“Who Wants To Be A Millionaire?” Inertia Style Created by Claire
... more inertia than others? A)Because they are stronger B)Because they are further away from gravity C)Because they have more mass D)Because they are favorites The answer is C. ...
... more inertia than others? A)Because they are stronger B)Because they are further away from gravity C)Because they have more mass D)Because they are favorites The answer is C. ...
Physics 130 - UND: University of North Dakota
... HW 10/9 “Skidding Objects” due Friday 10/11 Exam 2 Thursday, 10/17 5-7 Wit 116 6-8 Wit 114 (only if needed) Please send email if other time needed ...
... HW 10/9 “Skidding Objects” due Friday 10/11 Exam 2 Thursday, 10/17 5-7 Wit 116 6-8 Wit 114 (only if needed) Please send email if other time needed ...
3rd quarter study guide
... a. a bird taking off for flight b. a baseball released by a pitcher c. a bike approaching a stop sign d. an airplane following a straight flight ...
... a. a bird taking off for flight b. a baseball released by a pitcher c. a bike approaching a stop sign d. an airplane following a straight flight ...
Objects in Motion
... Question – Make an educated guess- a hypothesis to answer the question. Predict – Consequences that can be observed if hypothesis is correct. Test Predictions – Conduct experiments and make observations to see if predicted consequences are present. Draw a Conclusion – The acceptance, modification, o ...
... Question – Make an educated guess- a hypothesis to answer the question. Predict – Consequences that can be observed if hypothesis is correct. Test Predictions – Conduct experiments and make observations to see if predicted consequences are present. Draw a Conclusion – The acceptance, modification, o ...
Speed - TGHSLevel1Science
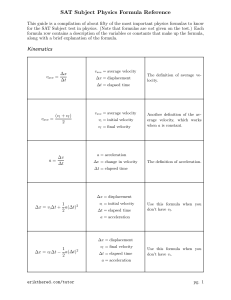
... 1. A cyclist travels 50km in 1.5 hours. Calculate her velocity. 2. An athlete records a time of 64s for a 400m race. What speed was he running at? 3. An Otago student takes 2.5 hours to return to Dunedin from Timaru (190km), with a short stop at Hampden from fish and chips. What was her average velo ...
... 1. A cyclist travels 50km in 1.5 hours. Calculate her velocity. 2. An athlete records a time of 64s for a 400m race. What speed was he running at? 3. An Otago student takes 2.5 hours to return to Dunedin from Timaru (190km), with a short stop at Hampden from fish and chips. What was her average velo ...
Study Guide - Motion Name Key Date Pd 1. An object is in ___
... 27. A golf ball and a bowling ball are moving at the same velocity. Which of the two has more momentum? Why? The bowling ball has more momentum because momentum is mass x velocity and the mass of the bowling ball is greater. 28. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. Balance ...
... 27. A golf ball and a bowling ball are moving at the same velocity. Which of the two has more momentum? Why? The bowling ball has more momentum because momentum is mass x velocity and the mass of the bowling ball is greater. 28. Explain the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces. Balance ...
Name: Date: Period: Physics Semester 1 Practice Problems 1. A car
... 10. Calculate the velocity of a mountain climber if that climber is moving northeast at a pace of 1.6 km in 1.4 hours? Give your answer in the SI unit for velocity. ...
... 10. Calculate the velocity of a mountain climber if that climber is moving northeast at a pace of 1.6 km in 1.4 hours? Give your answer in the SI unit for velocity. ...
Impulse Momentum (Problem and Solutions) 1. An object travels
... Impulse Momentum (Problem and Solutions) 1. An object travels with a velocity 4m/s to the east. Then, its direction of motion and magnitude of velocity are changed. Picture given below shows the directions and magnitudes of velocities. Find the impulse given to this object. ...
... Impulse Momentum (Problem and Solutions) 1. An object travels with a velocity 4m/s to the east. Then, its direction of motion and magnitude of velocity are changed. Picture given below shows the directions and magnitudes of velocities. Find the impulse given to this object. ...
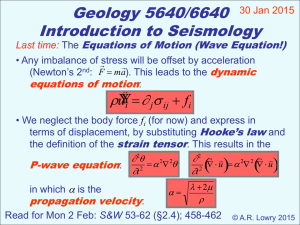
lecture2 - WordPress.com
... The bullet of mass m is given a velocity due to gas pressure caused by the burning of powder within the chamber of the gun. Assuming this pressure creates a force of F = F0sin(πt / t0) on the bullet, determine the velocity of the bullet at any instant it is in the barrel. What is the bullet’s maximu ...
... The bullet of mass m is given a velocity due to gas pressure caused by the burning of powder within the chamber of the gun. Assuming this pressure creates a force of F = F0sin(πt / t0) on the bullet, determine the velocity of the bullet at any instant it is in the barrel. What is the bullet’s maximu ...
Freefall
... • Does its velocity change by regular amounts each second that it’s falling? If yes, why; if no, why not? • Yes, changes by ten for every second the object falls • Is the distance it falls per second the same amount each second? Explain why. • No, as it falls it gets faster so for every second it fa ...
... • Does its velocity change by regular amounts each second that it’s falling? If yes, why; if no, why not? • Yes, changes by ten for every second the object falls • Is the distance it falls per second the same amount each second? Explain why. • No, as it falls it gets faster so for every second it fa ...