Velocity - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
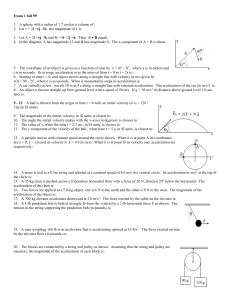
... The average speed is defined as the distance traveled divided by the time the trip took: Average speed = distance / elapsed time Is the average speed of the red car 40.0 mi/h, more than 40.0 mi/h, or less than 40.0 mi/h? ...
... The average speed is defined as the distance traveled divided by the time the trip took: Average speed = distance / elapsed time Is the average speed of the red car 40.0 mi/h, more than 40.0 mi/h, or less than 40.0 mi/h? ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant Acceleration
... Learning Objective : 1. To look at Newton’s Laws of Motions and to connect all recent work to them. 2. To understand terminal velocity ...
... Learning Objective : 1. To look at Newton’s Laws of Motions and to connect all recent work to them. 2. To understand terminal velocity ...
If the displacement of an object, x, is related to
... Since 1983 the standard meter has been defined in terms of which of the following? a. specific alloy bar housed at Sevres, France b. wavelength of light emitted by krypton-86 c. distance from the Earth's equator to the north pole d. the distance light travels in 1/(3 x 108) second ...
... Since 1983 the standard meter has been defined in terms of which of the following? a. specific alloy bar housed at Sevres, France b. wavelength of light emitted by krypton-86 c. distance from the Earth's equator to the north pole d. the distance light travels in 1/(3 x 108) second ...
Lecture Notes: Chapter 2 Motion
... Q: Frame of reference picture: Using the picture on this slide what would you use as your frame of reference? ...
... Q: Frame of reference picture: Using the picture on this slide what would you use as your frame of reference? ...
Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Motion Graphs, Energy and Work
... (TEKS 6.9C) Demonstrate energy transformations such as energy in a flashlight battery changing to light (radiant) energy. 9. What are the seven types of energy? 10. What are energy transformations? 11. What are the energy transformations that occur when using a battery in a flashlight? 12. Where doe ...
... (TEKS 6.9C) Demonstrate energy transformations such as energy in a flashlight battery changing to light (radiant) energy. 9. What are the seven types of energy? 10. What are energy transformations? 11. What are the energy transformations that occur when using a battery in a flashlight? 12. Where doe ...
waves
... moving in a straight line at a constant speed of 2 m/s. Which of the following must the 250 g toy car have in order to maintain the same momentum as the cart? F An acceleration of 5 m/s2 for 2 seconds G A potential energy of 20 J H A constant velocity of 4 m/s J An applied force of 5 N for 5 seconds ...
... moving in a straight line at a constant speed of 2 m/s. Which of the following must the 250 g toy car have in order to maintain the same momentum as the cart? F An acceleration of 5 m/s2 for 2 seconds G A potential energy of 20 J H A constant velocity of 4 m/s J An applied force of 5 N for 5 seconds ...
Ch. 7 Forces and Motion in Two Dimensions
... • Same magnitude as the resultant force but opposite in direction ...
... • Same magnitude as the resultant force but opposite in direction ...
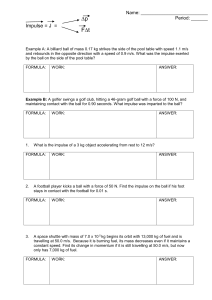
Worksheet 9 - Impulse
... A space shuttle with mass of 7.0 x 10 5 kg begins its orbit with 13,000 kg of fuel and is travelling at 50.0 m/s. Because it is burning fuel, its mass decreases even if it maintains a constant speed. Find its change in momentum if it is still travelling at 50.0 m/s, but now only has 7,000 kg of fuel ...
... A space shuttle with mass of 7.0 x 10 5 kg begins its orbit with 13,000 kg of fuel and is travelling at 50.0 m/s. Because it is burning fuel, its mass decreases even if it maintains a constant speed. Find its change in momentum if it is still travelling at 50.0 m/s, but now only has 7,000 kg of fuel ...
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference Kinematics
... electric field E, will feel a force on it, given by this formula (q is sometimes called a “test” charge, since it tests the electric field strength). This formula gives the electric field due to a charge q at a distance r from the charge. Unlike the “test” charge, the charge q here is actually gener ...
... electric field E, will feel a force on it, given by this formula (q is sometimes called a “test” charge, since it tests the electric field strength). This formula gives the electric field due to a charge q at a distance r from the charge. Unlike the “test” charge, the charge q here is actually gener ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average speed: __________________________________________ ...
... 20. What is the formula for speed: ______________________________________________________ Be able to calculate average speed: 21. What is average speed? _____________________________________________________________ 22. What is the formula for average speed: __________________________________________ ...