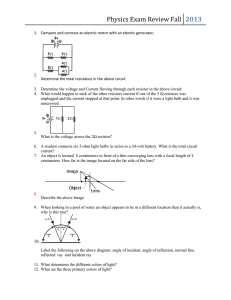
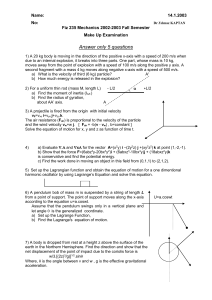
1. A body of mass m moves along the x
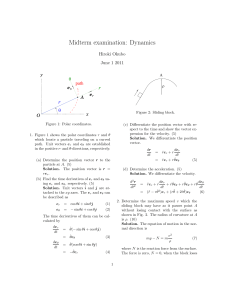
... A body of mass m moves along the x-axis subject to a potential V (x). Show that the period τ of small oscillations about a stable equilibrium point x0 , is given by r m ...
... A body of mass m moves along the x-axis subject to a potential V (x). Show that the period τ of small oscillations about a stable equilibrium point x0 , is given by r m ...
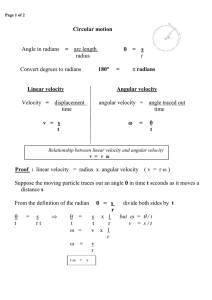
Speed
... time: s (second) acceleration: m/s/s or m/s2 Speed is the rate at which an object moves. Average speed = total distance total time Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. The rate of change of an object’s position. Constant velocity: an object’s velocity is constant only if its s ...
... time: s (second) acceleration: m/s/s or m/s2 Speed is the rate at which an object moves. Average speed = total distance total time Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. The rate of change of an object’s position. Constant velocity: an object’s velocity is constant only if its s ...
Magic Square Vocabulary Game Combinations
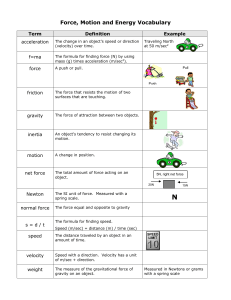
... Clue 1. Forces always act in equal but opposite pairs 2. A push or a pull 3. Distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance. 4. An object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed Unless acted upon by a force. 5. The change in velocity divided by the tim ...
... Clue 1. Forces always act in equal but opposite pairs 2. A push or a pull 3. Distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel the distance. 4. An object will remain at rest or move in a straight line with constant speed Unless acted upon by a force. 5. The change in velocity divided by the tim ...
Motion Dukes oHazzard 08t
... Velocity vector• a pictorial representation of velocity • An arrow that shows the direction of travel • Length of the arrow shows the speed of object ...
... Velocity vector• a pictorial representation of velocity • An arrow that shows the direction of travel • Length of the arrow shows the speed of object ...
advanced placement chemistry
... the maximum acceleration that Tom Cruise and the documents can experience without the cable breaking? 1) Draw a free-body diagram with all forces; 2) write a force balance; 3) Substitute and Solve for F net; 4) Find anet. 5) Tom has 6 seconds to get out of the room and be raised 50 meters starting f ...
... the maximum acceleration that Tom Cruise and the documents can experience without the cable breaking? 1) Draw a free-body diagram with all forces; 2) write a force balance; 3) Substitute and Solve for F net; 4) Find anet. 5) Tom has 6 seconds to get out of the room and be raised 50 meters starting f ...
Examples of Vectors 1. Velocity of Car on Race Track 2. Force Du
... Examples of Vectors 1. Velocity of Car on Race Track ...
... Examples of Vectors 1. Velocity of Car on Race Track ...
1 - FreeScienceStuff.com
... A Inertia B Friction C Gravity D A net force 8. In a head-on car crash, passengers not wearing seat belts continue to move forward with the same ___________ that the car had prior to impact. ...
... A Inertia B Friction C Gravity D A net force 8. In a head-on car crash, passengers not wearing seat belts continue to move forward with the same ___________ that the car had prior to impact. ...
PHYS 243, Exam 1
... _______7. When a wind blows towards the east, a plane heading due north winds up travelling 10 degrees east of north due to the wind. The wind speed divided by the plane’s air speed (speed relative to the air) is therefore given by the _______ of 10 degrees. (a) sine (b) cosine (c) tangent (d) cotan ...
... _______7. When a wind blows towards the east, a plane heading due north winds up travelling 10 degrees east of north due to the wind. The wind speed divided by the plane’s air speed (speed relative to the air) is therefore given by the _______ of 10 degrees. (a) sine (b) cosine (c) tangent (d) cotan ...