Chapter 11 - Trimble County Schools
... Fine-Tuning of the Response • There are four aspects of fine-tuning to consider – Amplifying the signal (and thus the response) – Specificity of the response (liver/heart) – Overall efficiency of response, enhanced by ...
... Fine-Tuning of the Response • There are four aspects of fine-tuning to consider – Amplifying the signal (and thus the response) – Specificity of the response (liver/heart) – Overall efficiency of response, enhanced by ...
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS I
... cAMP: - activates protein kinase A, which directly phosphorylates proteins (e.g. troponin I) essential for cardiac muscle contraction - stimulates sodium/potassium influx which opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels - inhibits uptake of Ca2+ into cellular stores - cAMP hydrolyzed by phosphodiesterases ...
... cAMP: - activates protein kinase A, which directly phosphorylates proteins (e.g. troponin I) essential for cardiac muscle contraction - stimulates sodium/potassium influx which opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels - inhibits uptake of Ca2+ into cellular stores - cAMP hydrolyzed by phosphodiesterases ...
Research with L-glutamate, a prototypical L-amino acid that activates umami... two G-protein coupled receptors, T1R1+T1R3 and t-mGluR4, are important in...
... than glutamate also utilize the PLC-β2 mediated pathway, and (3) L-amino acids also use a cAMPdependent pathway. In our calcium imaging study, we found that response patterns elicited by L-amino acids vary across TSCs. Further, TSCs also show synergy for different L-amino acids when mixed with IMP. ...
... than glutamate also utilize the PLC-β2 mediated pathway, and (3) L-amino acids also use a cAMPdependent pathway. In our calcium imaging study, we found that response patterns elicited by L-amino acids vary across TSCs. Further, TSCs also show synergy for different L-amino acids when mixed with IMP. ...
Excitation of Rat Locus Coeruleus Neurons by Adenosine 5
... release of noradrenaline (although adenosine is effective; Jackisch et al., 1985). Noradrenaline is released not only from the varicose terminals of the noradrenergic cells as they ramify in their several targets, but also from the soma-dendritic region (Egan et al., 1983). Here it acts at a,-adreno ...
... release of noradrenaline (although adenosine is effective; Jackisch et al., 1985). Noradrenaline is released not only from the varicose terminals of the noradrenergic cells as they ramify in their several targets, but also from the soma-dendritic region (Egan et al., 1983). Here it acts at a,-adreno ...
MECHANISMS OF INTERCELLULAR COMMUNICATION
... FROM ATP TO PHOSPHORYLATE ANOTHER ENZYME • ACTIVATE OR INACTIVATE ENZYME • OFTEN ACTIVATION OF ENZYME IS THE RATE LIMITING REACTION IN METABOLIC PATHWAY • COMMON IN CELLS ...
... FROM ATP TO PHOSPHORYLATE ANOTHER ENZYME • ACTIVATE OR INACTIVATE ENZYME • OFTEN ACTIVATION OF ENZYME IS THE RATE LIMITING REACTION IN METABOLIC PATHWAY • COMMON IN CELLS ...
Acetylcholine Receptor
... these chains, colored orange here, have binding sites for acetylcholine on the side, colored here in red. When acetylcholine binds to these two chains, the shape of the entire receptor changes slightly, opening the channel. This allows positively charged ions, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium ...
... these chains, colored orange here, have binding sites for acetylcholine on the side, colored here in red. When acetylcholine binds to these two chains, the shape of the entire receptor changes slightly, opening the channel. This allows positively charged ions, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium ...
adrenegics
... 3. Which of the following muscles are not affected by adrenaline and why? (cardiac muscles, skeletal muscles, smooth muscles). Of course it is skeletal muscle, but why? 4. Draw the structure of adrenaline 5. Mention names of two switches and two non-switches targets used to control the adrenergic ac ...
... 3. Which of the following muscles are not affected by adrenaline and why? (cardiac muscles, skeletal muscles, smooth muscles). Of course it is skeletal muscle, but why? 4. Draw the structure of adrenaline 5. Mention names of two switches and two non-switches targets used to control the adrenergic ac ...
Thyroid Hormone Receptor: Dimers, Dimers, Dimers
... Nuclear reactors are intracellular receptors as well as transcription factors. They respond through physical interactions with their respective ligands. These ligands are small, hydrophobic signaling molecules such as steroid hormones. Once the ligand is bound, co-activators or co-repressors may be ...
... Nuclear reactors are intracellular receptors as well as transcription factors. They respond through physical interactions with their respective ligands. These ligands are small, hydrophobic signaling molecules such as steroid hormones. Once the ligand is bound, co-activators or co-repressors may be ...
Photosynthesis
... Living organisms are divided into 2 groups according to the way they get food: 1. autotrophs • auto = self troph = feeder ...
... Living organisms are divided into 2 groups according to the way they get food: 1. autotrophs • auto = self troph = feeder ...
Cross-Talk among RORal and the Rev-erb Family
... Important biological processes including development (l-3) cell-cycle control (4, 5) apoptosis (6, 7) and oncogenesis (8-l 0) are regulated by complex transcriptional networks. Precise control of these networks requires the organism to coordinate and integrate signals from multiple regulatory pathwa ...
... Important biological processes including development (l-3) cell-cycle control (4, 5) apoptosis (6, 7) and oncogenesis (8-l 0) are regulated by complex transcriptional networks. Precise control of these networks requires the organism to coordinate and integrate signals from multiple regulatory pathwa ...
Cellular Respiration
... the tissues of plants and animals. Regardless of how they obtain it, cells must have a steady supply of glucose so that ATP production is continuous. Oxygen is present in the air, and also is found dissolved in water. It either diffuses into cells—as in bacteria, fungi, plants, and many aquatic anim ...
... the tissues of plants and animals. Regardless of how they obtain it, cells must have a steady supply of glucose so that ATP production is continuous. Oxygen is present in the air, and also is found dissolved in water. It either diffuses into cells—as in bacteria, fungi, plants, and many aquatic anim ...
Surface Infrared Spectroscopic Study of ATP Synthesis in Mitochondria
... results indicate that the ADP→ATP conversion was successfully monitored with MIR-IRAS. Then we stopped oxygen supply and added an uncoupler SF6847 to the mitochondrial suspension. Uncouplers inhibit ATP synthesis in mitochondria by dissipating the H+-electrochemical gradient across the inner membran ...
... results indicate that the ADP→ATP conversion was successfully monitored with MIR-IRAS. Then we stopped oxygen supply and added an uncoupler SF6847 to the mitochondrial suspension. Uncouplers inhibit ATP synthesis in mitochondria by dissipating the H+-electrochemical gradient across the inner membran ...
Negative regulation of oncogenic signaling by receptor tyrosine
... relatively late in evolution, and they exhibit unexpected variation and complexity. Concentrating on negative mechanisms, we found that ligand-induced endocytosis and degradation of active receptors is a major regulatory pathway involving not only phopshorylation, but also ubiquitination of receptor ...
... relatively late in evolution, and they exhibit unexpected variation and complexity. Concentrating on negative mechanisms, we found that ligand-induced endocytosis and degradation of active receptors is a major regulatory pathway involving not only phopshorylation, but also ubiquitination of receptor ...
GenII cells alld early de\,c/0l`lIlell! 227S Introduction.Neurotrophic
... Introduction. Neurotrophic factors are primarly known for their essential role in neuron development and function. Several studies have shown, however, that thay may also have important effects on various types of non-neuronal tissues. Neurotrophins'effects are initiated by their binding to two type ...
... Introduction. Neurotrophic factors are primarly known for their essential role in neuron development and function. Several studies have shown, however, that thay may also have important effects on various types of non-neuronal tissues. Neurotrophins'effects are initiated by their binding to two type ...
Intro Membranes WRLa..
... » Gs-alpha stimulates AC to enzymatically form cyclic-AMP from ATP » cAMP activates protein kinase A, which in turn, phosphosylates a target protein » Degradation of cAMP to AMP may overwhelm th ability to re-phosphorylate; adenosine is produced » Adenosine activates an inhibitory G-protein which in ...
... » Gs-alpha stimulates AC to enzymatically form cyclic-AMP from ATP » cAMP activates protein kinase A, which in turn, phosphosylates a target protein » Degradation of cAMP to AMP may overwhelm th ability to re-phosphorylate; adenosine is produced » Adenosine activates an inhibitory G-protein which in ...
Cell signalling and gene regulation Plant signal transduction
... members of the auxin response factor (ARF) family. As discussed above, in the case of auxin, the identification of genes through targeted Arabidopsis mutant screens has provided invaluable insights into the structure of several plant signalling pathways. More and more frequently, however, known horm ...
... members of the auxin response factor (ARF) family. As discussed above, in the case of auxin, the identification of genes through targeted Arabidopsis mutant screens has provided invaluable insights into the structure of several plant signalling pathways. More and more frequently, however, known horm ...
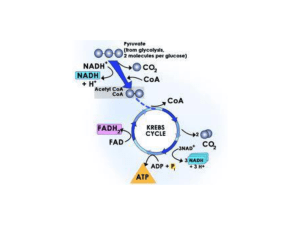
Respiration
... • GLYCOLYSIS-process in which one molecule of glucose is broken in half producing two molecules of Pyruvic Acid • 2 ATP go in (to get things going) 4 ATP are produced • NADH is made from NAD+ (helps energy get passed along) • Happens in the Cytosol/Cytoplasm ...
... • GLYCOLYSIS-process in which one molecule of glucose is broken in half producing two molecules of Pyruvic Acid • 2 ATP go in (to get things going) 4 ATP are produced • NADH is made from NAD+ (helps energy get passed along) • Happens in the Cytosol/Cytoplasm ...
Purinergic signalling
Purinergic signalling (or signaling: see American and British English differences) is a form of extracellular signalling mediated by purine nucleotides and nucleosides such as adenosine and ATP. It involves the activation of purinergic receptors in the cell and/or in nearby cells, thereby regulating cellular functions.The purinergic signalling complex of a cell is sometimes referred to as the “purinome”.