Document
... series circuit has a time constant of 600 μs, and the maximum current is 300 mA. What’s the value of the inductance? 3. Calculate the resistance in an RL circuit in which L = 2.50 H and the current increases to 90.0% of its final value in 3.00 s. 4. How much energy is stored in a 70 mH inductor at a ...
... series circuit has a time constant of 600 μs, and the maximum current is 300 mA. What’s the value of the inductance? 3. Calculate the resistance in an RL circuit in which L = 2.50 H and the current increases to 90.0% of its final value in 3.00 s. 4. How much energy is stored in a 70 mH inductor at a ...
ECE1250F14_PracticeEx1p2soln
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
... SOL'N: a) Because the problem says nothing about what method of solution must be used, we might use any of the tools studied thus far: Ohm's law, KVL, KCL, voltage-divider, current-divider, Thevenin source transformation, or Norton source transformation. The latter four methods require special confi ...
How to Create a Precision Current Source Using
... point at the high end of the current range can cause the transistor to saturate, which will result in a reduced maximum current. Conversely, if the op amp uses VCC and GND as its rails, then current settings at the low end of the current range can cause insufficient voltage to overcome the transisto ...
... point at the high end of the current range can cause the transistor to saturate, which will result in a reduced maximum current. Conversely, if the op amp uses VCC and GND as its rails, then current settings at the low end of the current range can cause insufficient voltage to overcome the transisto ...
Section 13.3: Alternating Current
... more sensitive to very small changes in current and opens the circuit much more quickly than a circuit breaker. An AFCI is similar to a GFCI. It acts quickly to shut off a circuit when an arc along the circuit is detected. 7. The difference between the voltage used in household circuits in North Ame ...
... more sensitive to very small changes in current and opens the circuit much more quickly than a circuit breaker. An AFCI is similar to a GFCI. It acts quickly to shut off a circuit when an arc along the circuit is detected. 7. The difference between the voltage used in household circuits in North Ame ...
DS9503 ESD Protection Diode with Resistors SPECIAL FEATURES
... This DS9503 is designed as an ESD protection device for 1–Wire MicroLAN interfaces. In contrast to the DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5isolation resistors on chip. Although 5are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event ...
... This DS9503 is designed as an ESD protection device for 1–Wire MicroLAN interfaces. In contrast to the DS9502, the DS9503 includes two 5isolation resistors on chip. Although 5are negligible during communication, they represent a high impedance relative to the conducting diode during an ESD event ...
Current Boosting Switches Using Transistors
... going to be switching from high to low at a user set period (see Figure 1). This pulse width modulated signal will go into a resistive, capacitive or inductive load. As mentioned earlier, when the output is high the chip will be able to source approximately 7mA. To be able to drive some of our loads ...
... going to be switching from high to low at a user set period (see Figure 1). This pulse width modulated signal will go into a resistive, capacitive or inductive load. As mentioned earlier, when the output is high the chip will be able to source approximately 7mA. To be able to drive some of our loads ...
Project Title: Active Power Filter
... The rapid increase in use of electronic equipment in recent years imposes nonlinear loads on the ac main that draws a reactive and harmonic current in addition to the active current. The reactive and harmonic current lead to low efficiency, harmful electromagnetic interference to neighboring applian ...
... The rapid increase in use of electronic equipment in recent years imposes nonlinear loads on the ac main that draws a reactive and harmonic current in addition to the active current. The reactive and harmonic current lead to low efficiency, harmful electromagnetic interference to neighboring applian ...
SHUNT REGULATOR
... If there is no load on the supply, all the current goes through the transistor. If there is a resistive load, some current goes through the load and the rest goes through the transistor. But here's the important part: if something tries to drive current back into the supply, the transistor will shun ...
... If there is no load on the supply, all the current goes through the transistor. If there is a resistive load, some current goes through the load and the rest goes through the transistor. But here's the important part: if something tries to drive current back into the supply, the transistor will shun ...
AI010 507(P)Industrial Electronics Lab
... Design and implementation of Ramp-Comparator and digital firing scheme for simple SCR circuits. 5. Automatic lighting control with SCRs and optoelectronic components. 6. AC phase control using SCR and TRIAC. 7. Speed control of DC motor using choppers and converters. 8. Generation and study the PWM ...
... Design and implementation of Ramp-Comparator and digital firing scheme for simple SCR circuits. 5. Automatic lighting control with SCRs and optoelectronic components. 6. AC phase control using SCR and TRIAC. 7. Speed control of DC motor using choppers and converters. 8. Generation and study the PWM ...
, One.. Temperature Pressure Dryness Proximity Voltage Current
... Peak One Cycle Surge (non-rep) On-State Current, ITS* Peak Gate Power Dissipation, POM Average Gate Power Dissipation, PQ ..:
Peak Positive Gate Current, Ion
Peak Negative Gate Voltage, V
... Peak One Cycle Surge (non-rep) On-State Current, ITS* Peak Gate Power Dissipation, POM Average Gate Power Dissipation, PQ
Series and Parallel Circuits
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
... 2) Find any parallel loads. Calculate their equivalent resistance with 1 1 1 1 RT R1 R2 R3 Draw a new schematic with one resistor with the new value. 3) Find any resistor in series. Calculate their equivalent resistance by adding. Draw a new schematic with a new resistor with that valu ...
Electricity and Circuit
... • A circuit is a loop of wire with its ends connected to an energy source such as a battery. One end of the wire is connected to the positive terminal; the other end of the wire is connected to the negative terminal. The wire is connected in this way so a current can flow through it. ...
... • A circuit is a loop of wire with its ends connected to an energy source such as a battery. One end of the wire is connected to the positive terminal; the other end of the wire is connected to the negative terminal. The wire is connected in this way so a current can flow through it. ...
Light dimmer class notes
... when bright (use P Vrms / R to get light bulb resistance R) • The light bulb resistance is small compared to the 3.3kΩ and potentiometer combination and can be ignored when analyzing the RC electronic circuit • The circuit resets and the process repeats every half-cycle of 60Hz ...
... when bright (use P Vrms / R to get light bulb resistance R) • The light bulb resistance is small compared to the 3.3kΩ and potentiometer combination and can be ignored when analyzing the RC electronic circuit • The circuit resets and the process repeats every half-cycle of 60Hz ...
Digital Multimeter Vocabulary
... Alternating Current – An electrical current that moves in one direction and then the other. Ammeter – Instrument used to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit in amperes; normally connected in series in a circuit. Amperes – The unit of measurement for the flow of electric current. Comple ...
... Alternating Current – An electrical current that moves in one direction and then the other. Ammeter – Instrument used to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit in amperes; normally connected in series in a circuit. Amperes – The unit of measurement for the flow of electric current. Comple ...
Physics Sample Test Papers Multiple Choice
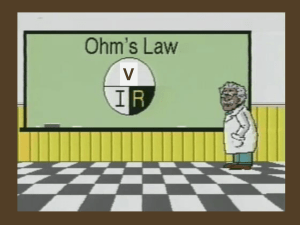
... In the first case, the resistance of the bulb is 1kΩ and in second case, it is 4.4 kΩ. It is not possible since ohm's law is not followed the increase in resistance is due to heating of the filament of the bulb when it is connected to 120 V mains None of these ...
... In the first case, the resistance of the bulb is 1kΩ and in second case, it is 4.4 kΩ. It is not possible since ohm's law is not followed the increase in resistance is due to heating of the filament of the bulb when it is connected to 120 V mains None of these ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.