for A Tutorial Computer
... translationally as if it were a particle mass influenced by one net force. A torque is similar to a force, except that it causes a rotational motion about a particular axis. Torques can be represented as 3D vectors describing their components about an x, y, and z-axis. Torque vectors'net action can ...
... translationally as if it were a particle mass influenced by one net force. A torque is similar to a force, except that it causes a rotational motion about a particular axis. Torques can be represented as 3D vectors describing their components about an x, y, and z-axis. Torque vectors'net action can ...
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... A) The car travels westward at constant speed. B) The car travels eastward and speeds up. C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
... A) The car travels westward at constant speed. B) The car travels eastward and speeds up. C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
Calculating Acceleration
... • Displacement is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. ...
... • Displacement is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. ...
Beyond the limits of cosmological perturbation theory: resummations
... the equations of motions are invariant under time-dependent, uniform boosts: ...
... the equations of motions are invariant under time-dependent, uniform boosts: ...
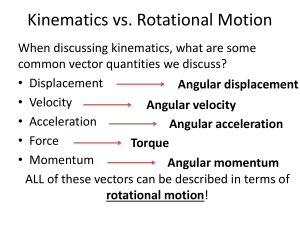
Rotational Kinematics
... Weislearned about torque earlier, but This the exact same equation that wehow can we describe it in terms of rotational motion? How did learned before, but now we see how it we writeallthe versionsones! for ALL the matches therotational other rotational kinematic equations??? t = rF ...
... Weislearned about torque earlier, but This the exact same equation that wehow can we describe it in terms of rotational motion? How did learned before, but now we see how it we writeallthe versionsones! for ALL the matches therotational other rotational kinematic equations??? t = rF ...
North Carolina Test of Physics - North Carolina Public Schools
... © 2009 All rights reserved. This document may not be reproduced by any means, in whole or in part, without prior written permission from the North Carolina Department of Public Instruction, Raleigh, North Carolina. ...
... © 2009 All rights reserved. This document may not be reproduced by any means, in whole or in part, without prior written permission from the North Carolina Department of Public Instruction, Raleigh, North Carolina. ...
Unit 2 - Angelfire
... says that if he throws his jello with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. With whom do you agree? Why? ...
... says that if he throws his jello with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. With whom do you agree? Why? ...
Acceleration - Cloudfront.net
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...
... • Displacement: is the distance and direction of an object's change in position from the starting point. • Average speed: is the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel. • Speed: is the distance an object travels per unit of time. ...