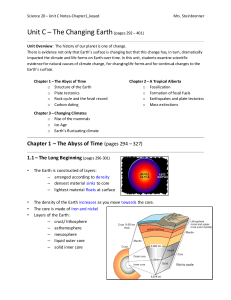
Features of Earthquakes
... paths of seismic waves changes as they travel through materials with different _______________________. By studying __________________________ waves that have traveled through Earth, scientists have identified different ____________________________ with different densities. In general the ______ ...
... paths of seismic waves changes as they travel through materials with different _______________________. By studying __________________________ waves that have traveled through Earth, scientists have identified different ____________________________ with different densities. In general the ______ ...
The Lithosphere - Westmount High School
... Plates move because of convection currents in magma, beneath the plates. As the magma is heated when it is close to the core, it rises. It moves horizontally because new molten rock is pushing it. As it moves horizontally, it takes the plate on its surface with it. The magma will cool down and fall ...
... Plates move because of convection currents in magma, beneath the plates. As the magma is heated when it is close to the core, it rises. It moves horizontally because new molten rock is pushing it. As it moves horizontally, it takes the plate on its surface with it. The magma will cool down and fall ...
File
... Zone are two well-known regions where normal faults are spreading apart Earth's crust. Reverse faults, also called thrust faults, squeeze the crust, pushing two blocks of crust on top of each other. These faults are commonly found in mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Rocky Mountains. ...
... Zone are two well-known regions where normal faults are spreading apart Earth's crust. Reverse faults, also called thrust faults, squeeze the crust, pushing two blocks of crust on top of each other. These faults are commonly found in mountain ranges such as the Himalayas and the Rocky Mountains. ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest - Ms. Murray`s Class Website
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
Earth Science Exam Review 7
... A Warm air rises, creating an area of low pressure under it. B Cool air rises, creating an area of low pressure under it. C Warm air rises, creating an area of high pressure under it. D Cool air rises, creating an area of high pressure under it. ...
... A Warm air rises, creating an area of low pressure under it. B Cool air rises, creating an area of low pressure under it. C Warm air rises, creating an area of high pressure under it. D Cool air rises, creating an area of high pressure under it. ...
Plate Tectonics
... The ideas of continental drift and seafloor spreading were tied together in the theory of plate tectonics. Main points of the theory: • Earth’s outer layer is divided into moving lithospheric plates. • The plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges, in a process called sea floor spreading. Magma rising a ...
... The ideas of continental drift and seafloor spreading were tied together in the theory of plate tectonics. Main points of the theory: • Earth’s outer layer is divided into moving lithospheric plates. • The plates move apart at mid-ocean ridges, in a process called sea floor spreading. Magma rising a ...
Document
... In the space provided, write the letter of the definition that best matches the term or phrase. ...
... In the space provided, write the letter of the definition that best matches the term or phrase. ...
holiday review packet - answer key
... Evaporation – water heats up and changes state from liquid to gas (boiling pot of water) Condensation – water cools down and changes state from gas back to liquid (morning dew) Transpiration – evaporation off of a plant/leaf Precipitation – water in vapor form (gas) in clouds gets heavy, fal ...
... Evaporation – water heats up and changes state from liquid to gas (boiling pot of water) Condensation – water cools down and changes state from gas back to liquid (morning dew) Transpiration – evaporation off of a plant/leaf Precipitation – water in vapor form (gas) in clouds gets heavy, fal ...
UNIT 3: DYNAMIC EARTH Chapter 9: Volcanoes
... located near several faults buried under large amounts of sediments. ...
... located near several faults buried under large amounts of sediments. ...
the earth´s relief - Junta de Andalucía
... THE EARTH´S RELIEF Summary 1. Inside Earth The Earth is made of many different and distinct layers. The deeper layers are composed of heavier materials, they are hotter, denser and under much greater pressure than the outer layers. ...
... THE EARTH´S RELIEF Summary 1. Inside Earth The Earth is made of many different and distinct layers. The deeper layers are composed of heavier materials, they are hotter, denser and under much greater pressure than the outer layers. ...
Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
... iron and nickel plus other heavy elements. It is theorized to be solid due to enormous pressure. ◦ The outer core is made up of the same elements. This layer is liquid and its movement is thought to produce earth’s magnetic field. ...
... iron and nickel plus other heavy elements. It is theorized to be solid due to enormous pressure. ◦ The outer core is made up of the same elements. This layer is liquid and its movement is thought to produce earth’s magnetic field. ...
Announcements
... ranges. (larger than the ones on land!) – Have a rift(tear) in the center - allows magma to flow to the surface. – Newest crust is in the center. (Igneous rock) – New crust forces old crust away from the ...
... ranges. (larger than the ones on land!) – Have a rift(tear) in the center - allows magma to flow to the surface. – Newest crust is in the center. (Igneous rock) – New crust forces old crust away from the ...
Earths History - Jefferson County School District
... Earth's crustal plates causes both 1.Mountain Building slow and rapid changes in Earth's 2. Seismic Activity surface, including volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and mountain building. Cognitive ...
... Earth's crustal plates causes both 1.Mountain Building slow and rapid changes in Earth's 2. Seismic Activity surface, including volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and mountain building. Cognitive ...
Chapter 28 Plate Tectonics Lab
... In this investigation, you will identify the tectonic plates of Earth’s lithosphere, learn which geologic features are associated with the boundaries of plates, and predict what Earth will look like in 50 million years. The theory of plate tectonics states that large pieces of Earth’s lithosphere ca ...
... In this investigation, you will identify the tectonic plates of Earth’s lithosphere, learn which geologic features are associated with the boundaries of plates, and predict what Earth will look like in 50 million years. The theory of plate tectonics states that large pieces of Earth’s lithosphere ca ...
Lab 2 Presentation slides
... rigid lithosphere, which are "floating" in isostatic equilibrium on a plastic region of earth's mantle called the asthenosphere. *Note that bottom figure is schematic and mantle lithosphere is much thicker than typical continental & oceanic crust. ...
... rigid lithosphere, which are "floating" in isostatic equilibrium on a plastic region of earth's mantle called the asthenosphere. *Note that bottom figure is schematic and mantle lithosphere is much thicker than typical continental & oceanic crust. ...
Chapter 14 PPT Lecture Notes with Blanks
... 2) 14-1 Dynamic processes move matter within the earth and on its surface, and can cause volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, erosion, and landslides. 3) The Earth Is a Dynamic Planet What is geology? o Dynamic processes taking place on earth’s surface and in earth’s interior Three major c ...
... 2) 14-1 Dynamic processes move matter within the earth and on its surface, and can cause volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, erosion, and landslides. 3) The Earth Is a Dynamic Planet What is geology? o Dynamic processes taking place on earth’s surface and in earth’s interior Three major c ...
Earthquakes
... crust that might signal an earthquake. – The ability to predict an earthquake could save thousands of lives. – http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/11898earthquakes-the-science-of-earthquake-predictionvideo.htm ...
... crust that might signal an earthquake. – The ability to predict an earthquake could save thousands of lives. – http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/11898earthquakes-the-science-of-earthquake-predictionvideo.htm ...
GCSE Geography OCR B Natural Hazards
... plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. The point inside the Earth's crust where the pressure is released is called the focus. The point above the focus, on ...
... plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. The point inside the Earth's crust where the pressure is released is called the focus. The point above the focus, on ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.