F ma = Or , 0 , 0 Integrating twice gives the solution for position at
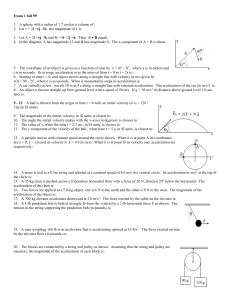
... 5. When an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force called friction. This force has a magnitude of , where is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of normal force that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 30 kg is released from t ...
... 5. When an object slides on a surface, it encounters a resistance force called friction. This force has a magnitude of , where is the coefficient of kinetic friction and N is the magnitude of normal force that the surface applies to the object. Suppose an object of mass 30 kg is released from t ...
Newton intro with hover pucks
... change its direction? 4. If the marble was rolling along, did you have to exert a force to keep it rolling? 5. In the absence of friction, and with an infinitely long table top, once the marble is rolling, would it stop on its own? ...
... change its direction? 4. If the marble was rolling along, did you have to exert a force to keep it rolling? 5. In the absence of friction, and with an infinitely long table top, once the marble is rolling, would it stop on its own? ...
8A Quick Quiz - Grade10ScienceISZL
... force, but if the mass is very, very ____________ as with a planet or a star, the gravity can be very ____________. The region where a gravitational force can be felt is often referred to as a gravitational ______________ . The Earth's gravitational field attracts every object on Earth. This gives a ...
... force, but if the mass is very, very ____________ as with a planet or a star, the gravity can be very ____________. The region where a gravitational force can be felt is often referred to as a gravitational ______________ . The Earth's gravitational field attracts every object on Earth. This gives a ...
Document
... t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - 2t2 , where t is in seconds. When it momentarily stops its acceleration is: 7. A car, initially at rest , t ...
... t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - 2t2 , where t is in seconds. When it momentarily stops its acceleration is: 7. A car, initially at rest , t ...
Unit 2 Objectives: Forces and Laws of Motion
... Fnet=ma. The harder you throw a ball, the more it will accelerate. The more mass a ball has, the less acceleration it will have 2. What amount of force was required to give a 40-kg wagon an acceleration of 3 m/s2? 120 N 3. Why the relationship between mass and acceleration is inversely proportional? ...
... Fnet=ma. The harder you throw a ball, the more it will accelerate. The more mass a ball has, the less acceleration it will have 2. What amount of force was required to give a 40-kg wagon an acceleration of 3 m/s2? 120 N 3. Why the relationship between mass and acceleration is inversely proportional? ...
EARTHQUAKE DIRECTED READING – DUACSEK EARTH SCIENCE
... 42. Which magnitude scale do scientists generally prefer now? _________________________________ 43. Upon what does the intensity of an earthquake depend? ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12.3 EARTHQUAKES AND SOCIE ...
... 42. Which magnitude scale do scientists generally prefer now? _________________________________ 43. Upon what does the intensity of an earthquake depend? ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12.3 EARTHQUAKES AND SOCIE ...
Instructions - People Server at UNCW
... d. A person pulls a toboggan for a distance of 35 m along the j. A recording engineer works in a soundproofed room that is 40.0 snow with a rope directed at 60o above the snow. The tension in dB quieter than outside. If the intensity in the room is the rope is 100 N. How much work is done on the tob ...
... d. A person pulls a toboggan for a distance of 35 m along the j. A recording engineer works in a soundproofed room that is 40.0 snow with a rope directed at 60o above the snow. The tension in dB quieter than outside. If the intensity in the room is the rope is 100 N. How much work is done on the tob ...
Study Guide for Physics Final Exam—1st semester
... to be the first woman to land on the moon, where the gravitational pull is 1/6 as much as earth’s. What would Betty’s mass be on the moon? Mass is not affected by gravity it is the “STUFF” in an object. Betty has just as much junk in her trunk on the moon as she has on Earth, so her mass is the same ...
... to be the first woman to land on the moon, where the gravitational pull is 1/6 as much as earth’s. What would Betty’s mass be on the moon? Mass is not affected by gravity it is the “STUFF” in an object. Betty has just as much junk in her trunk on the moon as she has on Earth, so her mass is the same ...
Earthquakes
... • Accurate and consistent short-term earthquake prediction not yet possible, three methods assist in determining probability that an earthquake will occur: – Measurement of changes in rock properties, such as magnetism, electrical resistivity, seismic velocity, and porosity, which may serve as precu ...
... • Accurate and consistent short-term earthquake prediction not yet possible, three methods assist in determining probability that an earthquake will occur: – Measurement of changes in rock properties, such as magnetism, electrical resistivity, seismic velocity, and porosity, which may serve as precu ...
Law of Inertia
... “The acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body” * “in the same direction as the net force” ◦ a in the same direction of body’s motion speed up ◦ a in opposite directi ...
... “The acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body” * “in the same direction as the net force” ◦ a in the same direction of body’s motion speed up ◦ a in opposite directi ...
Forces and Motion
... • __________ = object’s mass x acceleration. • F = ma • Force is measured in Newtons, mass in grams, and acceleration in meters/sec. • Shortly you will measure the amount of force necessary to move two objects across two different surfaces. • Newton was able to deduce the law of gravity using the mo ...
... • __________ = object’s mass x acceleration. • F = ma • Force is measured in Newtons, mass in grams, and acceleration in meters/sec. • Shortly you will measure the amount of force necessary to move two objects across two different surfaces. • Newton was able to deduce the law of gravity using the mo ...
Solar Energy Test (part 1)
... Know how to find velocity and speed if Calculating Forces you know distance and time Calculate force of Earth if Mass is Know the difference between speed and known velocity What is the acceleration of all objects on Understand how to find AVERAGE speed Earth? and velocity (this is for objects that ...
... Know how to find velocity and speed if Calculating Forces you know distance and time Calculate force of Earth if Mass is Know the difference between speed and known velocity What is the acceleration of all objects on Understand how to find AVERAGE speed Earth? and velocity (this is for objects that ...
Frames of Reference
... • A rotating frame is non-inertial. •Fictitious forces explains motion in a rotating (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious for ...
... • A rotating frame is non-inertial. •Fictitious forces explains motion in a rotating (non-inertial) frame of reference. •From fixed frame no unbalanced force is seen. •Objects moving in a circle have an acceleration toward the center called centripetal force. •Centrifugal force is the fictitious for ...
Advances in Earthquake Precursor Studies in Taiwan
... by the National Science Council and Ministry of Education. Since then, changes in seismicity, P wave velocity, groundwater level, ground surface deformation, and ionosphere electron content have been identified with precursory time ranging from a few days up to five years. Notably, these findings ha ...
... by the National Science Council and Ministry of Education. Since then, changes in seismicity, P wave velocity, groundwater level, ground surface deformation, and ionosphere electron content have been identified with precursory time ranging from a few days up to five years. Notably, these findings ha ...