Section 12.1 Temperature and Thermal Energy
... Thermal Energy – is also called internal energy. It is the Sum of Kinetic Energy (KE) and Potential Energy (PE) of the internal motion of particles that make up an object. ...
... Thermal Energy – is also called internal energy. It is the Sum of Kinetic Energy (KE) and Potential Energy (PE) of the internal motion of particles that make up an object. ...
Characteristics of a One Dimensional Longitudinal Wave
... assumed that the flux at the interface is high enough to maintain this temperature at all times. It would actually only be this temperature at the point welding is taking place, which is why this is conservative. This problem cannot be solved by conduction alone, as the model would show a steady sta ...
... assumed that the flux at the interface is high enough to maintain this temperature at all times. It would actually only be this temperature at the point welding is taking place, which is why this is conservative. This problem cannot be solved by conduction alone, as the model would show a steady sta ...
Heat - Ms. Bergman`s Classes at DCIS Montbello
... motion of atoms and molecules. – Measured in Joules (J) 1000 J = 1 kJ – Heat energy always evens out (heat transfers from warm objects to cool objects). ...
... motion of atoms and molecules. – Measured in Joules (J) 1000 J = 1 kJ – Heat energy always evens out (heat transfers from warm objects to cool objects). ...
How Do We Measure Total Energy? First Law of
... Specific Heat: amount of energy needed to change the temperature of a fixed mass of a substance by a fixed amount ...
... Specific Heat: amount of energy needed to change the temperature of a fixed mass of a substance by a fixed amount ...
File
... transferred into the system - if the system is constrained to a constant volume: the heat required to bring about a rise in temperature dT is some amount CvdT - if the system is permitted to expand (or contract) as the heat is added, the amount required to bring about the same rise in temperature is ...
... transferred into the system - if the system is constrained to a constant volume: the heat required to bring about a rise in temperature dT is some amount CvdT - if the system is permitted to expand (or contract) as the heat is added, the amount required to bring about the same rise in temperature is ...
Honors Physics Notes Nov 16, 20 Heat Persans
... • The temperature difference between two sides of a 1 cm thick sheet of foam board is T10C. The rate at which heat passes through it is 400 W per square meter. – What would the heat flow be if the thickness were increased to 2 cm? ...
... • The temperature difference between two sides of a 1 cm thick sheet of foam board is T10C. The rate at which heat passes through it is 400 W per square meter. – What would the heat flow be if the thickness were increased to 2 cm? ...
Concepts for specific heat
... The results is plotted in Fig. 1. In the case β~ω ≫ 1 (i.e. kB T ≪ ~ω) this becomes vanishingly small, while for β~ω ≪ 1 (i.e. kB T ≫ ~ω) we obtain the classical result kB . One says, that the degree of freedom freezes in around a temperature where kB T = ~ω. As the energies of the phonons for solid ...
... The results is plotted in Fig. 1. In the case β~ω ≫ 1 (i.e. kB T ≪ ~ω) this becomes vanishingly small, while for β~ω ≪ 1 (i.e. kB T ≫ ~ω) we obtain the classical result kB . One says, that the degree of freedom freezes in around a temperature where kB T = ~ω. As the energies of the phonons for solid ...
Heat And Thermodynamics - Figure B
... Heat is a form of energy which appears when two bodies at different temperature are placed into thermal contact. It can flow from high temperature to low temperature till temperature of the two bodies becomes same. Thus, we can say that heat is the energy in transit. Heat is not property of system, ...
... Heat is a form of energy which appears when two bodies at different temperature are placed into thermal contact. It can flow from high temperature to low temperature till temperature of the two bodies becomes same. Thus, we can say that heat is the energy in transit. Heat is not property of system, ...
Power & Heat
... Assuming the positive and negative going switching is symmetric, this occurs twice per switching cycle, so that the average power over one cycle is ...
... Assuming the positive and negative going switching is symmetric, this occurs twice per switching cycle, so that the average power over one cycle is ...
Lesson 3 - School Web Link
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms may be used more than once or not at all. ...
... Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms may be used more than once or not at all. ...
Thermos Flask
... good quality thermos flask with silvered lining filled with hot water Action The students examine the flask and explain how the three processes of heat transfer are affected by the flask. They should note that while the liquid inside is hot, and hence the inner wall is also hot, the outer wall is at ...
... good quality thermos flask with silvered lining filled with hot water Action The students examine the flask and explain how the three processes of heat transfer are affected by the flask. They should note that while the liquid inside is hot, and hence the inner wall is also hot, the outer wall is at ...
Lab 1: Temperature and Heat
... (a) Connect a 1.0 Ω resistor to a DC power supply, adjust the voltage to 5.0 V, and turn off the supply. (b) Add some liquid nitrogen to the insulated container and immerse the resistor. Once the resistor's temperature has dropped to liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K), measure the resistance of the ...
... (a) Connect a 1.0 Ω resistor to a DC power supply, adjust the voltage to 5.0 V, and turn off the supply. (b) Add some liquid nitrogen to the insulated container and immerse the resistor. Once the resistor's temperature has dropped to liquid nitrogen temperature (77 K), measure the resistance of the ...
Walter Lorenz Surgical, Inc
... The LactoSorb Air Activated Heat Pack is activated by opening the foil chevron pouch and then shaking the heat pack for at least one minute. This agitation allows oxygen to reach the mixture to begin the reaction. As the iron powder oxidizes, the surface temperature of the heat pack increases to opt ...
... The LactoSorb Air Activated Heat Pack is activated by opening the foil chevron pouch and then shaking the heat pack for at least one minute. This agitation allows oxygen to reach the mixture to begin the reaction. As the iron powder oxidizes, the surface temperature of the heat pack increases to opt ...
Energy - Montana State University Billings
... • Direct relationship between Density and Pressure (pressure goes up; density goes up if T constant) • Inverse relationship between Density and temperature (temperature goes up; density goes down if P constant) • Direct relationship between temperature and pressure (temperature goes up; pressure goe ...
... • Direct relationship between Density and Pressure (pressure goes up; density goes up if T constant) • Inverse relationship between Density and temperature (temperature goes up; density goes down if P constant) • Direct relationship between temperature and pressure (temperature goes up; pressure goe ...
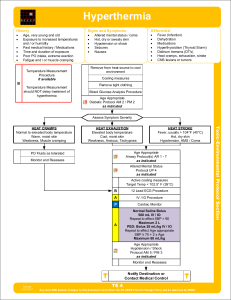
Hyperthermia
... Rapid cooling takes precedence over transport as early cooling decreases morbidity and mortality. If available, immerse in an ice water bath for 5 – minutes. Monitor rectal temperature and remove patient when temperature reaches 102.5°F (39°C). Your goal is to decrease rectal temperature below 104°F ...
... Rapid cooling takes precedence over transport as early cooling decreases morbidity and mortality. If available, immerse in an ice water bath for 5 – minutes. Monitor rectal temperature and remove patient when temperature reaches 102.5°F (39°C). Your goal is to decrease rectal temperature below 104°F ...
ME 435: Thermal Energy Systems Design
... Th,i, Th,o - the hot fluid inlet/outlet temperatures Tc,i, Tc,o - the cold fluid inlet/outlet temperatures h and m c-the hot and cold fluid mass flow rates m U - the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger. Remember that this value can be based on either the inside or outside su ...
... Th,i, Th,o - the hot fluid inlet/outlet temperatures Tc,i, Tc,o - the cold fluid inlet/outlet temperatures h and m c-the hot and cold fluid mass flow rates m U - the overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger. Remember that this value can be based on either the inside or outside su ...
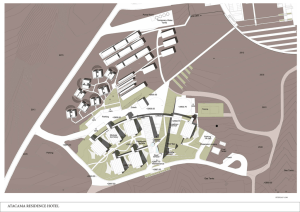
ATACAMA RESIDENCE HOTEL
... The aim of the proposal is good usability and long term technical upgrading and modification possibilities of the building in addition to reasonable investment costs. The building comprises of compact, energy efficient units that are designed to suit local environmental demands. The building is desi ...
... The aim of the proposal is good usability and long term technical upgrading and modification possibilities of the building in addition to reasonable investment costs. The building comprises of compact, energy efficient units that are designed to suit local environmental demands. The building is desi ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... 1. Heat flow is a transfer of energy. 2. Thermal systems have internal energy related to the system’s thermal properties. Heat transfer can happen via diffusion, thermal conduction or radiation, for an open system it can occur through absorption of water vapor (latent heat). For many applications, h ...
... 1. Heat flow is a transfer of energy. 2. Thermal systems have internal energy related to the system’s thermal properties. Heat transfer can happen via diffusion, thermal conduction or radiation, for an open system it can occur through absorption of water vapor (latent heat). For many applications, h ...
Physics 202 Homework
... The rate of heat that flows into the helium is P = (1)(5.67 × 10−8 )(1.1310)(77)4 = 2.2542 And the amount of heat lost from the helium is P = (1)(5.67 × 10−8 )(1.1310)(4.2)4 = 1.9954 × 10−5 Now, this is negligible compared to the heat flowing into the helium. In the time frame mentioned (one hour = ...
... The rate of heat that flows into the helium is P = (1)(5.67 × 10−8 )(1.1310)(77)4 = 2.2542 And the amount of heat lost from the helium is P = (1)(5.67 × 10−8 )(1.1310)(4.2)4 = 1.9954 × 10−5 Now, this is negligible compared to the heat flowing into the helium. In the time frame mentioned (one hour = ...