Unit 3 Dynamic Earth
... These plates fit together along Earth’s surface like a puzzle. The plates move along the surface very slowly. The upper part of the mantle acts like a plastic and is called the asthenosphere. It allows the plates to move. ...
... These plates fit together along Earth’s surface like a puzzle. The plates move along the surface very slowly. The upper part of the mantle acts like a plastic and is called the asthenosphere. It allows the plates to move. ...
Solution
... If the rider is riding at a constant speed, then the positive work input by the rider to the (bicycle + rider) combination must be equal to the negative work done by gravity as he moves up the incline. The net work must be 0 if there is no change in kinetic energy. (a) If the rider’s force is d ...
... If the rider is riding at a constant speed, then the positive work input by the rider to the (bicycle + rider) combination must be equal to the negative work done by gravity as he moves up the incline. The net work must be 0 if there is no change in kinetic energy. (a) If the rider’s force is d ...
to Ch. 8 Notes
... 14. Modified Mercalli scale: a measure of how strong an earthquake felt and how much damage it did at a particular location 15. Moment magnitude: a more precise measure of earthquake magnitude than the Richter scale, which is derived from the amount of displacement that occurs along a fault zone and ...
... 14. Modified Mercalli scale: a measure of how strong an earthquake felt and how much damage it did at a particular location 15. Moment magnitude: a more precise measure of earthquake magnitude than the Richter scale, which is derived from the amount of displacement that occurs along a fault zone and ...
Newton`s Formulas Practice Worksheet
... If you are pushing on a box with a force of 20 N and there is a force of 7 N on the box due to friction, what is the net force on the box? Hint: (The box is NOT moving up or down. the vertical forces are balanced. The net force is difference of the horizontal forces) a. 140 N b. - 7 N c. 27 N d. 13 ...
... If you are pushing on a box with a force of 20 N and there is a force of 7 N on the box due to friction, what is the net force on the box? Hint: (The box is NOT moving up or down. the vertical forces are balanced. The net force is difference of the horizontal forces) a. 140 N b. - 7 N c. 27 N d. 13 ...
Newton`s Second Law (PowerPoint)
... that determines how much gravitational force it feels near another object Different masses have different gravitational forces acting between them Gravitational force M(g) ...
... that determines how much gravitational force it feels near another object Different masses have different gravitational forces acting between them Gravitational force M(g) ...
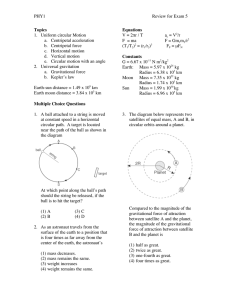
Sample Final Exam #2
... 15. Two carts on a frictionless track are launched toward each other. Cart A, on the left, has a mass of 2.00 kg and cart B, on the right, has a mass of 1.5 kg. After the collision, it is observed that cart A is moving to the right at a speed of 2 m/s and cart B is also moving to the right at a spee ...
... 15. Two carts on a frictionless track are launched toward each other. Cart A, on the left, has a mass of 2.00 kg and cart B, on the right, has a mass of 1.5 kg. After the collision, it is observed that cart A is moving to the right at a speed of 2 m/s and cart B is also moving to the right at a spee ...
Variable Mass - Northern Illinois University
... Rockets decrease their mass, so we usually write the mass change as a positive quantity. The equation can be integrated to get the relationship between the mass and increased velocity. ...
... Rockets decrease their mass, so we usually write the mass change as a positive quantity. The equation can be integrated to get the relationship between the mass and increased velocity. ...
Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num
... Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num _______ Unit 7 Matter in Motion Review Sheet Directions: Use your notes and worksheets to help you answer the questions. Also, be sure to study all Unit 7 vocabulary words. 7-1 Measuring Motion 1. Give an example of a reference point and explain wh ...
... Name_________________Date___________Period_____ Num _______ Unit 7 Matter in Motion Review Sheet Directions: Use your notes and worksheets to help you answer the questions. Also, be sure to study all Unit 7 vocabulary words. 7-1 Measuring Motion 1. Give an example of a reference point and explain wh ...
1 - Eickman
... to get a heavy object to start moving, but once it’s moving it only takes 2 people to keep it moving. Why? ...
... to get a heavy object to start moving, but once it’s moving it only takes 2 people to keep it moving. Why? ...
Gravitation and Grav fields
... • Definition: The weight of an object is a measure of the Fg one object feels in the presence of another. ...
... • Definition: The weight of an object is a measure of the Fg one object feels in the presence of another. ...
Chapter 1 Quick Review
... Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 5.1- 6.5) Working on this problem set is optional, but it is strongly recommended. It is highly likely that some of these problems will appear in the exams. Do it on a weekly basis. Cramming is tiring and sometimes it ends up in a disaster. ___________________________ ...
... Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 5.1- 6.5) Working on this problem set is optional, but it is strongly recommended. It is highly likely that some of these problems will appear in the exams. Do it on a weekly basis. Cramming is tiring and sometimes it ends up in a disaster. ___________________________ ...
neet test paper 06 - Sigma Physics Centre
... A machine gun fires a bullet of mass 40 g with a velocity 1200 ms -1. The man holding it, can exert a maximum force of 144 N on the gun. How many bullets can be fire per second at the most ? (a) One (b) Four (c) Two (d) Three Two masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 4.8 kg tied to a string are hanging over a l ...
... A machine gun fires a bullet of mass 40 g with a velocity 1200 ms -1. The man holding it, can exert a maximum force of 144 N on the gun. How many bullets can be fire per second at the most ? (a) One (b) Four (c) Two (d) Three Two masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 4.8 kg tied to a string are hanging over a l ...
Newton`s First and Second Laws
... continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a force stops it Gravity and friction are the 2 forces on Earth that often change an object ...
... continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a force stops it Gravity and friction are the 2 forces on Earth that often change an object ...
Lecture 9 Earthquakes
... because: a) they are too deep within the Earth to be detected by seismographs. b) lithostatic pressure at these depths prevents rocks from shifting relative to each other. c) slabs that descend that far have been heated sufficiently to deform plastically 8) Japan is the site of about 15% of the Eart ...
... because: a) they are too deep within the Earth to be detected by seismographs. b) lithostatic pressure at these depths prevents rocks from shifting relative to each other. c) slabs that descend that far have been heated sufficiently to deform plastically 8) Japan is the site of about 15% of the Eart ...