Lecture 14 - UMD Physics
... informally (ii): irreversible evolution from less-likely to more-likely ...
... informally (ii): irreversible evolution from less-likely to more-likely ...
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Review
... 10. What strange property of water does a glass of ice water illustrate? ...
... 10. What strange property of water does a glass of ice water illustrate? ...
Nats 101 S00 #8
... atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in buildings. Air inside the house is warmer than outside. The boundary is the walls and windows. The molecules of air are moving faster inside than outsi ...
... atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in buildings. Air inside the house is warmer than outside. The boundary is the walls and windows. The molecules of air are moving faster inside than outsi ...
Topic 6 CONTROLLING HEAT TRANSFER In this chapter you will
... inside the hair provides insulation. The outer parka is worn with the fur outside. This is particularly important on very cold days. The parka hood ________ ________ in front of the wearer’s face. Frigid air is warmed before being breathed. This protects the wearer’s __________. During ____________ ...
... inside the hair provides insulation. The outer parka is worn with the fur outside. This is particularly important on very cold days. The parka hood ________ ________ in front of the wearer’s face. Frigid air is warmed before being breathed. This protects the wearer’s __________. During ____________ ...
Homework #1: Energy Unit Conversions
... Solve the following problems using the conversions listed below. Report your answer with the correct units. Conversions: 1 calorie = 4.18 joules 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1kilocalorie= 1 Calorie (food) 1. How many calories are in 16.00 joules? ...
... Solve the following problems using the conversions listed below. Report your answer with the correct units. Conversions: 1 calorie = 4.18 joules 1 Calorie = 1000 calories 1kilocalorie= 1 Calorie (food) 1. How many calories are in 16.00 joules? ...
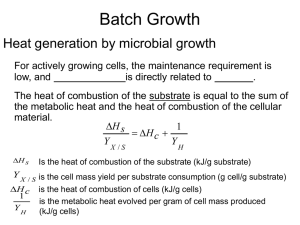
5.1 THERMAL QUANTITIES
... Power This is the ability to carry out a certain work in unit time (W), that is J/S. ...
... Power This is the ability to carry out a certain work in unit time (W), that is J/S. ...
Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion and Stress
... Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy (internal energy?) of the gas. For constant volume, pressure increases directly proportional to an increase in average kinetic energy (temperature) AND an increase in the number of molecules. But ...
... Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy (internal energy?) of the gas. For constant volume, pressure increases directly proportional to an increase in average kinetic energy (temperature) AND an increase in the number of molecules. But ...
CCD Apologia Chemistry Syllabus 2011-12
... Define Energy: The ability to do work – to cause motion. Work: The force applied to an object times the distance that the object travels parallel to that force. For work to occur, there must be motion. Heat: Energy transferred as a consequence of temperature differences. It is energy on its way from ...
... Define Energy: The ability to do work – to cause motion. Work: The force applied to an object times the distance that the object travels parallel to that force. For work to occur, there must be motion. Heat: Energy transferred as a consequence of temperature differences. It is energy on its way from ...
A Micro-Insulation Concept for MEMS Applications
... thin metal foils spaced by oxide particles. These structures have an apparent thermal conductivity as low as 0.001 W / m K when the cold-side temperature is 294 K 关5兴. The oxide particles are selected on the basis of their low thermal conductivity and compatibility with the foil chosen for the appli ...
... thin metal foils spaced by oxide particles. These structures have an apparent thermal conductivity as low as 0.001 W / m K when the cold-side temperature is 294 K 关5兴. The oxide particles are selected on the basis of their low thermal conductivity and compatibility with the foil chosen for the appli ...
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and Latent Heat In addition
... As a result, conduction is really only important right next to the ground.....over the lowest few cm, really a thin layer of air warmed by conduction ...
... As a result, conduction is really only important right next to the ground.....over the lowest few cm, really a thin layer of air warmed by conduction ...
Thermochemistry
... Measuring Energy Changes • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... Measuring Energy Changes • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
Slide 1
... failed. The bottom TEG should follow the temperature of the water closely as seen in the 24 hour test. If this were the case this would have produced a workable temperature difference capable of creating a large voltage. ...
... failed. The bottom TEG should follow the temperature of the water closely as seen in the 24 hour test. If this were the case this would have produced a workable temperature difference capable of creating a large voltage. ...
Heat Transfer conduction
... Heat energy is transferred from a high heat “source” to a low heat “sink”. Heat energy will “flow” from high temperature areas to low temperature ones through one of three methods; radiation, convection or conduction. Radiation is a mode of energy transfer that does not require a medium, or substanc ...
... Heat energy is transferred from a high heat “source” to a low heat “sink”. Heat energy will “flow” from high temperature areas to low temperature ones through one of three methods; radiation, convection or conduction. Radiation is a mode of energy transfer that does not require a medium, or substanc ...
Introduction - UniMAP Portal
... Calculate the convection heat transfer through forced convection heat transfer inside pipe (dimensionless no.), heat transfer coefficient for laminar flow inside pipe, heat transfer coefficient for turbulent flow inside pipe, heat transfer coefficient for transition flow inside pipe, heat transfer c ...
... Calculate the convection heat transfer through forced convection heat transfer inside pipe (dimensionless no.), heat transfer coefficient for laminar flow inside pipe, heat transfer coefficient for turbulent flow inside pipe, heat transfer coefficient for transition flow inside pipe, heat transfer c ...
Part L Overview
... upstands and any VCL in those elements. • Seal around all service penetrations. • 50mm minimum laps, sealed and have solid backing. • Polythene sheeting where used should be protected from heat & sunlight to reduce risk of degradation. • Foil back plasterboard joints should be sealed & allow for the ...
... upstands and any VCL in those elements. • Seal around all service penetrations. • 50mm minimum laps, sealed and have solid backing. • Polythene sheeting where used should be protected from heat & sunlight to reduce risk of degradation. • Foil back plasterboard joints should be sealed & allow for the ...
View a sample here
... metals, for example, are good conductors of heat—in fact, they conduct heat so well and so rapidly that there is little difference between the temperature of the “hot” side and that of the “cold” side. Other materials are very poor conductors of heat. Because they conduct heat very slowly, these mat ...
... metals, for example, are good conductors of heat—in fact, they conduct heat so well and so rapidly that there is little difference between the temperature of the “hot” side and that of the “cold” side. Other materials are very poor conductors of heat. Because they conduct heat very slowly, these mat ...
Substance Specific Heat Capacity
... temperature of gold rises much faster than the temperature of the same mass of aluminum. ...
... temperature of gold rises much faster than the temperature of the same mass of aluminum. ...
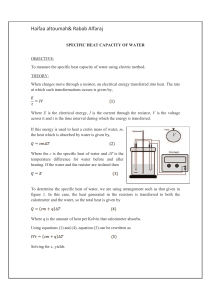
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER
... Where E is the electrical energy, I is the current through the resistor, V is the voltage across it and t is the time interval during which the energy is transferred. If this energy is used to heat a cretin mass of water, m, the heat which is absorbed by water is given by, ...
... Where E is the electrical energy, I is the current through the resistor, V is the voltage across it and t is the time interval during which the energy is transferred. If this energy is used to heat a cretin mass of water, m, the heat which is absorbed by water is given by, ...
Preview of Period 4: Transfer of Thermal Energy
... 4.1:Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the molecules of a substance. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance. 4.2:The transfer of thermal energy requires a difference in temperature. Heat may be transferred by means of conduction (substances touching), c ...
... 4.1:Thermal energy is the total internal energy of the molecules of a substance. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance. 4.2:The transfer of thermal energy requires a difference in temperature. Heat may be transferred by means of conduction (substances touching), c ...