixture of several metal cations that you must identify. The techniques you will learn can b ...
Basic Integrated Chemistry - Michigan City Area Schools
... Understand and explain that atoms have a positive nucleus (consisting of relatively massive positive protons and neutral neutrons) surrounded by negative electrons of much smaller mass, some of which may be lost, gained, or shared when interacting with other atoms. 1.2 Realize that and explain how a ...
... Understand and explain that atoms have a positive nucleus (consisting of relatively massive positive protons and neutral neutrons) surrounded by negative electrons of much smaller mass, some of which may be lost, gained, or shared when interacting with other atoms. 1.2 Realize that and explain how a ...
Electrons and “holes”
... An intrinsic semiconductor, also called an undoped semiconductor or i-type semiconductor, is a pure semiconductor without any significant dopant species present. The number of charge carriers is therefore determined by the properties of the material itself instead of the amount of impurities. In int ...
... An intrinsic semiconductor, also called an undoped semiconductor or i-type semiconductor, is a pure semiconductor without any significant dopant species present. The number of charge carriers is therefore determined by the properties of the material itself instead of the amount of impurities. In int ...
2003
... Substance C conducts electricity in solid and molten states due to free (delocalised) electrons which can move freely through the lattice. Substance D does not conduct electricity in the solid state because ions are fixed. However, when molten, the ions are mobile, free to move and conduct electrici ...
... Substance C conducts electricity in solid and molten states due to free (delocalised) electrons which can move freely through the lattice. Substance D does not conduct electricity in the solid state because ions are fixed. However, when molten, the ions are mobile, free to move and conduct electrici ...
PowerPoint Chapter 14 - Preparatory Chemistry
... • whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. • which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. • which atom in an ionic bond forms the cation and which forms the anion. • which of two covalent bonds are more polar. ...
... • whether a chemical bond is nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. • which atom in a polar covalent bond is partial negative and which is partial positive. • which atom in an ionic bond forms the cation and which forms the anion. • which of two covalent bonds are more polar. ...
Ch9_10notes maroon edition
... atom. We write the symbol of the atom in question, then draw the appropriate number of dots (= # of valence e-). Top, bottom, left right; these are not important, but it is standard to place a single dot on each side before doubling up. Sketch dot symbols for Li, N, Cl, O, B, and He in the space bel ...
... atom. We write the symbol of the atom in question, then draw the appropriate number of dots (= # of valence e-). Top, bottom, left right; these are not important, but it is standard to place a single dot on each side before doubling up. Sketch dot symbols for Li, N, Cl, O, B, and He in the space bel ...
Name: Beryllium Symbol: Be Atomic number:4 Mass
... Number of electrons:4 Electronic arrangement:2,2 Period number:2 Group number:2 (Alkaline earth metal) ...
... Number of electrons:4 Electronic arrangement:2,2 Period number:2 Group number:2 (Alkaline earth metal) ...
Chapter 1--Title
... More energy must be expended to overcome very strong forces between molecules ...
... More energy must be expended to overcome very strong forces between molecules ...
Document
... subscript means that each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms. Since each water molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms and there are two water molecules, there must be 4 (2 × 2) hydrogen atoms. ...
... subscript means that each water molecule has two hydrogen atoms. Since each water molecule has 2 hydrogen atoms and there are two water molecules, there must be 4 (2 × 2) hydrogen atoms. ...
Quantities, Units, Symbols and Nomenclature used in
... These are written in parentheses printed in italic type, immediately after the formula or substance and on the same line as chemical formula symbols. eg ...
... These are written in parentheses printed in italic type, immediately after the formula or substance and on the same line as chemical formula symbols. eg ...