Chap. 17 - Lemon Bay High School
... Free Energy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Free Energy and Chemical Reactions The Dependence of Free Energy on Pressure Free Energy and Equilibrium Free Energy and Work ...
... Free Energy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Free Energy and Chemical Reactions The Dependence of Free Energy on Pressure Free Energy and Equilibrium Free Energy and Work ...
13 CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM W MODULE - 5
... of all the reactants and products become constant. This happens when the rates of forward and reverse reactions become equal; and all the properties of the system become constant. It is said that the system has attained state of equilibration. However it may be noted that the state of equilibrium is ...
... of all the reactants and products become constant. This happens when the rates of forward and reverse reactions become equal; and all the properties of the system become constant. It is said that the system has attained state of equilibration. However it may be noted that the state of equilibrium is ...
Science Focus 9 Matter and Chemical Change Class Notes Topic 1
... as elements. Lavoisier was one of the first chemists to use a balanced view of chemical change, which we now call … The Law of Conservation of Mass In a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants, is always equal to the total mass of the products. This law ties in well with the atomic theory ...
... as elements. Lavoisier was one of the first chemists to use a balanced view of chemical change, which we now call … The Law of Conservation of Mass In a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants, is always equal to the total mass of the products. This law ties in well with the atomic theory ...
Gas review
... 1. A gas is composed of molecules that are separated from each other by distances far greater than their own dimensions. The molecules can be considered to be points; that is, they possess mass but have negligible volume. 2. Gas molecules are in constant motion in random directions. Collisions among ...
... 1. A gas is composed of molecules that are separated from each other by distances far greater than their own dimensions. The molecules can be considered to be points; that is, they possess mass but have negligible volume. 2. Gas molecules are in constant motion in random directions. Collisions among ...
Lab Manual - Center for Nonlinear Science
... about to perform that afternoon in your laboratory notebook. In addition, you should have prepared the tables (with the columns appropriately headed) into which you will enter the data you collect during the practical. The crude data collected during the laboratory session must be entered directly i ...
... about to perform that afternoon in your laboratory notebook. In addition, you should have prepared the tables (with the columns appropriately headed) into which you will enter the data you collect during the practical. The crude data collected during the laboratory session must be entered directly i ...
High capacitance of surface-modified 2D titanium
... rise to the broadened and convoluted spectra seen in the Ti 2p region (Fig. 2C). In this region, the Ti-carbide photoemission arises from Ti3C2, while the Ti (II) and Ti (III) components arise from these mixed oxides and carboxides, and the Ti (IV) component arises from TiO2 present on the surface o ...
... rise to the broadened and convoluted spectra seen in the Ti 2p region (Fig. 2C). In this region, the Ti-carbide photoemission arises from Ti3C2, while the Ti (II) and Ti (III) components arise from these mixed oxides and carboxides, and the Ti (IV) component arises from TiO2 present on the surface o ...
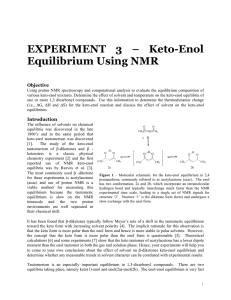
EXPERIMENT 3 – Keto-Enol Equilibrium Using NMR
... 1. Choose one of the β-diketones for study by the entire class. Prepare solutions of the chosen compound in at least four different solvents (C6D6, C6D12, CD3CN, H2O/D2O, CDCl3, acetone-d6 and/or dimethyl sulfoxide-d6) at a concentration of ~1 mM. Prepare them at least 60 minutes in advance of runni ...
... 1. Choose one of the β-diketones for study by the entire class. Prepare solutions of the chosen compound in at least four different solvents (C6D6, C6D12, CD3CN, H2O/D2O, CDCl3, acetone-d6 and/or dimethyl sulfoxide-d6) at a concentration of ~1 mM. Prepare them at least 60 minutes in advance of runni ...
C1 – Topic 2 notes - ARK Elvin Academy
... Word equations show what’s happening in a chemical reaction…: o E.g zinc carbonatezinc oxide + carbon dioxide Substances on the left of the arrow are called reactants (zinc carbonate in the above example) Substances on the right of the arrow are called products (zinc oxide and carbon dioxide in the ...
... Word equations show what’s happening in a chemical reaction…: o E.g zinc carbonatezinc oxide + carbon dioxide Substances on the left of the arrow are called reactants (zinc carbonate in the above example) Substances on the right of the arrow are called products (zinc oxide and carbon dioxide in the ...
ALE 23. Balancing Redox Reactions
... 7. Why in Step K of Example 2 is ―4 OH-‖ added to each side of the reaction? (Such a step did not take place in Example 1. What’s different about Example 2?) ...
... 7. Why in Step K of Example 2 is ―4 OH-‖ added to each side of the reaction? (Such a step did not take place in Example 1. What’s different about Example 2?) ...
Topic 2 notes - WordPress.com
... Word equations show what’s happening in a chemical reaction…: o E.g zinc carbonatezinc oxide + carbon dioxide Substances on the left of the arrow are called reactants (zinc carbonate in the above example) Substances on the right of the arrow are called products (zinc oxide and carbon dioxide in the ...
... Word equations show what’s happening in a chemical reaction…: o E.g zinc carbonatezinc oxide + carbon dioxide Substances on the left of the arrow are called reactants (zinc carbonate in the above example) Substances on the right of the arrow are called products (zinc oxide and carbon dioxide in the ...
chemical reaction
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
... • List three observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. • List three requirements for a correctly written chemical equation. • Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction. • Balance a formula equation by inspection. ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
... The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, internal temperature, etc.), tectonic activity, and the existence of life. As the sun generated heat, light, and solar wind through nuclea ...
Angular momentum
... Conclusions: effects due to alignment The alignment effect manifests itself in such processes as ionization, high harmonic generation; even configuration of molecular orbitals can be tested. Fragmentation of molecules also changes due to alignment. Alignment introduces changes of the refractive ind ...
... Conclusions: effects due to alignment The alignment effect manifests itself in such processes as ionization, high harmonic generation; even configuration of molecular orbitals can be tested. Fragmentation of molecules also changes due to alignment. Alignment introduces changes of the refractive ind ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.