Q1. A small mass is situated at a point on a line joining two large
... This question required candidates to appreciate that, for the total potential to be zero at the chosen point, the magnitude of V due to the +4 µC charge should be the same as the magnitude of V due to the –16 µC charge. This required (Q/r) to be the same and should give a distance ratio of 1:4. 58% ...
... This question required candidates to appreciate that, for the total potential to be zero at the chosen point, the magnitude of V due to the +4 µC charge should be the same as the magnitude of V due to the –16 µC charge. This required (Q/r) to be the same and should give a distance ratio of 1:4. 58% ...
Increased electric sail thrust through removal of
... from the surface. It is conceivable that some local microscopic protrusions may be torn off the surface by the electrostatic force. Such protrusions might exist on the metal surface originally or be caused by micrometeoroid cratering in space. If this happens, it should not cause any problems, since ...
... from the surface. It is conceivable that some local microscopic protrusions may be torn off the surface by the electrostatic force. Such protrusions might exist on the metal surface originally or be caused by micrometeoroid cratering in space. If this happens, it should not cause any problems, since ...
Physics of Complex Plasmas - Max-Planck
... Nonlinear sheath potential. The potential energy (in arbitrary units) of a dust particle, depending on its distance from the equilibrium height within the sheath. The usually assumed parabolic potential well (solid) is compared to a nonlinear sheath, evaluated with the first (dashed) and first and s ...
... Nonlinear sheath potential. The potential energy (in arbitrary units) of a dust particle, depending on its distance from the equilibrium height within the sheath. The usually assumed parabolic potential well (solid) is compared to a nonlinear sheath, evaluated with the first (dashed) and first and s ...
CHAPTER 23 The Interaction of Light with Matter: I
... which corresponds to Rayleigh scattering, which is characterized by a strong wavelength dependence for the effective cross section of the form σs ∝ σT λ−4 . Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charg ...
... which corresponds to Rayleigh scattering, which is characterized by a strong wavelength dependence for the effective cross section of the form σs ∝ σT λ−4 . Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charg ...
Which one of the following statements is correct? An
... An electron moves due North in a horizontal plane with uniform speed. It enters a uniform magnetic field directed due South in the same plane. Which one of the following statements concerning the motion of the electron in the magnetic field is correct? A ...
... An electron moves due North in a horizontal plane with uniform speed. It enters a uniform magnetic field directed due South in the same plane. Which one of the following statements concerning the motion of the electron in the magnetic field is correct? A ...
C - Thierry Karsenti
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
... The module, Physical Chemistry 2, focuses on five (5) areas of physical chemistry important to many aspects of our lives: solutions, colloids, phase equilibrium, electrochemistry and nuclear chemistry. Solutions are often necessary to facilitate many chemical reactions in life processes or industry ...
cp violation and the origins of matter
... a standard part of modern cosmology with the introduction of grand unified theories (GUTs), introduced in the 1970s, which establish a possible source for baryon number violation, an essential component of baryogenesis. More recent ideas have attempted to link the baron asymmetry with details of mod ...
... a standard part of modern cosmology with the introduction of grand unified theories (GUTs), introduced in the 1970s, which establish a possible source for baryon number violation, an essential component of baryogenesis. More recent ideas have attempted to link the baron asymmetry with details of mod ...
Thermoelectric effects in a Luttinger liquid
... does not contradict our previous claim, since the two problems under study 共infinite LL wire and LL wire adiabatically connected to metallic leads兲 are not identical. In particular, the driving voltage which enters the definition of the thermopower is different for the two cases in question. For an ...
... does not contradict our previous claim, since the two problems under study 共infinite LL wire and LL wire adiabatically connected to metallic leads兲 are not identical. In particular, the driving voltage which enters the definition of the thermopower is different for the two cases in question. For an ...
Monday, Oct. 3, 2016
... Nuclear Models: Fermi Gas Model • An early attempt to incorporate quantum effects • Assumes nucleus as a gas of free protons and neutrons confined to the nuclear volume – The nucleons occupy quantized (discrete) energy levels – Nucleons are moving inside a spherically symmetric well with the range ...
... Nuclear Models: Fermi Gas Model • An early attempt to incorporate quantum effects • Assumes nucleus as a gas of free protons and neutrons confined to the nuclear volume – The nucleons occupy quantized (discrete) energy levels – Nucleons are moving inside a spherically symmetric well with the range ...
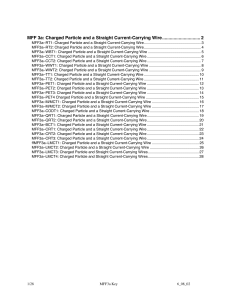
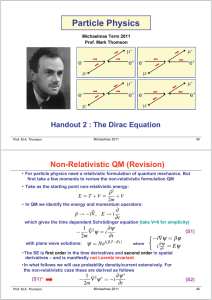
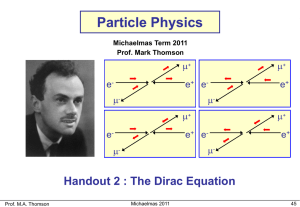
Particle Physics
... Historically, it was thought that there were two main problems with the Klein-Gordon equation: Negative energy solutions The negative particle densities associated with these solutions We now know that in Quantum Field Theory these problems are overcome and the KG equation is used to describe ...
... Historically, it was thought that there were two main problems with the Klein-Gordon equation: Negative energy solutions The negative particle densities associated with these solutions We now know that in Quantum Field Theory these problems are overcome and the KG equation is used to describe ...
Spin-orbit-coupled Bose
... laser intensity). We develop a many-body theory that provides quantitative agreement with the observed location of the transition. The engineered SO coupling—equally applicable for bosons and fermions—sets the stage for the realization of topological insulators in fermionic neutral atom systems. Qua ...
... laser intensity). We develop a many-body theory that provides quantitative agreement with the observed location of the transition. The engineered SO coupling—equally applicable for bosons and fermions—sets the stage for the realization of topological insulators in fermionic neutral atom systems. Qua ...
Atomic Structure
... This question is about oxygen atoms. The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer this question. ...
... This question is about oxygen atoms. The periodic table on the Data Sheet may help you to answer this question. ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.