QUESTIONS lesson 3 - JUANA
... measured and the display shows 0 V? And what if it displays a lower-case L? It means that you have selected is too high. You need to turn the selector to the next lower scale. The letter L means that the voltage is too high for the scale so you need to change the selector to a higer position ...
... measured and the display shows 0 V? And what if it displays a lower-case L? It means that you have selected is too high. You need to turn the selector to the next lower scale. The letter L means that the voltage is too high for the scale so you need to change the selector to a higer position ...
MS Word
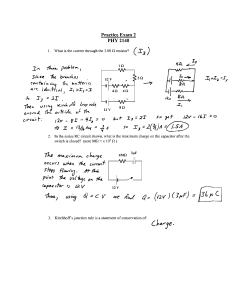
... (VRD) appearing across resistor RD = 1.5 volts with an applied gate-to-source voltage (VGS) of 0.7 volt. Small-signal AC measurements ) give a voltage gain Av = -10 V/V. (a) Find the threshold voltage Vt of the N-channel MOSFET. ...
... (VRD) appearing across resistor RD = 1.5 volts with an applied gate-to-source voltage (VGS) of 0.7 volt. Small-signal AC measurements ) give a voltage gain Av = -10 V/V. (a) Find the threshold voltage Vt of the N-channel MOSFET. ...
LED Resistor Calculation
... current that gives sufficient brightness to a standard Red LED is 20 mA. But this may be 40 mA for Blue and White LEDs. A current limiting resistor is necessary to protect LED from excess current that is flowing through it. The value of this series resistor should be carefully selected to prevent da ...
... current that gives sufficient brightness to a standard Red LED is 20 mA. But this may be 40 mA for Blue and White LEDs. A current limiting resistor is necessary to protect LED from excess current that is flowing through it. The value of this series resistor should be carefully selected to prevent da ...
Steady state
... Steady state • A system (e.g. circuit) is in the steady state when the current at each point in the circuit is constant (does not change with time). – In many practical circuits, the steady state is achieved in a short time. ...
... Steady state • A system (e.g. circuit) is in the steady state when the current at each point in the circuit is constant (does not change with time). – In many practical circuits, the steady state is achieved in a short time. ...
Ohms Law Notes
... Current from a battery travels from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. ...
... Current from a battery travels from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. ...
Bipolar Transistors I – Page 1 Bipolar Transistors I
... junction and then to read the voltage across it. For a silicon transistor like the 2N2219 you expect to find a forward voltage of 0.6 or 0.7 volts. Test both the basecollector and the base-emitter junctions of your transistor. (Note: With the multimeter in diode-test mode, you can determine which me ...
... junction and then to read the voltage across it. For a silicon transistor like the 2N2219 you expect to find a forward voltage of 0.6 or 0.7 volts. Test both the basecollector and the base-emitter junctions of your transistor. (Note: With the multimeter in diode-test mode, you can determine which me ...
EGM 180 Take Home Quiz 1
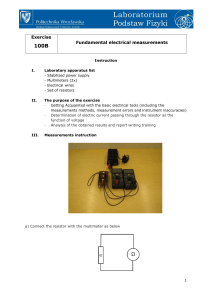
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
... discussion of an ammeter’s impact on a circuit. Note that an ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance and an ideal ammeter has zero resistance. With that in mind, explain how attempting to measure current by placing an ammeter in parallel with the circuit (as opposed to in series in the circuit) coul ...
click here
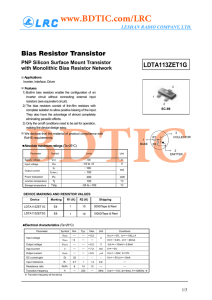
... The dual gate MOSFET was an especially popular device for commercial applications in the late 1970 and early 1980 period. Discrete components still dominated, especially when dealing with RF. It was not long after this that monolithic ICs began to take over, causing familiar parts to become scarce o ...
... The dual gate MOSFET was an especially popular device for commercial applications in the late 1970 and early 1980 period. Discrete components still dominated, especially when dealing with RF. It was not long after this that monolithic ICs began to take over, causing familiar parts to become scarce o ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.