Molecular Models Lab
... hydrogen molecule is H-H. Although such "models" help us in understanding the structure of molecules, flat models do not give us the three-dimensional view that is necessary to truly visualize most molecules. In this experiment, you will build three dimensional molecular models and then compare them ...
... hydrogen molecule is H-H. Although such "models" help us in understanding the structure of molecules, flat models do not give us the three-dimensional view that is necessary to truly visualize most molecules. In this experiment, you will build three dimensional molecular models and then compare them ...
Electrochemistry
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
... Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers (In order of priority): 1. The oxidation number of any pure element is _________. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is __________ to its charge. 3. The ______ of the oxidation numbers in a compound is zero if ____________, or equal to the ___________ if ...
2002 local exam - Virginia Section
... 59. Which of the following statements are correct? I In a family of elements, the largest atom has the highest electronegativity II In the third row of elements the halogen element has the highest electronegativity III For all elements its second ionization energy is greater than its first ionizatio ...
... 59. Which of the following statements are correct? I In a family of elements, the largest atom has the highest electronegativity II In the third row of elements the halogen element has the highest electronegativity III For all elements its second ionization energy is greater than its first ionizatio ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
Importance of Molecular Simulation for Studying Structural Properties
... computational techniques used to model or mimic the behavior of molecules. The techniques are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science for studying molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and m ...
... computational techniques used to model or mimic the behavior of molecules. The techniques are used in the fields of computational chemistry, drug design, computational biology and materials science for studying molecular systems ranging from small chemical systems to large biological molecules and m ...
1440247979
... Figure 2 shows a set up of apparatus to investigate the reaction between metals and steam. ...
... Figure 2 shows a set up of apparatus to investigate the reaction between metals and steam. ...
Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
... Another molecule having this geometry is SO3. Consider SO2: The total number of valence electrons is 6 + 12 = 18. The Lewis dot structure satisfying the octet rule, and having the smallest formal charges on atoms is: ...
... Another molecule having this geometry is SO3. Consider SO2: The total number of valence electrons is 6 + 12 = 18. The Lewis dot structure satisfying the octet rule, and having the smallest formal charges on atoms is: ...
S4 Standard Grade Revision Booklet
... c) heating with carbon? 4. Give (i) word equations and (ii) equations using the chemical formulae (not necessarily balanced) for the reactions between: a) potassium and oxygen b) lithium and water c) magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. 5. Calculate the percentage by mass of: a) Sodium in sodium ...
... c) heating with carbon? 4. Give (i) word equations and (ii) equations using the chemical formulae (not necessarily balanced) for the reactions between: a) potassium and oxygen b) lithium and water c) magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid. 5. Calculate the percentage by mass of: a) Sodium in sodium ...
15.The Doping of Semiconductors
... semiconductors are Silicon and Germanium. The reason semiconductors are important is that with some engineering they can sometimes both conduct and insulate depending on their connections. Thus they serve as the basis for switching and amplification, the fundamental actions of computer elements. A t ...
... semiconductors are Silicon and Germanium. The reason semiconductors are important is that with some engineering they can sometimes both conduct and insulate depending on their connections. Thus they serve as the basis for switching and amplification, the fundamental actions of computer elements. A t ...
Multiple Pathways To Success Quarter 3 Learning Module
... Students will identify five types of balanced equations including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion. Students will balance equations and identify types of reactions including including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and co ...
... Students will identify five types of balanced equations including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and combustion. Students will balance equations and identify types of reactions including including synthesis,decomposition, single replacement, double replacement and co ...
H - JMap
... 15 Which formula is correct for ammonium sulfate? (3) NH4(SO4)2 (1) NH4SO4 (2) (NH4)2SO4 (4) (NH4)2(SO4)2 16 An example of an empirical formula is (3) C2H4(OH)2 (1) CH4 (2) C2H4 (4) C6H12O6 ...
... 15 Which formula is correct for ammonium sulfate? (3) NH4(SO4)2 (1) NH4SO4 (2) (NH4)2SO4 (4) (NH4)2(SO4)2 16 An example of an empirical formula is (3) C2H4(OH)2 (1) CH4 (2) C2H4 (4) C6H12O6 ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... strong – completely dissociate (consult solubility rules—strong acids, strong bases and soluble salts) Barium chloride is an ionic salt that completely ionizes in water, HCl is a strong acid that completely dissociates into H+ ions and Cl− ions in water while NaOH is a strong base that completely di ...
... strong – completely dissociate (consult solubility rules—strong acids, strong bases and soluble salts) Barium chloride is an ionic salt that completely ionizes in water, HCl is a strong acid that completely dissociates into H+ ions and Cl− ions in water while NaOH is a strong base that completely di ...
Syracuse Syllabus
... Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (See Table 2.1 Comparing the proton, neutron, and electron ) Isotopes, Atomic Numbers, and Mass Numbers 2.4 The Periodic Table (Study figure showing the division of eleme ...
... Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (See Table 2.1 Comparing the proton, neutron, and electron ) Isotopes, Atomic Numbers, and Mass Numbers 2.4 The Periodic Table (Study figure showing the division of eleme ...
Worksheet 3A on Molecules
... Of the species listed, only O3 and CO are polar. CO is polar due to the difference in electronegativity between O and C; O3 is polar because it has 3 RHED and one lone pair on the central atom. This lone pair is an area where negative charge is concentrated, so this results in the molecule having an ...
... Of the species listed, only O3 and CO are polar. CO is polar due to the difference in electronegativity between O and C; O3 is polar because it has 3 RHED and one lone pair on the central atom. This lone pair is an area where negative charge is concentrated, so this results in the molecule having an ...
The Complete Notes - Joliet Junior College
... Examples: N2 (g) (Nitrogen gas, molecular), Pb(s) (metallic lead, a ‘giant’ structure) Compounds can also have either Molecular or ‘giant’ structures. Examples: H2O(l) (water, molecular), Fe2O3(s) (‘rust’ (iron oxide), a ‘giant’ structure) Recall: A molecule is an independent unit containing two or ...
... Examples: N2 (g) (Nitrogen gas, molecular), Pb(s) (metallic lead, a ‘giant’ structure) Compounds can also have either Molecular or ‘giant’ structures. Examples: H2O(l) (water, molecular), Fe2O3(s) (‘rust’ (iron oxide), a ‘giant’ structure) Recall: A molecule is an independent unit containing two or ...
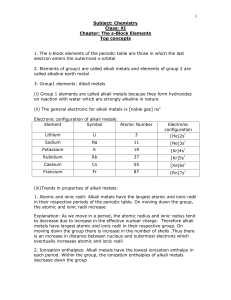
The s-Block Elements Top concepts 1. The s-block
... Explanation: Alkali metals have only one electron in their valence shell and therefore can lose the single valence electron readily to acquire the stable configuration of a noble gas. Since the second ionization energies are very high, they cannot form divalent ions. Thus, alkali metals are univalen ...
... Explanation: Alkali metals have only one electron in their valence shell and therefore can lose the single valence electron readily to acquire the stable configuration of a noble gas. Since the second ionization energies are very high, they cannot form divalent ions. Thus, alkali metals are univalen ...
Covalent Bonding
... occurs when it is possible to draw two or more valid electron dot structures that have the same number of electron pairs for a molecule or ion. • Actual bonding is a hybrid of all the ...
... occurs when it is possible to draw two or more valid electron dot structures that have the same number of electron pairs for a molecule or ion. • Actual bonding is a hybrid of all the ...
Writing Net Ionic Equations
... KBr (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgBr (s) + KNO3 (aq) Note that each cation pairs up with the anion in the other compound, thus switching partners. Anions do not pair up with anions and cations do not pair up with cations. Likes repel; opposites attract! ...
... KBr (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgBr (s) + KNO3 (aq) Note that each cation pairs up with the anion in the other compound, thus switching partners. Anions do not pair up with anions and cations do not pair up with cations. Likes repel; opposites attract! ...
Topic 4
... – A net ionic equation is a chemical equation from which the spectator ions have been removed. – A spectator ion is an ion in an ionic equation that does not take part in the reaction. Species does not change form from reactant to product (Na+(aq) and OH-(aq) are M.E. unchanged in this reaction and ...
... – A net ionic equation is a chemical equation from which the spectator ions have been removed. – A spectator ion is an ion in an ionic equation that does not take part in the reaction. Species does not change form from reactant to product (Na+(aq) and OH-(aq) are M.E. unchanged in this reaction and ...
Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4)
... Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4) Water has many unique chemical and physical properties. Possibly one of the most important is its ability to dissolve other substances to form solutions. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. The solvent (usually the su ...
... Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4) Water has many unique chemical and physical properties. Possibly one of the most important is its ability to dissolve other substances to form solutions. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances. The solvent (usually the su ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... Teaching chemistry - but ignoring the ‘why’ question? One way of avoiding the question of how to teach about ‘why reactions occur’ to relatively unsophisticated school pupils, is not to teach about this at all. Indeed some teachers have expressed the view that a good deal of the theoretical material ...
... Teaching chemistry - but ignoring the ‘why’ question? One way of avoiding the question of how to teach about ‘why reactions occur’ to relatively unsophisticated school pupils, is not to teach about this at all. Indeed some teachers have expressed the view that a good deal of the theoretical material ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... ◘ The modern periodic table arranges the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical prope ...
... ◘ The modern periodic table arranges the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ◘ Metals are separated from nonmetals by the “staircase line”. metals - shiny, malleable, ductile, conductors of heat and electricity. ◘ The columns are families (groups) of elements having similar chemical prope ...
Chapter 1
... 61. Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), cannot be stored in glass bottles because compounds called silicates in the glass are attacked by the HF(aq). Sodium silicate (Na2SiO3), for example, reacts as follows: Na2SiO3 (s) + 8 HF(aq) H2SiF6(aq) + 2 NaF(aq) + 3 H2O(l) a) How many moles of HF are needed to rea ...
... 61. Hydrofluoric acid, HF(aq), cannot be stored in glass bottles because compounds called silicates in the glass are attacked by the HF(aq). Sodium silicate (Na2SiO3), for example, reacts as follows: Na2SiO3 (s) + 8 HF(aq) H2SiF6(aq) + 2 NaF(aq) + 3 H2O(l) a) How many moles of HF are needed to rea ...