CHM112 Lab – Heat of Neutralization – Grading Rubric
... Safety and proper waste disposal procedures observed ...
... Safety and proper waste disposal procedures observed ...
C 3 H 8 (g) - Ms Critchley`s Lab
... Standard conditions are 298K, 100 kPa and 1M for solutions. All substances should be in their standard states The is the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen under standard conditions, all reactants and products being in their standard states. T ...
... Standard conditions are 298K, 100 kPa and 1M for solutions. All substances should be in their standard states The is the enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a substance reacts completely with oxygen under standard conditions, all reactants and products being in their standard states. T ...
Enthalpy of Neutralization
... In the course of most physical processes and chemical reactions there is a change in energy. In chemistry what is normally measured is H (enthalpy change), the change in heat at constant pressure and ignoring any work done by the reacting system. If the reaction is exothermic, heat is given off and ...
... In the course of most physical processes and chemical reactions there is a change in energy. In chemistry what is normally measured is H (enthalpy change), the change in heat at constant pressure and ignoring any work done by the reacting system. If the reaction is exothermic, heat is given off and ...
Unit 13 - Electrochemistry
... - Single replacement and combustion reactions are redox reactions, double replacement is not a redox reaction. ...
... - Single replacement and combustion reactions are redox reactions, double replacement is not a redox reaction. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Describing Chemical Change: • Chemical equations: using chemical formulas to describe in writing a chemical reaction • The arrow separates the formulas of the reactants from the formulas of the products ...
... Describing Chemical Change: • Chemical equations: using chemical formulas to describe in writing a chemical reaction • The arrow separates the formulas of the reactants from the formulas of the products ...
Reactions and Equations
... Balancing Chemical Equations • The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction—it is conserved. • In other words, the mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations • The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction—it is conserved. • In other words, the mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. ...
Section 1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... completely. • Relative masses can be found by multiplying the molecular mass of each substance by the mole ratio from the balanced equation. ...
... completely. • Relative masses can be found by multiplying the molecular mass of each substance by the mole ratio from the balanced equation. ...
Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Elephant`s Toothpaste
... 6 % hydrogen peroxide solution is available from most beauty supply stores. This demonstration results in a great deal of foam. Ensure that you perform the experiment in a pan to aid with the clean up. Any of the other suggested catalysts (manganese(IV) oxide, potassium iodide, and sodium iodide) al ...
... 6 % hydrogen peroxide solution is available from most beauty supply stores. This demonstration results in a great deal of foam. Ensure that you perform the experiment in a pan to aid with the clean up. Any of the other suggested catalysts (manganese(IV) oxide, potassium iodide, and sodium iodide) al ...
File - chemistryattweed
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
... and was interested in the effect of heat on the chemistry of gases. In the early 1900s, Haber reacted nitrogen with hydrogen, using an iron catalyst, to form ammonia. Ammonia can be readily converted to a range of valuable products. In 1908 he had improved the reaction and in 1911 he was rewarded wi ...
Chemical Reactions
... a single replacement reaction, normally an element and a component of a compound exchange places. Normally positive replaces positive, negative will replace negative REACTION TYPE: SINGLE REPLACEMENT ...
... a single replacement reaction, normally an element and a component of a compound exchange places. Normally positive replaces positive, negative will replace negative REACTION TYPE: SINGLE REPLACEMENT ...
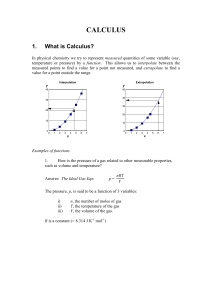
CALCULUS
... c) The rate of a chemical reaction is a function of the temperature. d) The energy of a photon is a function of its frequency. Rather than write out “... is a function of ...” each time, we use an abbreviation of the form f(x), which is read as “f of x”. We replace the f by the dependent quantity, a ...
... c) The rate of a chemical reaction is a function of the temperature. d) The energy of a photon is a function of its frequency. Rather than write out “... is a function of ...” each time, we use an abbreviation of the form f(x), which is read as “f of x”. We replace the f by the dependent quantity, a ...
What is an Enzym
... The role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, and their effect on enzyme activity. Appropriateness for Middle/High School Students Students will be able to observe a chemical reaction, identify the substrate ...
... The role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, and their effect on enzyme activity. Appropriateness for Middle/High School Students Students will be able to observe a chemical reaction, identify the substrate ...
Electrons
... Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine with one another in wholenumber ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine with one another in wholenumber ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
chapter 13 - Humble ISD
... EXAMPLE PROBLEM The following reaction is allowed to go to equilibrium. ...
... EXAMPLE PROBLEM The following reaction is allowed to go to equilibrium. ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.