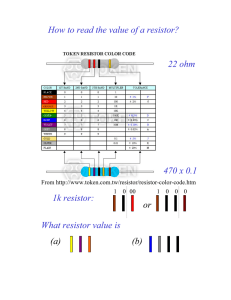
Physics 09-01 Current, Resistance, and Ohms Law
... 16. (a) Find the voltage drop in an extension cord having a 0.0600- Ω resistance and through which 5.00 A is flowing. (b) A cheaper cord utilizes thinner wire and has a resistance of 0.300 Ω. What is the voltage drop in it when 5.00 A flows? (c) Why is the voltage to whatever appliance is being used ...
... 16. (a) Find the voltage drop in an extension cord having a 0.0600- Ω resistance and through which 5.00 A is flowing. (b) A cheaper cord utilizes thinner wire and has a resistance of 0.300 Ω. What is the voltage drop in it when 5.00 A flows? (c) Why is the voltage to whatever appliance is being used ...
A p-channel MOSFET with a heavily-doped p
... Problem 4: MOS Threshold Voltage Adjustment In practice, dopants are implanted into the semiconductor surface of MOS devices in order to fine-tune their threshold voltages during the manufacturing process. The threshold voltage of a MOS transistor also can be dynamically adjusted (after the manufac ...
... Problem 4: MOS Threshold Voltage Adjustment In practice, dopants are implanted into the semiconductor surface of MOS devices in order to fine-tune their threshold voltages during the manufacturing process. The threshold voltage of a MOS transistor also can be dynamically adjusted (after the manufac ...
Pre-Lab: (Total 10 Points)
... Fuel cells are used for direction conversion of the energy of combustion reactions to ______________. A fuel cell is a ______________ in which electricity is generated by a combustion reaction. A fuel cell provides a ______________ voltage that can be used to power motors, lights or any number of el ...
... Fuel cells are used for direction conversion of the energy of combustion reactions to ______________. A fuel cell is a ______________ in which electricity is generated by a combustion reaction. A fuel cell provides a ______________ voltage that can be used to power motors, lights or any number of el ...
HighFinesse Product Details | Precision Current Sources | BCS series
... The BCS series (up to 20 A) comprise all functions of a precision current generator in a compact device. The linearly regulated bipolar current generators deliver highly stable, low noise source currents for high precision magnetic field control. The current output is floating or is on a used define ...
... The BCS series (up to 20 A) comprise all functions of a precision current generator in a compact device. The linearly regulated bipolar current generators deliver highly stable, low noise source currents for high precision magnetic field control. The current output is floating or is on a used define ...
Oct
... of 0.25 (lagging). If, the secondary supplies a current of 220A at a power factor of 0.8 (lagging), estimate the current taken by the primary from the supply. 5. If the a.c. resistance of each diode section of a thermionic full-wave rectifier is 400 and the circuit provides a d.c. output of 250V at ...
... of 0.25 (lagging). If, the secondary supplies a current of 220A at a power factor of 0.8 (lagging), estimate the current taken by the primary from the supply. 5. If the a.c. resistance of each diode section of a thermionic full-wave rectifier is 400 and the circuit provides a d.c. output of 250V at ...
Electrical Components and Circuits ver2
... low resistance to positive current. The triangular portion of the diode symbol may be imagined to point in the direction of current in a conducting diode. Figure 2-3c shows the mechanism of conduction of charge when the p region is made positive with respect to the n region by application of a poten ...
... low resistance to positive current. The triangular portion of the diode symbol may be imagined to point in the direction of current in a conducting diode. Figure 2-3c shows the mechanism of conduction of charge when the p region is made positive with respect to the n region by application of a poten ...
Session 25 Answers - Iowa State University
... 5) A transformer connected to a 120-V(rms) ac line is to supply 13000 V(rms) for a neon sign. To reduce shock hazard, a fuse is to be inserted in the primary circuit; the fuse is to blow when the rms current in the secondary circuit exceeds 8.50 mA. (Book 31.38) a) What is the ratio of secondary to ...
... 5) A transformer connected to a 120-V(rms) ac line is to supply 13000 V(rms) for a neon sign. To reduce shock hazard, a fuse is to be inserted in the primary circuit; the fuse is to blow when the rms current in the secondary circuit exceeds 8.50 mA. (Book 31.38) a) What is the ratio of secondary to ...
Building a Better Voltage Regulator for Your Test Fixtures
... Building a Better Voltage Regulator for Your Test Fixtures For those of you who roll your own test fixtures here is a suggestion for an improved Voltage Regulator for powering the Device Under Test (DUT). The voltage is easily set by selecting one resistor. Output current is designed for one Amp or ...
... Building a Better Voltage Regulator for Your Test Fixtures For those of you who roll your own test fixtures here is a suggestion for an improved Voltage Regulator for powering the Device Under Test (DUT). The voltage is easily set by selecting one resistor. Output current is designed for one Amp or ...
1 Alternating Current (AC) Current that constantly and rapidly
... A component which has resistance to flow of current; can have a fixed or variable resistance. ...
... A component which has resistance to flow of current; can have a fixed or variable resistance. ...
Chapter-10 Electricity
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
... Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854), a German physicist, discovered Ohm’s law in 1826. This is an experimental law, valid for both alternating current (ac) and direct current (dc) circuits. ...
1 - Colyton High School
... 12. When connecting an ammeter in a circuit, the positive terminal, which is coloured ............................ should be connected to the ................................ terminal on the power supply. The negative terminal on the ammeter is coloured .............................. and should be c ...
... 12. When connecting an ammeter in a circuit, the positive terminal, which is coloured ............................ should be connected to the ................................ terminal on the power supply. The negative terminal on the ammeter is coloured .............................. and should be c ...
Warmup
... Students can solve problems to determine characteristics of circuits involving voltage sources, resistors, and capacitors using Ohm’s Law and the Power Law. Students can draw and interpret field diagrams and relate them to the force on a charged particle. Students understand how a transistor operate ...
... Students can solve problems to determine characteristics of circuits involving voltage sources, resistors, and capacitors using Ohm’s Law and the Power Law. Students can draw and interpret field diagrams and relate them to the force on a charged particle. Students understand how a transistor operate ...
ENGR 311 - Bipolar Junction Transistors
... 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the base-emitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic follow to the emitter. Note: the collector current is ...
... 2 – The base-emitter and base-collector circuits behave like diodes. Normally the base-emitter diode is conducting and the base-collector diode is reverse-biased 3 – When 1 and 2 are obeyed Ic is proportional to Ib (Ic = beta . Ib) Both Ib and Ic follow to the emitter. Note: the collector current is ...
electricity - chapter 1 quiz
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.