Geology Test
... 2. Rocks formed by cooling from a molten state are a. Precipitated rocks. b. Igneous rocks. c. Sedimentary rocks. d. Metamorphic rocks. 3. Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are a. Intrusive igneous rocks b. Extrusive sedimentary rocks c. Metamorphic rocks d. Igneous rock ...
... 2. Rocks formed by cooling from a molten state are a. Precipitated rocks. b. Igneous rocks. c. Sedimentary rocks. d. Metamorphic rocks. 3. Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are a. Intrusive igneous rocks b. Extrusive sedimentary rocks c. Metamorphic rocks d. Igneous rock ...
Formation of Gems and Minerals
... • Some gems crystallize in magmas or in gas bubbles (holes) in volcanic rocks. – Examples include: zircon and topaz ...
... • Some gems crystallize in magmas or in gas bubbles (holes) in volcanic rocks. – Examples include: zircon and topaz ...
Document
... 2. E.SE.06.52 Demonstrate how major geological events (earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mountain building) result from these plate motions. 3. E.SE.06.53 Describe layers of the Earth as a lithosphere (crust and upper mantle), convecting mantle, and dense metallic core. 4. E.SE.06.41 Compare and cont ...
... 2. E.SE.06.52 Demonstrate how major geological events (earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, mountain building) result from these plate motions. 3. E.SE.06.53 Describe layers of the Earth as a lithosphere (crust and upper mantle), convecting mantle, and dense metallic core. 4. E.SE.06.41 Compare and cont ...
Key concepts
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
Lecture 19 - The First Living Things on Earth
... Were Extremophiles the first forms of life on Earth? The earliest life was probably like prokaryotes today. Prokaryotes tend to be more heat tolerant. Deep hydrothermal vents are isolated from the harsh surface of the young Earth, and rich in inorganics. ...
... Were Extremophiles the first forms of life on Earth? The earliest life was probably like prokaryotes today. Prokaryotes tend to be more heat tolerant. Deep hydrothermal vents are isolated from the harsh surface of the young Earth, and rich in inorganics. ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... Oceanic Crust - dark brown Continental Crust - light brown Ocean - blue ...
... Oceanic Crust - dark brown Continental Crust - light brown Ocean - blue ...
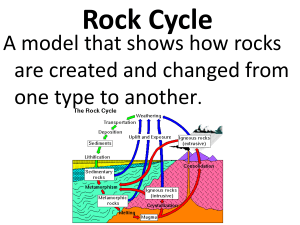
Rock Cycle
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
... Metamorphic Rock Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
Hazardous Environments resulting from crustal (tectonic) movement
... • Unconsolidated sediments such as sand shake in a less predictable way than solid rock. • P-waves can turn solid sediments into fluids like quicksand by disrupting sub-surface water conditions. • This is known as liquefaction or fluidisation and can wreck foundations of large buildings. ...
... • Unconsolidated sediments such as sand shake in a less predictable way than solid rock. • P-waves can turn solid sediments into fluids like quicksand by disrupting sub-surface water conditions. • This is known as liquefaction or fluidisation and can wreck foundations of large buildings. ...
Lecture 2
... relatively light and brittle. Most earthquakes occur within the crust. Scientists believe that below the lithosphere is a relatively narrow, mobile zone in the mantle called the asthenosphere (from asthenes, Greek for weak). CORE Beneath the mantle is the Earth's core. The Earth's core consists of a ...
... relatively light and brittle. Most earthquakes occur within the crust. Scientists believe that below the lithosphere is a relatively narrow, mobile zone in the mantle called the asthenosphere (from asthenes, Greek for weak). CORE Beneath the mantle is the Earth's core. The Earth's core consists of a ...
2nd 6 week test review 2015-2016 ppt
... What are tectonic plates? • Tectonic plates are large plates of rock that make up the foundation of the Earth's crust and the shape of the continents. The tectonic plates comprise the bottom of the crust and the top of the Earth's mantle. ...
... What are tectonic plates? • Tectonic plates are large plates of rock that make up the foundation of the Earth's crust and the shape of the continents. The tectonic plates comprise the bottom of the crust and the top of the Earth's mantle. ...
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
... • Fossils of Mesosaurus are found on _______________________ and on Africa. • Coastline _______ is what started the thinking on plate tectonics. • The Appalachian Mts. Match mountains found in _________ when the plates are put back together. • The ____________________ is diverging at a rate of 2.5 ...
... • Fossils of Mesosaurus are found on _______________________ and on Africa. • Coastline _______ is what started the thinking on plate tectonics. • The Appalachian Mts. Match mountains found in _________ when the plates are put back together. • The ____________________ is diverging at a rate of 2.5 ...
Earth as a System - Bakersfield College
... Interaction of all water processes, only planet with water, 71% ocean 12,500 feet deep, streams, lakes, groundwater ...
... Interaction of all water processes, only planet with water, 71% ocean 12,500 feet deep, streams, lakes, groundwater ...
Lecture Notes
... • When is the next reversal coming? How does the Earth’s magnetic field reverse? What causes the reversals? • What could be creating the Earth’s magnetic field? • Do we have a bar magnet inside the Earth? That is flipping over?? NO • Magnetized rocks in the crust or mantle? o This wouldn’t explain ...
... • When is the next reversal coming? How does the Earth’s magnetic field reverse? What causes the reversals? • What could be creating the Earth’s magnetic field? • Do we have a bar magnet inside the Earth? That is flipping over?? NO • Magnetized rocks in the crust or mantle? o This wouldn’t explain ...
Article of the Week on Geologic Time Scale
... New mammals appeared while others became extinct. The diversity of life forms increased. Flowering plants became most common. Humans are also part of the most recent period of this era. that various models, diagrams, and pictures can be used to illustrate the vastness of time involved in g ...
... New mammals appeared while others became extinct. The diversity of life forms increased. Flowering plants became most common. Humans are also part of the most recent period of this era. that various models, diagrams, and pictures can be used to illustrate the vastness of time involved in g ...
1 Introduction to Marine Ecology jh part 2 2009
... • Each 1/9 of WL, orbit diameters drop by ½, so by ½ depth motion imperceptible ...
... • Each 1/9 of WL, orbit diameters drop by ½, so by ½ depth motion imperceptible ...
Solar System - MrsAllisonMagee
... • Orbital Period: 365 days • One rotation on its axis every day. • Earth is unique with water being in a liquid state. • Moderate Temperatures due to atmosphere. • Oxygen in atmosphere because of plants. ...
... • Orbital Period: 365 days • One rotation on its axis every day. • Earth is unique with water being in a liquid state. • Moderate Temperatures due to atmosphere. • Oxygen in atmosphere because of plants. ...
Earth Science Study guide answers
... Know how to read a weather map and forecast future weather *Cold fronts- bring violent storms that are followed by fair, cooler weather *Warm fronts- bring rain and showers followed by warmer, more humid weather Occluded fronts- usually produce light ...
... Know how to read a weather map and forecast future weather *Cold fronts- bring violent storms that are followed by fair, cooler weather *Warm fronts- bring rain and showers followed by warmer, more humid weather Occluded fronts- usually produce light ...
Plate Tectonics - Aspen View Academy
... Integrity in the Little Things Astronauts aboard a trip of space shuttle Columbia were unable to make two scheduled space walks. The problem…a half-inch screw had fallen from its hole and lodged in the gears of the hatch. So a small, half-inch screw foiled an important segment of an expensive missio ...
... Integrity in the Little Things Astronauts aboard a trip of space shuttle Columbia were unable to make two scheduled space walks. The problem…a half-inch screw had fallen from its hole and lodged in the gears of the hatch. So a small, half-inch screw foiled an important segment of an expensive missio ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide TEST ON LESSON 1 Use your textbook
... the coasts of these continents, although they were now separated by vast oceans. 3. He noticed geological formations like mountain ranges, on the two continents also matched up. ...
... the coasts of these continents, although they were now separated by vast oceans. 3. He noticed geological formations like mountain ranges, on the two continents also matched up. ...
8th Grade Fourth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... Revolution Seasons Hemisphere Equator 6.11B Gravity Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Orbit Mass ...
... Revolution Seasons Hemisphere Equator 6.11B Gravity Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Orbit Mass ...
Geology Content from Frameworks The content listed below comes
... Igneous rock undergoes weathering (or breakdown) to form sediment. The sediment is transported and deposited somewhere (such as at the beach or in a delta, or in the deep sea). Igneous rocks are classified (or named) based on their composition (which minerals they contain) and texture (or the si ...
... Igneous rock undergoes weathering (or breakdown) to form sediment. The sediment is transported and deposited somewhere (such as at the beach or in a delta, or in the deep sea). Igneous rocks are classified (or named) based on their composition (which minerals they contain) and texture (or the si ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.