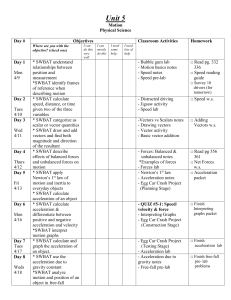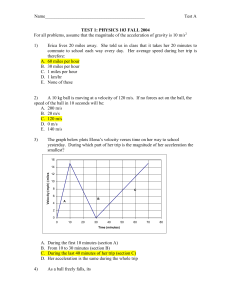
SAMPLE TEST 1: PHYSICS 103
... Two balls are rolled off a table at the same time, one with a speed of 10 m/s and the other with a speed of 50 m/s. Which of the following is true: A. The two balls hit the ground at the same time B. The ball with the greater speed reaches the ground first C. The ball with the greater speed will acc ...
... Two balls are rolled off a table at the same time, one with a speed of 10 m/s and the other with a speed of 50 m/s. Which of the following is true: A. The two balls hit the ground at the same time B. The ball with the greater speed reaches the ground first C. The ball with the greater speed will acc ...
ppt
... From this, Galileo determined that the falling time varied proportional to the square root of the falling distance. ...
... From this, Galileo determined that the falling time varied proportional to the square root of the falling distance. ...
Circular
... (c) A closed tube containing a mixture of two liquids of densities and ( > ) is attached at the end by a hinge (allowing vertical motion) to a rigid rod. If this rod, and also the tube, is rapidly rotated in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity w, compare the excess forces on a sm ...
... (c) A closed tube containing a mixture of two liquids of densities and ( > ) is attached at the end by a hinge (allowing vertical motion) to a rigid rod. If this rod, and also the tube, is rapidly rotated in a horizontal plane with an angular velocity w, compare the excess forces on a sm ...
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Rotational Motion
... • Length of the velocity vector does not change (speed stays constant), but the vector’s direction constantly changes • Since acceleration = Change in velocity, the object accelerates as it moves around the track ...
... • Length of the velocity vector does not change (speed stays constant), but the vector’s direction constantly changes • Since acceleration = Change in velocity, the object accelerates as it moves around the track ...
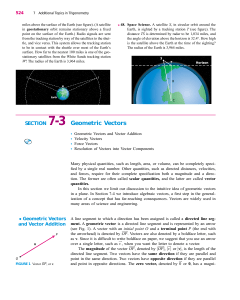
SECTION 7-3 Geometric Vectors
... tude of zero and an arbitrary direction. Two vectors are equal if they have the same magnitude and direction. Thus, a vector may be translated from one location to another as long as the magnitude and direction do not change. The sum of two vectors u and v can be defined using the tail-to-tip rule: ...
... tude of zero and an arbitrary direction. Two vectors are equal if they have the same magnitude and direction. Thus, a vector may be translated from one location to another as long as the magnitude and direction do not change. The sum of two vectors u and v can be defined using the tail-to-tip rule: ...
ICP Motion
... the right, find the net force on the melon. Astronauts in the space shuttle experience an acceleration of about 35 m/sec/sec during liftoff. What is the force on a 75 kg? A 6.0 kg object undergoes an acceleration of 2.0 m/sec/sec. What is the net force acting on it? If this same force is applied to ...
... the right, find the net force on the melon. Astronauts in the space shuttle experience an acceleration of about 35 m/sec/sec during liftoff. What is the force on a 75 kg? A 6.0 kg object undergoes an acceleration of 2.0 m/sec/sec. What is the net force acting on it? If this same force is applied to ...
Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint
... What is the speed of a sailboat that is traveling 120 meters in 60 seconds? Step 1: Decide what the problem is asking? A boat traveled 120 meters in 60 seconds. What was the speed of the boat? Step 2: What is the formula to calculate speed? Speed = Distance/Time Step 3: Solve the problem using the f ...
... What is the speed of a sailboat that is traveling 120 meters in 60 seconds? Step 1: Decide what the problem is asking? A boat traveled 120 meters in 60 seconds. What was the speed of the boat? Step 2: What is the formula to calculate speed? Speed = Distance/Time Step 3: Solve the problem using the f ...
Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
... motion of objects. • a. Determine the relationship between velocity and acceleration. Additional vocabulary: reference point, meter, speed, average speed, instantaneous speed, slope, distance, displacement • b. Demonstrate the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object in terms of gravity ...
... motion of objects. • a. Determine the relationship between velocity and acceleration. Additional vocabulary: reference point, meter, speed, average speed, instantaneous speed, slope, distance, displacement • b. Demonstrate the effect of balanced and unbalanced forces on an object in terms of gravity ...
Physics 112/111 Exam Review – Problems
... b) How much time does it take for the bicyclist to stop? (3.1 s) 70. A 10.0 kg object is accelerated horizontally from rest to a velocity of 11.0 m/s in 5.00 s by a horizontal force. How much work is done on this object assuming the object is on a frictionless surface? (605 J) 71. A student wearing ...
... b) How much time does it take for the bicyclist to stop? (3.1 s) 70. A 10.0 kg object is accelerated horizontally from rest to a velocity of 11.0 m/s in 5.00 s by a horizontal force. How much work is done on this object assuming the object is on a frictionless surface? (605 J) 71. A student wearing ...