AP Chemistry Unit 3 Test Review Topics Covered: Gases Liquids
... of calcium carbonate, a student added a 50.0 gram sample of powdered, solid CaCO3 to a 1.00L rigid container. The student sealed the container, pumped out all the gases, then heated the container in an oven at 1100 K. As the container was heated, the total pressure of CO2 gas in the container was me ...
... of calcium carbonate, a student added a 50.0 gram sample of powdered, solid CaCO3 to a 1.00L rigid container. The student sealed the container, pumped out all the gases, then heated the container in an oven at 1100 K. As the container was heated, the total pressure of CO2 gas in the container was me ...
Chemical Equations TrackStar Assignment
... 3. Write the reaction for a silver spoon tarnishing. What type of reaction is this? 4. Write the reaction for the burning of Methane gas (the gas used in Chemistry lab). What type of reaction is this? 5. Write the reaction of the neutralization of stomach acid. What type of reaction is this? 6. Does ...
... 3. Write the reaction for a silver spoon tarnishing. What type of reaction is this? 4. Write the reaction for the burning of Methane gas (the gas used in Chemistry lab). What type of reaction is this? 5. Write the reaction of the neutralization of stomach acid. What type of reaction is this? 6. Does ...
The effect of confinement on chemical reactions
... significantly higher density than the bulk phase. The combination of these two factors naturally causes an enhancement of the equilibrium yield, as the increased density of the adsorbed phase displaces the equilibrium to the side with a lower number of moles. It would be interesting to consider now ...
... significantly higher density than the bulk phase. The combination of these two factors naturally causes an enhancement of the equilibrium yield, as the increased density of the adsorbed phase displaces the equilibrium to the side with a lower number of moles. It would be interesting to consider now ...
CHEM 481. Assignment 0. Review of General Chemistry. Answers
... Break one O=O double bond and two H–H bonds (+ve signs); form 4 H–O single bonds (-ve signs). 56. Describe the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table. Electronegativity increases from left to right and from bottom to top across the PT; Fr is the lowest, F (or He) the highest. 57. Describe ...
... Break one O=O double bond and two H–H bonds (+ve signs); form 4 H–O single bonds (-ve signs). 56. Describe the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table. Electronegativity increases from left to right and from bottom to top across the PT; Fr is the lowest, F (or He) the highest. 57. Describe ...
① Name AP CHEM __/__/__ Chapter 12 Outline
... The collision model is built around the central idea that molecules must collide to react. The kinetic molecular theory of gases predicts that an increase in temperature raises molecular velocities and so increases the frequency of collisions between molecules. This agrees with the observation t ...
... The collision model is built around the central idea that molecules must collide to react. The kinetic molecular theory of gases predicts that an increase in temperature raises molecular velocities and so increases the frequency of collisions between molecules. This agrees with the observation t ...
Answers to Assignment #1
... Break one O=O double bond and two H–H bonds (+ve signs); form 4 H–O single bonds (-ve signs). 56. Describe the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table. Electronegativity increases from left to right and from bottom to top across the PT; Fr is the lowest, F (or He) the highest. 57. Describe ...
... Break one O=O double bond and two H–H bonds (+ve signs); form 4 H–O single bonds (-ve signs). 56. Describe the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table. Electronegativity increases from left to right and from bottom to top across the PT; Fr is the lowest, F (or He) the highest. 57. Describe ...
Print › Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary | Quizlet
... Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary Study online at quizlet.com/_2i1qo4 ...
... Honors Chemistry Unit 02 Vocabulary Study online at quizlet.com/_2i1qo4 ...
Contents and Concepts
... The Effect of Temperature on the Free Energy of a Reaction Beware of Oversimplification Stand-State Free Energies of Reaction Equilibria Expressed in Partial Pressures Interpreting Stand-State Free Energy of Reaction Data Relationship Between Free Energy and Equilibrium Constants Temperature Depende ...
... The Effect of Temperature on the Free Energy of a Reaction Beware of Oversimplification Stand-State Free Energies of Reaction Equilibria Expressed in Partial Pressures Interpreting Stand-State Free Energy of Reaction Data Relationship Between Free Energy and Equilibrium Constants Temperature Depende ...
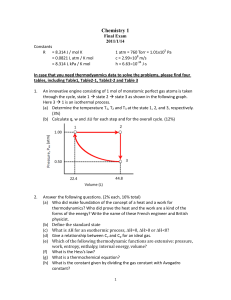
Chemistry 1
... (b) Define the standard state (c) What is H for an exothermic process, H=0, H>0 or H<0? (d) Give a relationship between Cv and Cp for an ideal gas. (e) Which of the following thermodynamic functions are extensive: pressure, work, entropy, enthalpy, internal energy, volume? (f) What is the Hess’s ...
... (b) Define the standard state (c) What is H for an exothermic process, H=0, H>0 or H<0? (d) Give a relationship between Cv and Cp for an ideal gas. (e) Which of the following thermodynamic functions are extensive: pressure, work, entropy, enthalpy, internal energy, volume? (f) What is the Hess’s ...
Predicting Products online assistance #3
... 1. synthesis - two reactants combine to form one product 2. decomposition - one reactant decomposes, or breaks apart, into two or more products. 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new co ...
... 1. synthesis - two reactants combine to form one product 2. decomposition - one reactant decomposes, or breaks apart, into two or more products. 3. single replacement - an element replaces another in a compound. 4. double replacement - the elements in two compounds switch partners to form two new co ...
Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... In a solution of salt water, what is the solute? What is the solvent? What is molarity? What is the symbol for molarity? Describe how you would prepare 2L of a 10M sodium chloride solution. Describe how you would make a 0.5M solution of BaNO3 given 1L of 5M BaNO3. What is a precipitate? Is it solubl ...
... In a solution of salt water, what is the solute? What is the solvent? What is molarity? What is the symbol for molarity? Describe how you would prepare 2L of a 10M sodium chloride solution. Describe how you would make a 0.5M solution of BaNO3 given 1L of 5M BaNO3. What is a precipitate? Is it solubl ...
Rate
... • Activation Energy (Ea) – the minimum amount of energy required in a collision to allow a reaction to take place. ...
... • Activation Energy (Ea) – the minimum amount of energy required in a collision to allow a reaction to take place. ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.