Chapter 7 – Chemical Reactions and Energy Flow
... Despite extensive tables containing the standard enthalpy of formation for literally hundreds of chemical compounds, they are not sufficient. Many reactions are outside of the scope of the tables. However, we can approximate the energy by using the average bond energies for all of the chemical bond ...
... Despite extensive tables containing the standard enthalpy of formation for literally hundreds of chemical compounds, they are not sufficient. Many reactions are outside of the scope of the tables. However, we can approximate the energy by using the average bond energies for all of the chemical bond ...
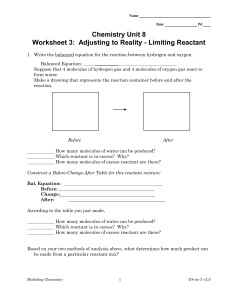
Types of Reactions Lab
... 1.) List the 5 types of reactions. For each type, describe them in terms of elements and compounds and describe what generally happens. 2.) A) What is bromothymol blue and how can it be used to identify an acid or a base (use your book or the internet to look this up)? B) Look up the same for univer ...
... 1.) List the 5 types of reactions. For each type, describe them in terms of elements and compounds and describe what generally happens. 2.) A) What is bromothymol blue and how can it be used to identify an acid or a base (use your book or the internet to look this up)? B) Look up the same for univer ...
Matter- Types and Changes
... • CO2 contains 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen all chemically linked. • H2SO4 contains 2 hydrogen, 1 sulfur, and 4 oxygen atoms. • (NH4)2C2O4 - A subscript outside parentheses applies to everything within the parentheses; 2 N, 8 H, 2 C, 4 O ...
... • CO2 contains 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen all chemically linked. • H2SO4 contains 2 hydrogen, 1 sulfur, and 4 oxygen atoms. • (NH4)2C2O4 - A subscript outside parentheses applies to everything within the parentheses; 2 N, 8 H, 2 C, 4 O ...
Review of Thermodynamics
... • The Gibbs free energy, G, is energy available in a form that can be used to do work. • Cane be broken down into two further components: enthalpy H; and entropy S for a given temperature T (in Kelvin): ...
... • The Gibbs free energy, G, is energy available in a form that can be used to do work. • Cane be broken down into two further components: enthalpy H; and entropy S for a given temperature T (in Kelvin): ...
슬라이드 1
... ∂c/∂t = D∇2c - v∙∇c: generalized diffusion equation • If a reaction occurs, it has also to be included. For a 1st-order reaction - kc term is included. • This is the key equation in designing a chemical reactor. • Finite element method in carrying out computer calculation. ...
... ∂c/∂t = D∇2c - v∙∇c: generalized diffusion equation • If a reaction occurs, it has also to be included. For a 1st-order reaction - kc term is included. • This is the key equation in designing a chemical reactor. • Finite element method in carrying out computer calculation. ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
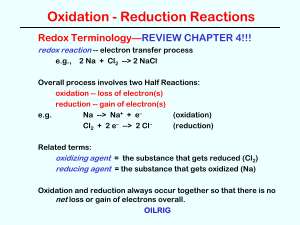
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
... • The transfer of electrons between species, meaning that one species is oxidized and one is reduced. The two processes will always occur together. • When has a redox reaction occurred? – If there is a change in the oxidation state of any element in the reaction, a redox reaction has happened. – Rem ...
A New Energy Efficient Chemical Pathway For Extracting Ti From Ti
... where F80 and P80 are the particle sizes (80% passing) of the feed and product, respectively, and Wi is the Bond work index, which is a material specific index of “grindability.” Titania slag has a Bond work index of 17.6 kWhr/ton [S2]. The size distribution of the slag was experimentally determined ...
... where F80 and P80 are the particle sizes (80% passing) of the feed and product, respectively, and Wi is the Bond work index, which is a material specific index of “grindability.” Titania slag has a Bond work index of 17.6 kWhr/ton [S2]. The size distribution of the slag was experimentally determined ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
... 13. 6.0 mol of aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide. What is the amount of oxygen, in mol, needed for complete reaction? 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Al2O3(s) 14. What is the total number of nitrogen atoms in two mol of NH4NO3? 15. On analysis, a compound with molar mass 60 g mol-1 was found t ...
About writing chemical equations ppt
... 3. Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. A delta indicates heat is applied. 4. Coefficients 2 H2O are placed in front to balance the equation. One is never placed there, it is just understood. ...
... 3. Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. A delta indicates heat is applied. 4. Coefficients 2 H2O are placed in front to balance the equation. One is never placed there, it is just understood. ...
Supplementary Materials for original manuscript submitted
... propose that CO oxidation to CO2 should not be a limiting stage. Then the Cu-carbonate formation via the reactions between CO2 and CuOXCu moieties can be tested similarly to the route from EA oxide MeOXMe clusters [S5-S6], X = 1 - 2. The Part 3.2 justifies the application of the DFT tools relative t ...
... propose that CO oxidation to CO2 should not be a limiting stage. Then the Cu-carbonate formation via the reactions between CO2 and CuOXCu moieties can be tested similarly to the route from EA oxide MeOXMe clusters [S5-S6], X = 1 - 2. The Part 3.2 justifies the application of the DFT tools relative t ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.