Smell, Taste, Texture, and Temperature
... time in the experiment, the contingency between the odor and the taste was reversed, and when the “meaning” of the two odors altered, so did the behavior. It would be interesting to investigate in which parts of the olfactory system the neurons show reversal, because where they do, it can be conclud ...
... time in the experiment, the contingency between the odor and the taste was reversed, and when the “meaning” of the two odors altered, so did the behavior. It would be interesting to investigate in which parts of the olfactory system the neurons show reversal, because where they do, it can be conclud ...
The prototype effect revisited: Evidence for an abstract feature model
... (1994) argued that their results with line drawings in a divided attention task might reflect naive, feature-specific processes at work. Where their thinking diverges from our own is that they were referring to simple features, that is, nameable parts. They concluded that face recognition must requi ...
... (1994) argued that their results with line drawings in a divided attention task might reflect naive, feature-specific processes at work. Where their thinking diverges from our own is that they were referring to simple features, that is, nameable parts. They concluded that face recognition must requi ...
Deep Brain stimulation in the Treatment of Dystonia – The
... Externus] Adapted from Breakefield et al.2 ...
... Externus] Adapted from Breakefield et al.2 ...
MEMORY FOR SINGLE ITEMS, WORD PAIRS, AND TEMPORAL
... disproportionately impaired temporal order memory in Korsakoff, but not in MTL, amnesics have been used to support the hypothesis that amnesia may be functionally and anatomically heterogeneous in a specific kind of way. Thus, Parkin and colleagues (see Hunkin and Parkin, 1993; Parkin, 1992; Parkin ...
... disproportionately impaired temporal order memory in Korsakoff, but not in MTL, amnesics have been used to support the hypothesis that amnesia may be functionally and anatomically heterogeneous in a specific kind of way. Thus, Parkin and colleagues (see Hunkin and Parkin, 1993; Parkin, 1992; Parkin ...
Adaptive Gain and Optimal Performance
... mechanisms. The importance of arousal is undeniable: It is closely related to other phenomena such as sleep, attention, anxiety, stress, and motivation. Dampened arousal leads to drowsiness and, in the limit, sleep. Heightened arousal (brought on by the sudden appearance of an environmentally salien ...
... mechanisms. The importance of arousal is undeniable: It is closely related to other phenomena such as sleep, attention, anxiety, stress, and motivation. Dampened arousal leads to drowsiness and, in the limit, sleep. Heightened arousal (brought on by the sudden appearance of an environmentally salien ...
Depolarization stimulates lamellipodia formation and
... examined the effects of depolarization on neocortical neurons from fetal rats growing in culture. The effects of depolarization were investigated quantitatively along two lines: Ž1. short-term effects on the morphology of individual growth cones were studied with a high spatial resolution at one min ...
... examined the effects of depolarization on neocortical neurons from fetal rats growing in culture. The effects of depolarization were investigated quantitatively along two lines: Ž1. short-term effects on the morphology of individual growth cones were studied with a high spatial resolution at one min ...
Turning on the alarm - Center for Healthy Minds
... not, in fact, signal danger. Many chronic pain disorders are characterized by oversensitivity to sensory input (i.e. allodynia or hyperalgesia). Thus, understanding the biological mechanisms of the transition from innocuous to painful levels of sensation will help us understand not only the neural r ...
... not, in fact, signal danger. Many chronic pain disorders are characterized by oversensitivity to sensory input (i.e. allodynia or hyperalgesia). Thus, understanding the biological mechanisms of the transition from innocuous to painful levels of sensation will help us understand not only the neural r ...
Modulation of Inhibitory Synaptic Potentials in the Piriform Cortex
... linear function is used for computing the summed firing rate of the inhibitory population. The constant A represents the afferent input to a population of neurons during a period of time. This constant represents both the summed firing rate across a population of mitral cells in the olfactory bulb i ...
... linear function is used for computing the summed firing rate of the inhibitory population. The constant A represents the afferent input to a population of neurons during a period of time. This constant represents both the summed firing rate across a population of mitral cells in the olfactory bulb i ...
Pierre Berthet Computational Modeling of the Basal Ganglia – Functional Pathways
... very large number of interdependent dynamical systems, at different levels. It is suggested that the evolutionary reason for the brain is to produce adaptable and complex movements. The human brain, and its disproportionally large neocortex, seems to be capable of much more, but some argue that it a ...
... very large number of interdependent dynamical systems, at different levels. It is suggested that the evolutionary reason for the brain is to produce adaptable and complex movements. The human brain, and its disproportionally large neocortex, seems to be capable of much more, but some argue that it a ...
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: Decomposing the
... ms before the test pulse are thought to probe GABAergic intracortical inhibitory circuits, thus providing an assay to link inhibitory neurotransmission with motor behavior. This is of relevance as different assays of inhibitory and excitatory circuits undergo distinct changes during different tasks ...
... ms before the test pulse are thought to probe GABAergic intracortical inhibitory circuits, thus providing an assay to link inhibitory neurotransmission with motor behavior. This is of relevance as different assays of inhibitory and excitatory circuits undergo distinct changes during different tasks ...
Common and Distinct Neural Substrates for Pragmatic, Semantic
... right hemisphere may play a role in processing sentences that are semantically violated, although, whether this is a result of violated semantic constraints between individual words within the sentence, or as a result of violations of real-world knowledge, is unknown. In the ERP literature, a bilate ...
... right hemisphere may play a role in processing sentences that are semantically violated, although, whether this is a result of violated semantic constraints between individual words within the sentence, or as a result of violations of real-world knowledge, is unknown. In the ERP literature, a bilate ...
ORGANIZATION OF NEUROPIL
... and methylene blue stains suggest that differences exist between the arborization patterns of pre- and post-units. The neurons whose processes form glomeruli range widely in function and anatomy. They may be motor, but more commonly are sensory or internuncial elements. Among the latter, the dendrit ...
... and methylene blue stains suggest that differences exist between the arborization patterns of pre- and post-units. The neurons whose processes form glomeruli range widely in function and anatomy. They may be motor, but more commonly are sensory or internuncial elements. Among the latter, the dendrit ...
Alterations in Synaptic Strength Preceding Axon Withdrawal
... The experimenters examined the functional and structural synaptic changes that occur when muscle fibers transition from polyneuronal to singly innervated cells during postnatal development (P1 – P9). In adult mammals a one-to-one relationship exists between motor nerve terminals and muscle fibers. H ...
... The experimenters examined the functional and structural synaptic changes that occur when muscle fibers transition from polyneuronal to singly innervated cells during postnatal development (P1 – P9). In adult mammals a one-to-one relationship exists between motor nerve terminals and muscle fibers. H ...
Distinct representations of olfactory information in different cortical
... mitral cells innervating an individual glomerulus discard the insular and invariant spatial segregation of the bulb and project dense, dispersed axons to the piriform cortex with no discernible spatial bias. Next we examined the patterns of projections of single glomeruli to the cortical amygdala. T ...
... mitral cells innervating an individual glomerulus discard the insular and invariant spatial segregation of the bulb and project dense, dispersed axons to the piriform cortex with no discernible spatial bias. Next we examined the patterns of projections of single glomeruli to the cortical amygdala. T ...
Role of Active Movement in Place-Specific Firing of Hippocampal
... (bottom) during A1, P, and A2 sessions. Figure 2b shows pixel-bypixel correlations (transformed to Fisher’s z) among firing rate maps in A1, P, and A2 sessions of all analyzed units (n ⫽ 46). As shown, spatial firing patterns of most units were poorly correlated between A1 and P sessions and P and A2 ...
... (bottom) during A1, P, and A2 sessions. Figure 2b shows pixel-bypixel correlations (transformed to Fisher’s z) among firing rate maps in A1, P, and A2 sessions of all analyzed units (n ⫽ 46). As shown, spatial firing patterns of most units were poorly correlated between A1 and P sessions and P and A2 ...
Anatomy - Nervous System Test Chpt 9
... ____ 22. The largest and most prominent region of the human brain, which is responsible for the voluntary, or conscious, activities of the body, is the cerebellum. _________________________ ____ 23. The propagation of an action potential is slower in myelinated axons than in axons that lack a myelin ...
... ____ 22. The largest and most prominent region of the human brain, which is responsible for the voluntary, or conscious, activities of the body, is the cerebellum. _________________________ ____ 23. The propagation of an action potential is slower in myelinated axons than in axons that lack a myelin ...
Feedforward and feedback inhibition in neostriatal GABAergic spiny
... from rodent to primate (Kemp and Powell, 1971; Luk and Sadikot, 2001; Wilson, 2004 but see also Graveland and DiFiglia, 1985) are medium-sized spiny projection neurons that are also the only source of output from the nucleus. The remaining cell types comprise large aspiny cholinergic interneurons, a ...
... from rodent to primate (Kemp and Powell, 1971; Luk and Sadikot, 2001; Wilson, 2004 but see also Graveland and DiFiglia, 1985) are medium-sized spiny projection neurons that are also the only source of output from the nucleus. The remaining cell types comprise large aspiny cholinergic interneurons, a ...
Pathways for emotions and memory
... c New England Regional Primate Research Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Accepted 25 May 2002 ...
... c New England Regional Primate Research Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Accepted 25 May 2002 ...
Brain Stimulation for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
... Anderson did show, however, a reduced burst firing pattern during DBS, which may support the notion that DBS may exert its therapeutic effects via a modulation of basal ganglia firing patterns rather than by changing firing rates. Similar results have also been observed with a rodent model of DBS (C ...
... Anderson did show, however, a reduced burst firing pattern during DBS, which may support the notion that DBS may exert its therapeutic effects via a modulation of basal ganglia firing patterns rather than by changing firing rates. Similar results have also been observed with a rodent model of DBS (C ...
Neural circuit rewiring: insights from DD synapse remodeling
... in some cases, even the death of inappropriately connected neurons,32 DD remodeling appears to be unique. However, the discovery of this unique form of neural plasticity is primarily because of our complete understanding of the neural connectivity of C. elegans, made possible by work from John White ...
... in some cases, even the death of inappropriately connected neurons,32 DD remodeling appears to be unique. However, the discovery of this unique form of neural plasticity is primarily because of our complete understanding of the neural connectivity of C. elegans, made possible by work from John White ...
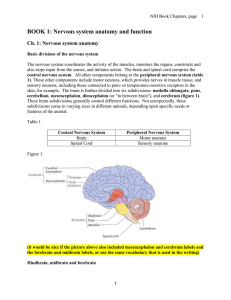
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... Collectively, the medulla, pons and cerebellum are called the hindbrain and perform “lowerlevel functions.” Closest to the spinal cord, the medulla controls breathing and heart beat. On the opposite side of the medulla towards the rest of the brain is the pons (or “bridge”). It relays sensory inform ...
... Collectively, the medulla, pons and cerebellum are called the hindbrain and perform “lowerlevel functions.” Closest to the spinal cord, the medulla controls breathing and heart beat. On the opposite side of the medulla towards the rest of the brain is the pons (or “bridge”). It relays sensory inform ...
Searching for Arthur Koestler`s Holons – a systemstheoretical
... Further properties which are introduced by Arthur Koestler to specify a SOHO-structure concern the degree of arborisation of a holarchy and the degree of reticulation of such a structure. Further he discusses the importance of regulation channels, which take care that in a holarchy signals are trans ...
... Further properties which are introduced by Arthur Koestler to specify a SOHO-structure concern the degree of arborisation of a holarchy and the degree of reticulation of such a structure. Further he discusses the importance of regulation channels, which take care that in a holarchy signals are trans ...
Increased D-amino acid oxidase
... What are the functional consequences of enhanced DAO activity? Many factors other than DAO activity likely influence D-serine availability at the NMDA receptor, including the rate of its synthesis by serine racemase, and its release into and reuptake from the synapse. Alterations in these processes ...
... What are the functional consequences of enhanced DAO activity? Many factors other than DAO activity likely influence D-serine availability at the NMDA receptor, including the rate of its synthesis by serine racemase, and its release into and reuptake from the synapse. Alterations in these processes ...
Dynamics of Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness Across
... from wakefulness to unconsciousness is not a continuous process, but rather a series of discrete neural changes. Key words: general anesthesia; local field potential; loss of consciousness; primate; sensory premotor network; single-neuron activity ...
... from wakefulness to unconsciousness is not a continuous process, but rather a series of discrete neural changes. Key words: general anesthesia; local field potential; loss of consciousness; primate; sensory premotor network; single-neuron activity ...