This review is not comprehensive it covers most but not all topics
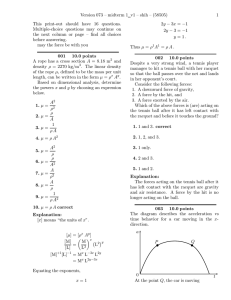
... 60. An object of mass m has E Joules of potential energy and is dropped from a height of h meters. Calculate the velocity v of the object when it hits the ground ...
... 60. An object of mass m has E Joules of potential energy and is dropped from a height of h meters. Calculate the velocity v of the object when it hits the ground ...
Physics HSC - Kotara High School
... deemed to be heretical (and possibly punished by death). Galileo was not only a thinker but also an experimenter. He, like all good scientists, was not prepared to accept someone else’s word for things that could be tested. However, since experimentation was frowned upon, he sometimes had to perform ...
... deemed to be heretical (and possibly punished by death). Galileo was not only a thinker but also an experimenter. He, like all good scientists, was not prepared to accept someone else’s word for things that could be tested. However, since experimentation was frowned upon, he sometimes had to perform ...
Conceptual Physics
... 40. Identify the relationship of different launch angles with a projectiles range (the horizontal distance traveled.) 41. What is the vertical speed of a horizontally launched projectile two seconds after it is launched? 42. Explain how a satellite orbiting the earth is actually just “falling around ...
... 40. Identify the relationship of different launch angles with a projectiles range (the horizontal distance traveled.) 41. What is the vertical speed of a horizontally launched projectile two seconds after it is launched? 42. Explain how a satellite orbiting the earth is actually just “falling around ...
Two-Dimensional Motion
... Projectile Motion “Range formula” Note that if q becomes the complement of 41o, that is, q is now 49o, then, ...
... Projectile Motion “Range formula” Note that if q becomes the complement of 41o, that is, q is now 49o, then, ...
Practice Exam
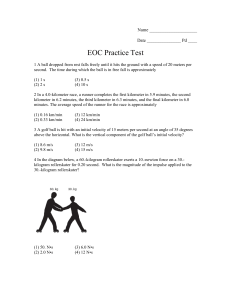
... 18 A 60.0-kilogram runner has 1920 joules of kinetic energy. At what speed is she running? (1) 5.66 m/s (3) 32.0 m/s (2) 8.00 m/s (4) 64.0 m/s 19 The diagram below shows points A, B, and C at or near Earth’s surface. As a mass is moved from A to B, 100 joules of work are done against gravity. What i ...
... 18 A 60.0-kilogram runner has 1920 joules of kinetic energy. At what speed is she running? (1) 5.66 m/s (3) 32.0 m/s (2) 8.00 m/s (4) 64.0 m/s 19 The diagram below shows points A, B, and C at or near Earth’s surface. As a mass is moved from A to B, 100 joules of work are done against gravity. What i ...
1 PY105 Uniform and Vertical Circular Motions
... Neither, both coin start to slide at the same time. ...
... Neither, both coin start to slide at the same time. ...
AP Physics 1 Circular Motion Multiple
... b. Derive an expression for v min the minimum speed the ball can have at point Z without leaving the circular path. c. The maximum tension the string can have without breaking is T max Derive an expression for v max , the maximum speed the ball can have at point Q without breaking the string. d. Sup ...
... b. Derive an expression for v min the minimum speed the ball can have at point Z without leaving the circular path. c. The maximum tension the string can have without breaking is T max Derive an expression for v max , the maximum speed the ball can have at point Q without breaking the string. d. Sup ...
Net force = 0 Net force = 0 - University of Iowa Physics
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) Æ if it is at rest, it stays at rest Æ if it is moving, it keeps moving with constant velocity • forces can overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) ...
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) Æ if it is at rest, it stays at rest Æ if it is moving, it keeps moving with constant velocity • forces can overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) ...