Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
... An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter • Focus is the point within Earth where the earthquake starts. • Epicenter is the location on the surface directly above the focus. ...
Study Guide Answers
... 6. When a roller coaster makes a sharp turn, you slide in the opposite direction of the turn because of __inertia___. 7. Newton’s first law of motion states that a. an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. b. an object in motion eventually comes to a stop. c. ...
... 6. When a roller coaster makes a sharp turn, you slide in the opposite direction of the turn because of __inertia___. 7. Newton’s first law of motion states that a. an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. b. an object in motion eventually comes to a stop. c. ...
Unit 2a Force and Motion Study Guide Label the following with the
... 6. When a roller coaster makes a sharp turn, you slide in the opposite direction of the turn because of __inertia___. 7. Newton’s first law of motion states that a. an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. b. an object in motion eventually comes to a stop. c. ...
... 6. When a roller coaster makes a sharp turn, you slide in the opposite direction of the turn because of __inertia___. 7. Newton’s first law of motion states that a. an object in motion remains in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. b. an object in motion eventually comes to a stop. c. ...
Packet 3 - Work Energy Power
... I. The swing continues down until the cord is exactly vertical at which time the child jumps off in a horizontal direction. The swing continues in the same direction until its cord makes a 45° angle with the vertical as shown in Figure II: at that point it begins to swing in the reverse direction. W ...
... I. The swing continues down until the cord is exactly vertical at which time the child jumps off in a horizontal direction. The swing continues in the same direction until its cord makes a 45° angle with the vertical as shown in Figure II: at that point it begins to swing in the reverse direction. W ...
Centripetal Force
... • True lack of weight can only occur at huge distances from any other mass • Apparent weightlessness occurs during freefall where all parts of you body are accelerating at the same rate ...
... • True lack of weight can only occur at huge distances from any other mass • Apparent weightlessness occurs during freefall where all parts of you body are accelerating at the same rate ...
Circular Motion Problem Set
... 1) A 5 kg bucket is attached to a string that is 2 meters long and is whirled in a perfectly horizontal circle above a person’s head. The speed of the bucket is a constant 4 m/s. a) What is the period of the bucket’s motion? b) What is the centripetal acceleration of the bucket? c) What is the tensi ...
... 1) A 5 kg bucket is attached to a string that is 2 meters long and is whirled in a perfectly horizontal circle above a person’s head. The speed of the bucket is a constant 4 m/s. a) What is the period of the bucket’s motion? b) What is the centripetal acceleration of the bucket? c) What is the tensi ...
CH 13
... *object that orbits another object ~it is a result of the object’s forward inertia and the downward pull of gravity on the object ...
... *object that orbits another object ~it is a result of the object’s forward inertia and the downward pull of gravity on the object ...
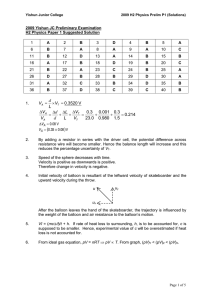
2009-YJC-PH-H2-P1-Prelim-soln
... Speed and magnitude of acceleration are constant but direction of velocity and acceleration are changing. Velocity and hence momentum are tangential to the path. Acceleration and hence force (rate of change of momentum) are perpendicular to the path (towards centre). ...
... Speed and magnitude of acceleration are constant but direction of velocity and acceleration are changing. Velocity and hence momentum are tangential to the path. Acceleration and hence force (rate of change of momentum) are perpendicular to the path (towards centre). ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... Mac and Tosh are arguing in the cafeteria. Mac says that if he flings the Jell-O with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. Who do you agree ...
... Mac and Tosh are arguing in the cafeteria. Mac says that if he flings the Jell-O with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. Who do you agree ...
hp1f2013_class06_momentum
... Momentum is still conserved, independent of the type of collision. Elastic collision: Just use conservation of momentum. For a completely specified initial condition (m1, m2, v1, v2) , we have one equation, two unknowns. From what me know so far, we can deduce the relationship between the velocities ...
... Momentum is still conserved, independent of the type of collision. Elastic collision: Just use conservation of momentum. For a completely specified initial condition (m1, m2, v1, v2) , we have one equation, two unknowns. From what me know so far, we can deduce the relationship between the velocities ...
Earth`s Structure and Processes Test 1 1. What are the only things
... Which phenomenon is believed to be the cause of Earth’s magnetic field? The iron in the ocean floor lines up from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth’s atmosphere holds in all magnetic particles. A solid inner core spins inside a molten moving outer core. A molten inner core moves inside of a so ...
... Which phenomenon is believed to be the cause of Earth’s magnetic field? The iron in the ocean floor lines up from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth’s atmosphere holds in all magnetic particles. A solid inner core spins inside a molten moving outer core. A molten inner core moves inside of a so ...