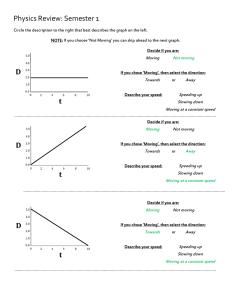
AP Projectile,circular, gravitation test (final)
... 35. A punter in a football game kicks the ball with an initial speed of 28.3 m/s at an angle of 60° with respect to the ground. The ball is in the air for a total of 5.00 s before hitting the ground. If we assume that air resistance is negligible, what would be the ball's horizontal displacement? (A ...
... 35. A punter in a football game kicks the ball with an initial speed of 28.3 m/s at an angle of 60° with respect to the ground. The ball is in the air for a total of 5.00 s before hitting the ground. If we assume that air resistance is negligible, what would be the ball's horizontal displacement? (A ...
29006_L6_M
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving with constant velocity • forces can overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) Ch ...
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving with constant velocity • forces can overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) Ch ...
Document
... the mass m of the object. a = F/m. If the mass changes over time, the more general statement of the law is F = d(mv)/dt = ma + (dm/dt)v. ...
... the mass m of the object. a = F/m. If the mass changes over time, the more general statement of the law is F = d(mv)/dt = ma + (dm/dt)v. ...
PDF#10
... the mass m of the object. a = F/m. If the mass changes over time, the more general statement of the law is F = d(mv)/dt = ma + (dm/dt)v. ...
... the mass m of the object. a = F/m. If the mass changes over time, the more general statement of the law is F = d(mv)/dt = ma + (dm/dt)v. ...
Physics 3550, Fall 2011 Newton`s Second Law
... First of all, let us deal with a common mental mistake made by beginners. It is perhaps tempting to read Newton’s second law as a literal identification of force with mass times acceleration. This is not the way to think of it. Think of it as follows. You are in the lab. You have set up an experimen ...
... First of all, let us deal with a common mental mistake made by beginners. It is perhaps tempting to read Newton’s second law as a literal identification of force with mass times acceleration. This is not the way to think of it. Think of it as follows. You are in the lab. You have set up an experimen ...
Concept of Force and Newton`s Laws of Motion Concept of
... 4. Add vector components to find vector decomposition of the total force ...
... 4. Add vector components to find vector decomposition of the total force ...
Physphax Review
... As you move charges closer, F increases: (1/2)r 4F, (1/3)r 9F, etc An electric field E = Fe/q exists around every charge q. See diagram 10. Units: [E] = [Fe]/[q] = N/C. E is a vector with direction given by the direction of the electric force Fe on positive test charge q. E = 0 inside a conducto ...
... As you move charges closer, F increases: (1/2)r 4F, (1/3)r 9F, etc An electric field E = Fe/q exists around every charge q. See diagram 10. Units: [E] = [Fe]/[q] = N/C. E is a vector with direction given by the direction of the electric force Fe on positive test charge q. E = 0 inside a conducto ...