Exercises for Notes II
... A block is free to slide without friction on a horizontal table. William exerts a constant force of 5 Newtons on the block. The direction of the force is 37◦ with respect to the horizontal. William keeps applying the force on the block as it moves a distance of 10 meters on the table top. a) How muc ...
... A block is free to slide without friction on a horizontal table. William exerts a constant force of 5 Newtons on the block. The direction of the force is 37◦ with respect to the horizontal. William keeps applying the force on the block as it moves a distance of 10 meters on the table top. a) How muc ...
Sliders – High School Worksheet
... easy to move at the same time. Use the information about friction you just learned. In order to build a structure that is difficult to move and easy to move at the same time, I would build a structure made of a material so that it has a high coefficient of static friction but a low coefficient of ki ...
... easy to move at the same time. Use the information about friction you just learned. In order to build a structure that is difficult to move and easy to move at the same time, I would build a structure made of a material so that it has a high coefficient of static friction but a low coefficient of ki ...
Chapter 8 Problems - University of Colorado Colorado Springs
... At 11:00 AM on September 7, 2001, more than one million British school children jumped up and down for one minute. The curriculum focus of the “Giant Jump” was on earthquakes, but it was integrated with many other topics, such as exercise, geography, cooperation, testing hypotheses, and setting worl ...
... At 11:00 AM on September 7, 2001, more than one million British school children jumped up and down for one minute. The curriculum focus of the “Giant Jump” was on earthquakes, but it was integrated with many other topics, such as exercise, geography, cooperation, testing hypotheses, and setting worl ...
Solutions to Problems
... A free-body diagram for the car at one instant of time is shown. In the diagram, the car is coming out of the paper at the reader, and the center of the circular path is to the right of the car, in the plane of the paper. If the car has its maximum speed, it would be on the verge of slipping, and th ...
... A free-body diagram for the car at one instant of time is shown. In the diagram, the car is coming out of the paper at the reader, and the center of the circular path is to the right of the car, in the plane of the paper. If the car has its maximum speed, it would be on the verge of slipping, and th ...
A 1 - Andes Physics Tutor
... driver who does not wear a seatbelt continues to move forward with a speed of 20 m/s (due to inertia) until something solid is encountered. The driver now comes to rest in a much shorter distance -- perhaps only a centimeter. Find the net force acting on a 52 kg driver who is decelerated from 20 m/s ...
... driver who does not wear a seatbelt continues to move forward with a speed of 20 m/s (due to inertia) until something solid is encountered. The driver now comes to rest in a much shorter distance -- perhaps only a centimeter. Find the net force acting on a 52 kg driver who is decelerated from 20 m/s ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
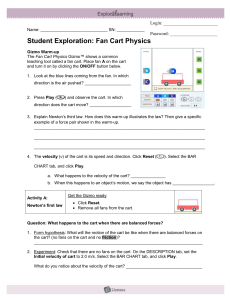
... Student Exploration: Fan Cart Physics Gizmo Warm-up The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ shows a common teaching tool called a fan cart. Place fan A on the cart and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ___________ ...
... Student Exploration: Fan Cart Physics Gizmo Warm-up The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ shows a common teaching tool called a fan cart. Place fan A on the cart and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ___________ ...
Document
... students to work constructively and independently, teaches them to analyze phenomena, define principal factors, and neglect unimportant details thus brining them to scientific research. The goal of this manual is to help students master basic methods of problem solving in physics. Problems given in ...
... students to work constructively and independently, teaches them to analyze phenomena, define principal factors, and neglect unimportant details thus brining them to scientific research. The goal of this manual is to help students master basic methods of problem solving in physics. Problems given in ...
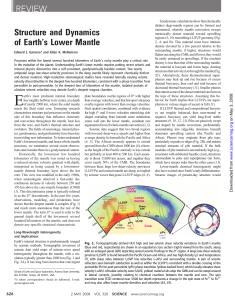
Structure and Dynamics of EarthLs Lower Mantle
... Another challenge is that the P-wave jump associated with the entrance into the pPv phase is predicted to be small and negligible—fractions of a percent, and possibly even negative (32). Horizontal and vertical components of shear waves with appreciable path lengths in the deepest mantle have slight ...
... Another challenge is that the P-wave jump associated with the entrance into the pPv phase is predicted to be small and negligible—fractions of a percent, and possibly even negative (32). Horizontal and vertical components of shear waves with appreciable path lengths in the deepest mantle have slight ...
A cyclist intends to cycle up a 7.8º hill whose vertical height is 150 m
... (III) An engineer is designing a spring to be placed at the bottom of an elevator shaft. If the elevator cable should break when the elevator is at a height h above the top of the spring, calculate the value that the spring stiffness constant k should have so that passengers undergo an acceleration ...
... (III) An engineer is designing a spring to be placed at the bottom of an elevator shaft. If the elevator cable should break when the elevator is at a height h above the top of the spring, calculate the value that the spring stiffness constant k should have so that passengers undergo an acceleration ...
4 VECTORS 2
... When the force exerted on the slider by the string attached to the mass holder is just sufficient to move the slider, record this point in the table. Under these circumstances the frictional force on the slider, opposing the motion of the slider, is just balanced by the tension in the string. You ca ...
... When the force exerted on the slider by the string attached to the mass holder is just sufficient to move the slider, record this point in the table. Under these circumstances the frictional force on the slider, opposing the motion of the slider, is just balanced by the tension in the string. You ca ...
Vectors [1
... 3) Bill is sitting on a tree limb that is 4 meters above the ground with a bucket of water. He wants to dump the water so that it falls on his friend Tim who is approaching on a bike at a constant speed of 8 meters per second. How far away should Tim be from a point directly under Bill when Bill dum ...
... 3) Bill is sitting on a tree limb that is 4 meters above the ground with a bucket of water. He wants to dump the water so that it falls on his friend Tim who is approaching on a bike at a constant speed of 8 meters per second. How far away should Tim be from a point directly under Bill when Bill dum ...
Ch 4 Newton`s First Law
... 4.4 Newton’s Law of Inertia Blasts of air from many tiny holes provide a nearly friction-free surface on the air table. If you slide a hockey puck along the surface of a city street, the puck soon comes to rest. If you slide it along an air table where friction is practically absent, it slides with ...
... 4.4 Newton’s Law of Inertia Blasts of air from many tiny holes provide a nearly friction-free surface on the air table. If you slide a hockey puck along the surface of a city street, the puck soon comes to rest. If you slide it along an air table where friction is practically absent, it slides with ...
Work and Energy - Blue Valley Schools
... 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring you used, but for most springs will be a straight line. This corresponds to Hooke’s law, or F = – kx, where F is the force applied by the spring when it is stretched a distance x. k is ...
... 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring you used, but for most springs will be a straight line. This corresponds to Hooke’s law, or F = – kx, where F is the force applied by the spring when it is stretched a distance x. k is ...