Ch 23 ppt: Light and Our World
... broadcast from space to satellite dishes on Earth. • Satellites allow more people to receive the signals and to receive higher quality signals than if antennas on Earth were used. • The Global Positioning System The GPS is a network of 27 satellites that orbit Earth. A GPS receiver receives signals ...
... broadcast from space to satellite dishes on Earth. • Satellites allow more people to receive the signals and to receive higher quality signals than if antennas on Earth were used. • The Global Positioning System The GPS is a network of 27 satellites that orbit Earth. A GPS receiver receives signals ...
Haze detection and characterisation by light scattering
... same type pattern. It can also be observed that when amount & size of haze particles were equal, the intensity of light increased the most in Fig. 7.1 (blue light) followed by Fig. 7.2 (green light) then Fig. 7.3 (red light). From this, we can conclude that blue light scatters the most, then green, ...
... same type pattern. It can also be observed that when amount & size of haze particles were equal, the intensity of light increased the most in Fig. 7.1 (blue light) followed by Fig. 7.2 (green light) then Fig. 7.3 (red light). From this, we can conclude that blue light scatters the most, then green, ...
Presentation Lesson 24 Reflection and Refraction
... front travel at different speeds. This usually takes place when sound is traveling through air of uneven ...
... front travel at different speeds. This usually takes place when sound is traveling through air of uneven ...
Refractive Index
... •recall and apply the relationship sin i/sin r = constant to new situations or to solve related problems. •understand relative refractive index and absolute refractive index. •explain refraction by means of a change in speed of light in different optical media. •explain the terms critical angle and ...
... •recall and apply the relationship sin i/sin r = constant to new situations or to solve related problems. •understand relative refractive index and absolute refractive index. •explain refraction by means of a change in speed of light in different optical media. •explain the terms critical angle and ...
chapter25
... Maxwell asserted that light was a form of high-frequency electromagnetic wave Hertz confirmed Maxwell’s predictions ...
... Maxwell asserted that light was a form of high-frequency electromagnetic wave Hertz confirmed Maxwell’s predictions ...
Refraction of Light - Australian International School
... •recall and apply the relationship sin i/sin r = constant to new situations or to solve related problems. •understand relative refractive index and absolute refractive index. •explain refraction by means of a change in speed of light in different optical media. •explain the terms critical angle and ...
... •recall and apply the relationship sin i/sin r = constant to new situations or to solve related problems. •understand relative refractive index and absolute refractive index. •explain refraction by means of a change in speed of light in different optical media. •explain the terms critical angle and ...
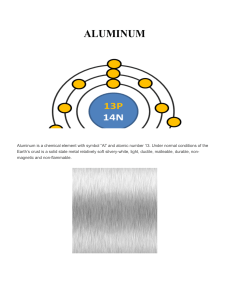
ALUMINUM
... superconductor at 1.2 ° K. Its low electrical resistance is 2.65 x10-18 Ohm meters. It is also a good conductor of heat (80-230 W / (m • K), so it is very useful for heat exchangers, evaporators, electrical appliances and auto parts. Aluminum surfaces can be extremely reflective (71% if not polished ...
... superconductor at 1.2 ° K. Its low electrical resistance is 2.65 x10-18 Ohm meters. It is also a good conductor of heat (80-230 W / (m • K), so it is very useful for heat exchangers, evaporators, electrical appliances and auto parts. Aluminum surfaces can be extremely reflective (71% if not polished ...
Module 3 Copper,Optical Media Presentation
... The periodic table categorizes some groups of atoms by listing them in the form of columns. The atoms in each column belong to particular chemical families. Although they may have different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons, their outermost electrons have similar orbits and behave similarl ...
... The periodic table categorizes some groups of atoms by listing them in the form of columns. The atoms in each column belong to particular chemical families. Although they may have different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons, their outermost electrons have similar orbits and behave similarl ...
Experiment 2 Chemistry with Light – Using Photons as Reagents
... Photochemical reactions involve the absorption of light. An important example of photochemistry in Nature is photosynthesis, where plants and algae use the energy from light to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Photodegradation, where sunlight is used to break down plastic bags, is an envi ...
... Photochemical reactions involve the absorption of light. An important example of photochemistry in Nature is photosynthesis, where plants and algae use the energy from light to make glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Photodegradation, where sunlight is used to break down plastic bags, is an envi ...
Stray Light – Measurement and Effect on Performance in UV
... is due to stray light. the cut-off point of the filter; otherwise, a portion of the stray light would be absorbed by the filter. This would lead to an erroneously high absorbance that does not accurately represent the stray light present in the instrument. Therefore, stray light filters must be sele ...
... is due to stray light. the cut-off point of the filter; otherwise, a portion of the stray light would be absorbed by the filter. This would lead to an erroneously high absorbance that does not accurately represent the stray light present in the instrument. Therefore, stray light filters must be sele ...
Student Activity: Refraction of Light—Reappearing Penny
... When the penny is first viewed, the light from the penny travels in a straight line to the observers’ eyes (Fig.1). The observers then adjust their positions so that the penny disappears from view because there are no light rays travelling from the penny to the eye (Fig.2). When water is added to th ...
... When the penny is first viewed, the light from the penny travels in a straight line to the observers’ eyes (Fig.1). The observers then adjust their positions so that the penny disappears from view because there are no light rays travelling from the penny to the eye (Fig.2). When water is added to th ...
Polarization
... A standing wave is created when the electromagnetic wave wavelength is an integer multiple of /2 Measuring the node positions → measurement of wavelength Reflections generally also happen on surfaces of two materials: ...
... A standing wave is created when the electromagnetic wave wavelength is an integer multiple of /2 Measuring the node positions → measurement of wavelength Reflections generally also happen on surfaces of two materials: ...
FoundationsofChemistryppt
... • When thermal energy is added to a solid, the particles in the solid move faster and faster, and the temperature increases. • When the particles are moving too fast for attractive forces to hold them tightly together, the solid reaches its melting ...
... • When thermal energy is added to a solid, the particles in the solid move faster and faster, and the temperature increases. • When the particles are moving too fast for attractive forces to hold them tightly together, the solid reaches its melting ...
Chapter 22
... of refraction of the glass is ng, find the angle of incidence, θ1, in the air that would result in the reflected ray and the refracted ray being perpendicular to each other. ...
... of refraction of the glass is ng, find the angle of incidence, θ1, in the air that would result in the reflected ray and the refracted ray being perpendicular to each other. ...
Chapter 35
... A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part of the incident ray is reflected back into the first medium. This means it is directed backward into the first medium. For light waves traveling in three-dimensional space, the reflected ...
... A ray of light, the incident ray, travels in a medium. When it encounters a boundary with a second medium, part of the incident ray is reflected back into the first medium. This means it is directed backward into the first medium. For light waves traveling in three-dimensional space, the reflected ...
D. biflorus
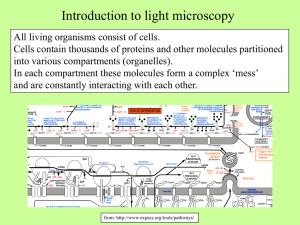
... To understand how organisms or cells function it is critical to identify the cell type under study and to know which cells or molecules are where (morphological organization) and when (temporal dynamic) they are there. ...
... To understand how organisms or cells function it is critical to identify the cell type under study and to know which cells or molecules are where (morphological organization) and when (temporal dynamic) they are there. ...
atomic physics worksheet
... (1) sin c = n2 / n1 (2) n1 = n2 / sin c (3) n1 = 1.00 / sin 48o (4) n1 = 1.35 Example 6. A laser beam, incident at 30 degrees onto the surface of a block of glass, is partially reflected and partially transmitted (with refraction) at the block’s upper surface. The index of refraction of the glass ...
... (1) sin c = n2 / n1 (2) n1 = n2 / sin c (3) n1 = 1.00 / sin 48o (4) n1 = 1.35 Example 6. A laser beam, incident at 30 degrees onto the surface of a block of glass, is partially reflected and partially transmitted (with refraction) at the block’s upper surface. The index of refraction of the glass ...
elliptically polarized light to plane polarized
... when a beam of plane polarized light propagates through certain substances or crystals, the plane of polarization of the emergent beam is not the same as that of the incident polarized beam but has been rotated through a certain angle. This phenomenon of rotation of the plane of vibration is called ...
... when a beam of plane polarized light propagates through certain substances or crystals, the plane of polarization of the emergent beam is not the same as that of the incident polarized beam but has been rotated through a certain angle. This phenomenon of rotation of the plane of vibration is called ...
Photopolymer
A photopolymer is a polymer that changes its properties when exposed to light, often in the ultraviolet or visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These changes are often manifested structurally, for example hardening of the material occurs as a result of cross-linking when exposed to light. An example is shown below depicting a mixture of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators that conform into a hardened polymeric material through a process called curing,.A wide variety of technologically useful applications rely on photopolymers, for example some enamels and varnishes depend on photopolymer formulation for proper hardening upon exposure to light. In some instances, an enamel can cure in a fraction of a second when exposed to light, as opposed to thermally cured enamels which can require half an hour or longer. Curable materials are widely used for medical, printing, and photoresist technologies. Changes in structural and chemical properties can be induced internally by chromophores that the polymer subunit already possesses, or externally by addition of photosensitive molecules. Typically a photopolymer consists of a mixture of multifunctional monomers and oligomers in order to achieve the desired physical properties, and therefore a wide variety of monomers and oligomers have been developed that can polymerize in the presence of light either through internal or external initiation. Photopolymers undergo a process called curing, where oligomers are cross-linked upon exposure to light, forming what is known as a network polymer. The result of photo curing is the formation of a thermoset network of polymers. One of the advantages of photo-curing is that it can be done selectively using high energy light sources, for example lasers, however, most systems are not readily activated by light, and in this case a photoinitiator is required. Photoinitiators are compounds that upon radiation of light decompose into reactive species that activate polymerization of specific functional groups on the oligomers. An example of a mixture that undergoes cross-linking when exposed to light is shown below. The mixture consists of monomeric styrene and oligomeric acrylates.Most commonly, photopolymerized systems are typically cured through UV radiation, since ultraviolet light is more energetic; however, the development of dye-based photoinitiator systems have allowed for the use of visible light, having potential advantages of processes that are more simple and safe to handle. UV curing in industrial processes has greatly expanded over the past several decades. Many traditional thermally cured and solvent-based technologies can be replaced by photopolymerization technologies. The advantages of photopolymerization over thermally cured polymerization include high rates of polymerization and environmental benefits from elimination of volatile organic solvents.There are two general routes for photoinitiation: free radical and ionic. The general process involves doping a batch of neat polymer with small amounts of photoinitiator, followed by selective radiation of light, resulting a highly cross-linked product. Many of these reactions do not require solvent which eliminates termination path via reaction of initiators with solvent and impurities, in addition to decreasing the overall cost.