Chapter 5 Lecture
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
rotation and angular momentum
... around the pole to bring the large block back to its original location. The small blocks are detached from the rod and then suspended from each end of the rod, using strings of length l. The system is again released from rest so that as the large block descends and the apparatus rotates, the small b ...
... around the pole to bring the large block back to its original location. The small blocks are detached from the rod and then suspended from each end of the rod, using strings of length l. The system is again released from rest so that as the large block descends and the apparatus rotates, the small b ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Blasts of air from many tiny holes provide a nearly friction-free surface on the air table. If you slide a hockey puck along the surface of a city street, the puck soon comes to rest. If you slide it along an air table where friction is practically absent, it slides with no apparent loss in speed. ...
... Blasts of air from many tiny holes provide a nearly friction-free surface on the air table. If you slide a hockey puck along the surface of a city street, the puck soon comes to rest. If you slide it along an air table where friction is practically absent, it slides with no apparent loss in speed. ...
3.6MB Word - Clydeview Academy
... Each time this repeats some energy is lost as heat (and sound), so the ball does not rise to the same height as before. The gradient of the graph is negative and constant – which shows that acceleration due to gravity is constant at -9.8 ms-2. The area under the graph represents the displacement dur ...
... Each time this repeats some energy is lost as heat (and sound), so the ball does not rise to the same height as before. The gradient of the graph is negative and constant – which shows that acceleration due to gravity is constant at -9.8 ms-2. The area under the graph represents the displacement dur ...
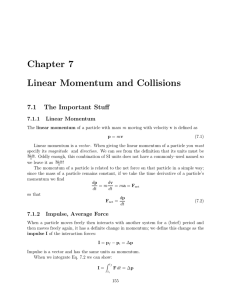
Chapter 7 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... For such an event, the two particles have well-defined momenta p1i and p2i before the collision event and p1f and p2f afterwards. But the sum of the momenta before and after the collision is conserved, as written in Eq. 7.3. While the total momentum is conserved for a system of isolated colliding pa ...
... For such an event, the two particles have well-defined momenta p1i and p2i before the collision event and p1f and p2f afterwards. But the sum of the momenta before and after the collision is conserved, as written in Eq. 7.3. While the total momentum is conserved for a system of isolated colliding pa ...
chapter FORCES AND NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
... 34. Two satellites of different masses are in the same circular orbit about the earth. Which one of the following statements is true concerning the magnitude of the gravitational force that acts on each of them? (a) The magnitude of the gravitational force is zero newtons for both satellites. (b) ...
... 34. Two satellites of different masses are in the same circular orbit about the earth. Which one of the following statements is true concerning the magnitude of the gravitational force that acts on each of them? (a) The magnitude of the gravitational force is zero newtons for both satellites. (b) ...
Force and Motion II 2.0
... 2. Measuring F(x) with a Spring Scale Now that you have deduced the force function F(x) from the motion data x(t), you can check your result by directly measuring F(x) using a spring scale. This may seem like an easy method to find the force, but remember, someone had to calibrate the force meter to ...
... 2. Measuring F(x) with a Spring Scale Now that you have deduced the force function F(x) from the motion data x(t), you can check your result by directly measuring F(x) using a spring scale. This may seem like an easy method to find the force, but remember, someone had to calibrate the force meter to ...
Period 5 Activity Sheet: Forces and Newton’s Laws
... Is friction always undesirable? 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. 2) Balance a meter stick on two fingers. Start with one finger under each end of the meter stick. Slowly slide your fing ...
... Is friction always undesirable? 1) Your instructor will demonstrate two toy cars moving up an incline. Explain the differences in the motion of the cars as they go up the incline. 2) Balance a meter stick on two fingers. Start with one finger under each end of the meter stick. Slowly slide your fing ...
chapter 4 forces and newton`s laws of motion
... to gravity. When the rocket is fired horizontally, these accelerations will be at right angles to each other. When the rocket is fired straight up, these accelerations will be in opposite directions. The magnitude of the resultant will be greater when these two accelerations are at right angles rath ...
... to gravity. When the rocket is fired horizontally, these accelerations will be at right angles to each other. When the rocket is fired straight up, these accelerations will be in opposite directions. The magnitude of the resultant will be greater when these two accelerations are at right angles rath ...
Mrs. Burns: 2012185859 Day 1 Physics consist of a variety of topics
... The Mathematical quantities that are used to describe the motion of object can be divided into scalers and vectors ...
... The Mathematical quantities that are used to describe the motion of object can be divided into scalers and vectors ...
Ch04CQ5e
... be at right angles to each other. When the rocket is fired straight up, these accelerations will be in opposite directions. The magnitude of the resultant will be greater when these two accelerations are at right angles rather than when they are in opposition. Therefore, the acceleration will be gre ...
... be at right angles to each other. When the rocket is fired straight up, these accelerations will be in opposite directions. The magnitude of the resultant will be greater when these two accelerations are at right angles rather than when they are in opposition. Therefore, the acceleration will be gre ...
Uniform Circular Motion 2
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizo ...
... In that case, you treat this case the same way you did in any dynamics problem, the sum of the forces matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizo ...
Fall 2009 solutions - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Problem 18. A monkey starts to slide down a rope. As it speeds up, it tightens its grip, until it slides at a constant velocity down the rope. Which of these choices is true now? a. The gravitational force is equal to the frictional force. b. The gravitational force is greater than the frictional fo ...
... Problem 18. A monkey starts to slide down a rope. As it speeds up, it tightens its grip, until it slides at a constant velocity down the rope. Which of these choices is true now? a. The gravitational force is equal to the frictional force. b. The gravitational force is greater than the frictional fo ...
Dynamics: Newton`s Laws
... space, you are weightless, but your mass is still unchanged. You still have inertia in space! In deep space, an astronaut would have a hard time “juggling” 1000 kg lead bricks. Yes, they’d be “weightless”, floating around the cabin, but F=ma, their large mass means that when you push them, they bare ...
... space, you are weightless, but your mass is still unchanged. You still have inertia in space! In deep space, an astronaut would have a hard time “juggling” 1000 kg lead bricks. Yes, they’d be “weightless”, floating around the cabin, but F=ma, their large mass means that when you push them, they bare ...
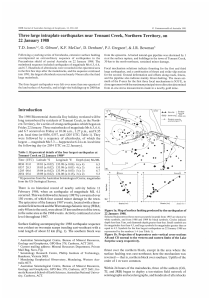
2. Data processing and group velocity measurements
... distribution of earthquakes around the world, seismic surface waves only sample certain preferential azimuths. In addition, in aseismic regions surface wave dispersion can be measured only from distant earthquakes. Second, it is difficult to obtain high-quality short-period (<20 s) dispersion measu ...
... distribution of earthquakes around the world, seismic surface waves only sample certain preferential azimuths. In addition, in aseismic regions surface wave dispersion can be measured only from distant earthquakes. Second, it is difficult to obtain high-quality short-period (<20 s) dispersion measu ...