Aalborg Universitet Online Detection of Aggregation Processes Using Dielectric Spectroscopy
... colloidal range (1 nm to 1µm) form aggregates due to the addition of chemicals. Often the use of the term flocculation is reserved for aggregation processes where polymeric substances are used, but in this study it will be used to describe the formation of aggregates independent of the chemical in u ...
... colloidal range (1 nm to 1µm) form aggregates due to the addition of chemicals. Often the use of the term flocculation is reserved for aggregation processes where polymeric substances are used, but in this study it will be used to describe the formation of aggregates independent of the chemical in u ...
Stage 2 Physics Subject Outline (for teaching in 2018)
... Physics is a 10-credit subject or a 20-credit subject at Stage 1 and a 20-credit subject at Stage 2. The study of Physics is constructed around using qualitative and quantitative models, laws, and theories to better understand matter, forces, energy, and the interaction among them. Physics seeks to ...
... Physics is a 10-credit subject or a 20-credit subject at Stage 1 and a 20-credit subject at Stage 2. The study of Physics is constructed around using qualitative and quantitative models, laws, and theories to better understand matter, forces, energy, and the interaction among them. Physics seeks to ...
pptx - University of Washington
... What happens when there are not enough partners for everyone to pair with? (In particular this is what one expects to happen in color superconductivity, due to a heavier strange quark) ...
... What happens when there are not enough partners for everyone to pair with? (In particular this is what one expects to happen in color superconductivity, due to a heavier strange quark) ...
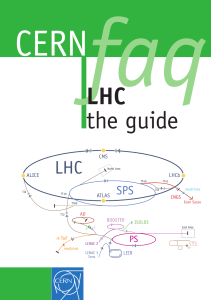
LHC the guide
... our present knowledge of particle physics. The Standard Model has been tested by various experiments and it has proven particularly successful in anticipating the existence of previously undiscovered particles. However, it leaves many unsolved questions, which the LHC will help to answer. } The Sta ...
... our present knowledge of particle physics. The Standard Model has been tested by various experiments and it has proven particularly successful in anticipating the existence of previously undiscovered particles. However, it leaves many unsolved questions, which the LHC will help to answer. } The Sta ...
Lecture 13 - PPD - STFC Particle Physics Department
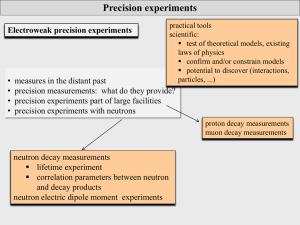
... precision experiments: particle physics Scientific precision experiments: testing the limits of our description and understanding of nature particle physics: masses and lifetimes of particles (quarks, leptons, hadrons, ...) matrix elements of transitions (CKM, PMNS, nuclear trs, ...) forces a ...
... precision experiments: particle physics Scientific precision experiments: testing the limits of our description and understanding of nature particle physics: masses and lifetimes of particles (quarks, leptons, hadrons, ...) matrix elements of transitions (CKM, PMNS, nuclear trs, ...) forces a ...
cavity types - CERN Accelerator School
... number of full-period • number of zeros of • number of half-period variations of the field the axial field variations of the field components in the ...
... number of full-period • number of zeros of • number of half-period variations of the field the axial field variations of the field components in the ...
Is Matter Made of Light? - Superluminal quantum models of the
... is larger in a specific way than the electron’s energy E mc 2 at rest, where m is the electron’s rest mass. The total energy E of a moving electron is given by E mc 2 , where is defined previously. An equation (called the Einstein/de Broglie equation) containing this same information but exp ...
... is larger in a specific way than the electron’s energy E mc 2 at rest, where m is the electron’s rest mass. The total energy E of a moving electron is given by E mc 2 , where is defined previously. An equation (called the Einstein/de Broglie equation) containing this same information but exp ...
Concept Tests 16 17
... that is down and to the right. The –Q charge has an E field up and to the left, but smaller in magnitude. Therefore, the total electric field is down and to the right. Follow-up: What if all three charges reversed their signs? ...
... that is down and to the right. The –Q charge has an E field up and to the left, but smaller in magnitude. Therefore, the total electric field is down and to the right. Follow-up: What if all three charges reversed their signs? ...
Nitrogen vacancy and oxygen impurity in AlN: spintronic
... cases (see the tables), different states are resolved by amounts well beyond normal experimental tolerances. Alternatively, if a particular defect states is found from the calculations to have a particularly desirable property from the viewpoint of technical application, then it may be possible to c ...
... cases (see the tables), different states are resolved by amounts well beyond normal experimental tolerances. Alternatively, if a particular defect states is found from the calculations to have a particularly desirable property from the viewpoint of technical application, then it may be possible to c ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... orbitals. The carbon forms two covalent sigma, σ , bonds which gives a bond angle of 180◦ with diagonal symmetry. The two remaining electrons in the 2p y and 2pz orbital form pi, π , orbitals perpendicular to the σ bonds. When two sp hybridized carbons are brought together the π orbitals surround th ...
... orbitals. The carbon forms two covalent sigma, σ , bonds which gives a bond angle of 180◦ with diagonal symmetry. The two remaining electrons in the 2p y and 2pz orbital form pi, π , orbitals perpendicular to the σ bonds. When two sp hybridized carbons are brought together the π orbitals surround th ...
Electromagnetic Shells of Atoms and the Periodic System of Elements
... experiments, determined by charged state of the particles and charged namely by magnetic charges different signs. However, interpretation of the experimental results which was built by Ehrenhaft on analogy with behavior of electric particles in the electrostatic field, does not appear convincing eno ...
... experiments, determined by charged state of the particles and charged namely by magnetic charges different signs. However, interpretation of the experimental results which was built by Ehrenhaft on analogy with behavior of electric particles in the electrostatic field, does not appear convincing eno ...
Chapter III. Scattering and Extinction of Evanescent waves by small
... half widths, but merely the amplitudes of the resonances. Due to the oscillatory nature of the Ricatti-Bessel functions in the denominator of the wavelength-dependent Mie-coefficients multipole resonances of the same orders n exist in the UV regime but are not considered here. For this reason, the m ...
... half widths, but merely the amplitudes of the resonances. Due to the oscillatory nature of the Ricatti-Bessel functions in the denominator of the wavelength-dependent Mie-coefficients multipole resonances of the same orders n exist in the UV regime but are not considered here. For this reason, the m ...
CJ Electrostatics Assignment 1 Solutions
... when pushed closer to another particle that is fixed in position and has a charge of the same polarity. In spite of the similarity, the charged particle will not exhibit simple harmonic motion on being released, as will the particle on the spring. Explain why not. In order for a particle to execute ...
... when pushed closer to another particle that is fixed in position and has a charge of the same polarity. In spite of the similarity, the charged particle will not exhibit simple harmonic motion on being released, as will the particle on the spring. Explain why not. In order for a particle to execute ...
the full course notes are available here in book form for downloading
... Figure 1.2: Initial conditions for the three-body problem. • Third point-like mass executes complicated motion (’chaos’) for a while but is ejected from the system eventually. • Plots of conserved quantities such as the energy tell us if our numerical method is performing well. For example, our ener ...
... Figure 1.2: Initial conditions for the three-body problem. • Third point-like mass executes complicated motion (’chaos’) for a while but is ejected from the system eventually. • Plots of conserved quantities such as the energy tell us if our numerical method is performing well. For example, our ener ...
2 the phases of matter
... We know that there is a blanket of air around the Earth called the atmosphere, and that this results in what we call air pressure. But how can we actually prove that air has weight? Isn’t it just an invisible mixture of gases that we need to breathe? The air in the atmosphere is kept close to the Ea ...
... We know that there is a blanket of air around the Earth called the atmosphere, and that this results in what we call air pressure. But how can we actually prove that air has weight? Isn’t it just an invisible mixture of gases that we need to breathe? The air in the atmosphere is kept close to the Ea ...
Elastic Collisions: Conservation of Momentum and Me
... Please print the worksheet for this lab. You will need this sheet to record your data. The elastic collision apparatus consists of a grooved track mounted on a wooden base. One of the steel balls (called the projectile since it will be projected along the track) is held against a small metal stop at ...
... Please print the worksheet for this lab. You will need this sheet to record your data. The elastic collision apparatus consists of a grooved track mounted on a wooden base. One of the steel balls (called the projectile since it will be projected along the track) is held against a small metal stop at ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.