8. Rotatory Motion
... rigid support. The maximum angle through which the wire can be displaced from the mean position, so that the wire does not break when the load passes through the position of equilibrium, is (2006 E) ...
... rigid support. The maximum angle through which the wire can be displaced from the mean position, so that the wire does not break when the load passes through the position of equilibrium, is (2006 E) ...
July 2016 Exam Review
... velocity-time diagram is also effective. Even if you don't like velocity-time diagrams, if you get stuck use one as a last resort instead of giving up. ...
... velocity-time diagram is also effective. Even if you don't like velocity-time diagrams, if you get stuck use one as a last resort instead of giving up. ...
F - Cloudfront.net
... the kinetic energy of an object is equal to the total amount of work done on the object. Note: the net work can be found by either finding the sum of the work done by each individual force or by finding the work done by the net force. ...
... the kinetic energy of an object is equal to the total amount of work done on the object. Note: the net work can be found by either finding the sum of the work done by each individual force or by finding the work done by the net force. ...
Anonymous-VibrationTheoryFundamentals.pdf
... be expressed at any instant in time by one number only. For example, a piston moving in a cylinder can be specified by giving the distance from the cylinder end, thus classifying it as a single degree of freedom system. Another example is a crankshaft in rigid bearings; the system is fully described ...
... be expressed at any instant in time by one number only. For example, a piston moving in a cylinder can be specified by giving the distance from the cylinder end, thus classifying it as a single degree of freedom system. Another example is a crankshaft in rigid bearings; the system is fully described ...
Unit Nine Circular Motion
... the tides. – Since the water directly below the moon is closer than Earth as a whole, it accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than Earth, and the water rises. – Similarly, Earth accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than the water on the far side. Earth moves away from the water, leaving a bu ...
... the tides. – Since the water directly below the moon is closer than Earth as a whole, it accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than Earth, and the water rises. – Similarly, Earth accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than the water on the far side. Earth moves away from the water, leaving a bu ...
File
... 11. Choose ‘Table 2 – Cork’. Insert the data values of “0,0” in the first row of Table 2. Weigh the felt friction accessory and insert the Normal Force value in the table. (Note: Remember the Normal Force is the mass, in kilograms, multiplied by the acceleration of gravity.) 12. Select the Frictiona ...
... 11. Choose ‘Table 2 – Cork’. Insert the data values of “0,0” in the first row of Table 2. Weigh the felt friction accessory and insert the Normal Force value in the table. (Note: Remember the Normal Force is the mass, in kilograms, multiplied by the acceleration of gravity.) 12. Select the Frictiona ...
Biomechanics - study
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
... skill and sport. Some skills, such as punches in boxing, require tremendous forces applied over a very short time frame. Other skills like throwing a javelin require forces applied over a longer timeframe. An expert javelin thrower accelerates the javelin by pulling it from way behind his body and r ...
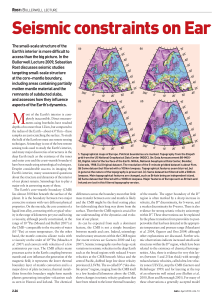
Structure and Dynamics of EarthLs Lower Mantle
... Another challenge is that the P-wave jump associated with the entrance into the pPv phase is predicted to be small and negligible—fractions of a percent, and possibly even negative (32). Horizontal and vertical components of shear waves with appreciable path lengths in the deepest mantle have slight ...
... Another challenge is that the P-wave jump associated with the entrance into the pPv phase is predicted to be small and negligible—fractions of a percent, and possibly even negative (32). Horizontal and vertical components of shear waves with appreciable path lengths in the deepest mantle have slight ...
Calibrating the “Dual
... the graph from –1.0 to 1.0 Newtons (you may have to use a different scale to suit your particular fan). With the fan set at the angle of interest (see the table on the next page), switch the fan on to the desired speed so that it pushes against the arm of the force sensor. Wait for two or three sec ...
... the graph from –1.0 to 1.0 Newtons (you may have to use a different scale to suit your particular fan). With the fan set at the angle of interest (see the table on the next page), switch the fan on to the desired speed so that it pushes against the arm of the force sensor. Wait for two or three sec ...
Newtons laws best 11. 2009
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This is Neuton’s First Law. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a change in its state of motion. There are examples ...
... • An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This is Neuton’s First Law. Inertia is the resistance of an object to a change in its state of motion. There are examples ...
PHYS 1405 – Conceptual Physics I The Equilibrium Rule Leader
... will continue in a state of uniform motion. If it is at rest, it will remain at rest and if the object is moving at constant velocity, it will remain moving at constant velocity. In this activity we will explore Newton’s 1st Law from the point of view of finding the forces necessary to produce equil ...
... will continue in a state of uniform motion. If it is at rest, it will remain at rest and if the object is moving at constant velocity, it will remain moving at constant velocity. In this activity we will explore Newton’s 1st Law from the point of view of finding the forces necessary to produce equil ...
Momentum
... C) it always moves in a straight line even if the particles are rotating about it. D) the kinetic energy of the system is a maximum about any axis through the center of mass. E) its location depends only on the masses of the particles and their locations. Answer: E Circular Motion/Gravity 24. When a ...
... C) it always moves in a straight line even if the particles are rotating about it. D) the kinetic energy of the system is a maximum about any axis through the center of mass. E) its location depends only on the masses of the particles and their locations. Answer: E Circular Motion/Gravity 24. When a ...
KEY - NNHS Tigerscience
... 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work). 1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve problems involving displacement, ...
... 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration force, linear momentum) and scalar quantities (e.g., distance, speed, energy, mass, work). 1.2 Distinguish between displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and acceleration. Solve problems involving displacement, ...