$doc.title
... casts a shadow of the moon on the earth. The moon’s shadow had a dark center surrounded by a region of increasing brightness as shown in (b). ...
... casts a shadow of the moon on the earth. The moon’s shadow had a dark center surrounded by a region of increasing brightness as shown in (b). ...
The$light$that$surrounds$us$ Augusto$Beléndez$
... amaze!us!as!they!did!our!ancestors!before!us.!The!truth!is!that!light!affects!every!day!of! our!lives.!Clearly,!the!light!emitted!by!the!Sun!plays!a!fundamental!role!in!the!development! of!life!on!Earth!and!it!is!the!main!source!of!energy!for!our!planet.!If!someone!asks!“what! do!we!get!from!the!Sun ...
... amaze!us!as!they!did!our!ancestors!before!us.!The!truth!is!that!light!affects!every!day!of! our!lives.!Clearly,!the!light!emitted!by!the!Sun!plays!a!fundamental!role!in!the!development! of!life!on!Earth!and!it!is!the!main!source!of!energy!for!our!planet.!If!someone!asks!“what! do!we!get!from!the!Sun ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... at which the solid form of the element or compound is at equilibrium with the liquid form. • Basically the range at which the solid changes its state •The melting point of into a liquid. water is 0 degrees Celsius ...
... at which the solid form of the element or compound is at equilibrium with the liquid form. • Basically the range at which the solid changes its state •The melting point of into a liquid. water is 0 degrees Celsius ...
Light and Atoms • The only thing we can get out of stars (and most
... • This light identifies which atoms are present. • Atoms also will only absorb very specific wavelengths of light • How does this all tie into blackbody radiation which is continuous? Two kinds of light produced by objects: Gaseous (not dense) give off discrete spectra and can absorb discrete types ...
... • This light identifies which atoms are present. • Atoms also will only absorb very specific wavelengths of light • How does this all tie into blackbody radiation which is continuous? Two kinds of light produced by objects: Gaseous (not dense) give off discrete spectra and can absorb discrete types ...
DISCOVERING THE LIGHT OF LIFE
... • "You are the light of the world. A city on a hill cannot be hidden. Neither do people light a lamp and put it under a bowl. Instead they put it on its stand, and it gives light to everyone in the house. In the same way, let your light shine before men, that they may see your good deeds and praise ...
... • "You are the light of the world. A city on a hill cannot be hidden. Neither do people light a lamp and put it under a bowl. Instead they put it on its stand, and it gives light to everyone in the house. In the same way, let your light shine before men, that they may see your good deeds and praise ...
The Electromagnetic spectrum and light
... Luminous- give off their own light (candle) Illuminated- light reflects off of it (moon) Transparent- See through Translucent- Partially see through (blurry) Opaque- not see through (us) Reflection- Light bounces off Refraction- light bends going through Absorption- light that gets absorbed in the ...
... Luminous- give off their own light (candle) Illuminated- light reflects off of it (moon) Transparent- See through Translucent- Partially see through (blurry) Opaque- not see through (us) Reflection- Light bounces off Refraction- light bends going through Absorption- light that gets absorbed in the ...
الشريحة 1
... The instruments are arranged so that liquid in a cuvette can be placed between the spectrometer beam and the photometer. ...
... The instruments are arranged so that liquid in a cuvette can be placed between the spectrometer beam and the photometer. ...
Colorimeters or photometers
... If a substance can be converted to a soluble, colored material, its concentration may be determined by the amount of color present in the solution. Photometer & spectrophotometer are instruments used for this type of measurement, in which a photocell or photomultiplier tube is used to detect the ...
... If a substance can be converted to a soluble, colored material, its concentration may be determined by the amount of color present in the solution. Photometer & spectrophotometer are instruments used for this type of measurement, in which a photocell or photomultiplier tube is used to detect the ...
Document
... particles from one location to another • Chemical—Chemical changes can occur in rocks when calcium carbonate in limestone changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate due to acid rain. ...
... particles from one location to another • Chemical—Chemical changes can occur in rocks when calcium carbonate in limestone changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate due to acid rain. ...
What is light? - UCI Department of Chemistry
... “This velocity is so nearly that of light, that it seems we have strong reason to conclude that light itself (including radiant heat, and other radiations if any) is an electromagnetic disturbance in the form of waves propagated through the electromagnetic field according to electromagnetic laws.” ...
... “This velocity is so nearly that of light, that it seems we have strong reason to conclude that light itself (including radiant heat, and other radiations if any) is an electromagnetic disturbance in the form of waves propagated through the electromagnetic field according to electromagnetic laws.” ...
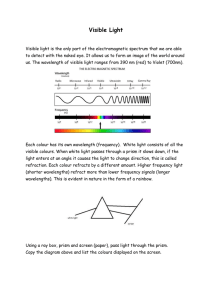
Visible Light - Eyemouth High School
... Visible light is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we are able to detect with the naked eye. It allows us to form an image of the world around us. The wavelength of visible light ranges from 390 nm (red) to Violet (700nm). ...
... Visible light is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we are able to detect with the naked eye. It allows us to form an image of the world around us. The wavelength of visible light ranges from 390 nm (red) to Violet (700nm). ...
key stage 2 year group : t - Aldingbourne Primary School
... the source Know that light Look at natural shadows in the school grounds. At 4 hours cannot pass through what other times might they have seen shadows. some materials and Have they played the shadow chasing game? that this leads to the What can the children remember about how they ...
... the source Know that light Look at natural shadows in the school grounds. At 4 hours cannot pass through what other times might they have seen shadows. some materials and Have they played the shadow chasing game? that this leads to the What can the children remember about how they ...
6.P.1 - energy_properties_of_waves
... Energy: Properties of Waves 1. A person produces two sound waves with a flute, one immediately after the other. Both sound waves have the same pitch, but the second one is louder. Which of the following properties is greater for the second sound wave? (6.P.1.3) A Frequency B Amplitude C Wavelength D ...
... Energy: Properties of Waves 1. A person produces two sound waves with a flute, one immediately after the other. Both sound waves have the same pitch, but the second one is louder. Which of the following properties is greater for the second sound wave? (6.P.1.3) A Frequency B Amplitude C Wavelength D ...
Activity 14: Physical and Chemical Properties of Materials
... • A property is a quality or trait that characterizes a material or object. • Physical Properties can be determined without a chemical reaction. • Chemical Properties can only be determined by looking for a reaction. • Chemical Reaction is when a substance changes chemically into another substance. ...
... • A property is a quality or trait that characterizes a material or object. • Physical Properties can be determined without a chemical reaction. • Chemical Properties can only be determined by looking for a reaction. • Chemical Reaction is when a substance changes chemically into another substance. ...
Chapter 22: Light
... The bouncing back of a wave when it strikes a surface Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of ...
... The bouncing back of a wave when it strikes a surface Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of ...
UNIT 9 REflection refraction diffraction
... Diffraction: The bending of a wave around an obstacle . ( light coming into a dark room from a door slightly Open, water waves around a rock in the water) Optical Density: property of the medium that determines the speed of light in the medium. ( more optically dense, the slower the lights velocity) ...
... Diffraction: The bending of a wave around an obstacle . ( light coming into a dark room from a door slightly Open, water waves around a rock in the water) Optical Density: property of the medium that determines the speed of light in the medium. ( more optically dense, the slower the lights velocity) ...
doc 3.5.1 photosynthesis revision Student notes for section
... These are converted into ………………………… …………………………… using the energy from ATP and using the hydrogen from reduced NADP. Most of this ………………………. ……………………………… is used to regenerate ……………………………………, but some is used to produce 6-carbon sugars from which complex carbohydrates, amino acids and other substance ...
... These are converted into ………………………… …………………………… using the energy from ATP and using the hydrogen from reduced NADP. Most of this ………………………. ……………………………… is used to regenerate ……………………………………, but some is used to produce 6-carbon sugars from which complex carbohydrates, amino acids and other substance ...
Introduction to Light and Color
... of what hits the eye is reflected light. When light strikes some materials, it is bounced off or reflected. If the material is not opaque, the light goes through it at a slower speed, and it is bent or refracted. Some light is absorbed into the material and changed into other forms of energy, usuall ...
... of what hits the eye is reflected light. When light strikes some materials, it is bounced off or reflected. If the material is not opaque, the light goes through it at a slower speed, and it is bent or refracted. Some light is absorbed into the material and changed into other forms of energy, usuall ...
Examining the Photoprotective Role of Anthocyanins in Coleus spp
... Examining the Photoprotective Role of Anthocyanins in Coleus spp. William Stafstrom, Class of 2012 Although sunlight is an essential requirement for photosynthesis, an excess of sunlight causes severe problems for a plant as high energy wavelengths of light damage vital photosynthetic machinery and ...
... Examining the Photoprotective Role of Anthocyanins in Coleus spp. William Stafstrom, Class of 2012 Although sunlight is an essential requirement for photosynthesis, an excess of sunlight causes severe problems for a plant as high energy wavelengths of light damage vital photosynthetic machinery and ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.