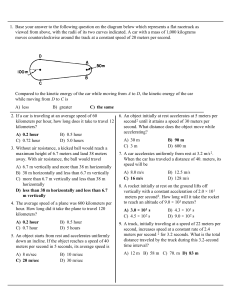
Pushes and Pulls Content 3. Daily examples of force
... • There are some disadvantages of friction. For example, in the movable parts of machines, energy is wasted as sound and heat to overcome friction. Friction will also cause the wear in gears. ...
... • There are some disadvantages of friction. For example, in the movable parts of machines, energy is wasted as sound and heat to overcome friction. Friction will also cause the wear in gears. ...
Luis Anchordoqui
... The astronaut's mass is 60 kg and the panel's mass is 80 kg. Both the astronaut and the panel initially are at rest relative to the telescope. The astronaut then gives a panel a shove. After the shove it is moving at 0.3 m/s relative to the telescope. What is her subsequent velocity relative to the ...
... The astronaut's mass is 60 kg and the panel's mass is 80 kg. Both the astronaut and the panel initially are at rest relative to the telescope. The astronaut then gives a panel a shove. After the shove it is moving at 0.3 m/s relative to the telescope. What is her subsequent velocity relative to the ...
Physics 430
... So we see that the (x, y) part of the trajectory is a circle that may be offset from our coordinate system. However, choosing our coordinate system origin to be the center of the circle, we simply have: x x iy Ceiwt Note, however, that the position at t = 0 is not zero, but rather is x (0) ...
... So we see that the (x, y) part of the trajectory is a circle that may be offset from our coordinate system. However, choosing our coordinate system origin to be the center of the circle, we simply have: x x iy Ceiwt Note, however, that the position at t = 0 is not zero, but rather is x (0) ...
Physics - Oak Park Unified School District
... 2. change in time: t = t – to (s) (usually to = 0 t = t) 3. velocity (speed): vav = d/t (m/s) 4. acceleration: a = (vt – vo)/t (m/s2) a. instantaneous velocity, vt, is velocity at time, t special case: if vo = 0, then vt = 2vav b. falling objects 1. all objects fall with the same constant accele ...
... 2. change in time: t = t – to (s) (usually to = 0 t = t) 3. velocity (speed): vav = d/t (m/s) 4. acceleration: a = (vt – vo)/t (m/s2) a. instantaneous velocity, vt, is velocity at time, t special case: if vo = 0, then vt = 2vav b. falling objects 1. all objects fall with the same constant accele ...
tri-quarterly practice answers
... C) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 10-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 5-N ball. D) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 5-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 10-N ball. 27. A bicycle and its rider have a combined mass of 80. kilograms and a speed of 6.0 meters pe ...
... C) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 10-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 5-N ball. D) At the end of 3 seconds of free-fall, the 5-N ball will have a greater momentum than the 10-N ball. 27. A bicycle and its rider have a combined mass of 80. kilograms and a speed of 6.0 meters pe ...
ppt
... Projectile motion is two-dimensional, but it does not repeat. Projectiles do not move all along their trajectories more than once. Periodic motion can also be an example of 2 dimensional motion however it involves motion that repeats itself at regular intervals. Examples of periodic motion are a yo- ...
... Projectile motion is two-dimensional, but it does not repeat. Projectiles do not move all along their trajectories more than once. Periodic motion can also be an example of 2 dimensional motion however it involves motion that repeats itself at regular intervals. Examples of periodic motion are a yo- ...
Jeopardy
... What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion? When the hammer strikes the nail, the nail exerts equal but opposite force on the ...
... What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion? When the hammer strikes the nail, the nail exerts equal but opposite force on the ...
High School - cloudfront.net
... direction of motion from up to down or vice versa, the velocity must equal zero at some point. Typically on a rollercoaster, this occurs at the top and bottom of hills. 3. Where does The Intimidator have a vertical velocity of zero? _______________________________________________________ ...
... direction of motion from up to down or vice versa, the velocity must equal zero at some point. Typically on a rollercoaster, this occurs at the top and bottom of hills. 3. Where does The Intimidator have a vertical velocity of zero? _______________________________________________________ ...
Circular Motion
... Things to remember about UCM: • UCM is circular motion at a constant speed. • The only acceleration there is will be centripetal acceleration. • The centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of the circle. ALWAYS! • Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net for ...
... Things to remember about UCM: • UCM is circular motion at a constant speed. • The only acceleration there is will be centripetal acceleration. • The centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of the circle. ALWAYS! • Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net for ...