Lecture 1 - GEOCITIES.ws
... as input the initial location, mass, and velocity of the sun, each of the planets and their moons, and some set of asteroids and comets. The program should then simulate the specified solar system in action by repeatedly computing the next position of each of the specified bodies over a period rangi ...
... as input the initial location, mass, and velocity of the sun, each of the planets and their moons, and some set of asteroids and comets. The program should then simulate the specified solar system in action by repeatedly computing the next position of each of the specified bodies over a period rangi ...
Λ - Piazza
... Things You can do with a Physics System • Detect collisions between dynamic objects and static world geometry • Simulate free rigid bodies under the influence of gravity and other forces • Spring-mass systems • Destructible buildings and structures • Ray and shape casts (to determine line of sight, ...
... Things You can do with a Physics System • Detect collisions between dynamic objects and static world geometry • Simulate free rigid bodies under the influence of gravity and other forces • Spring-mass systems • Destructible buildings and structures • Ray and shape casts (to determine line of sight, ...
Color
... Q: Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? A: Moving toward the pivot reduces rotational mass Lever arm is a vector from p pivot to rider Gravitation torque is proportional to lever arm Rotational mass is proportional to lever arm2 Angular acceleration is proportional to 1/lever arm ...
... Q: Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? A: Moving toward the pivot reduces rotational mass Lever arm is a vector from p pivot to rider Gravitation torque is proportional to lever arm Rotational mass is proportional to lever arm2 Angular acceleration is proportional to 1/lever arm ...
Chapter 15
... Drag increases approximately with the square of velocity when relative velocity is low. According to this law, if cyclists double their speed and other factors remain constant, the drag force opposing them increases fourfold. ...
... Drag increases approximately with the square of velocity when relative velocity is low. According to this law, if cyclists double their speed and other factors remain constant, the drag force opposing them increases fourfold. ...
Angular Momentum about Center of Mass
... are proportional to the mass of the spinning wheel, so they cancel form both sides of the torque equation and thus the precessional angular speed is independent of mass. ...
... are proportional to the mass of the spinning wheel, so they cancel form both sides of the torque equation and thus the precessional angular speed is independent of mass. ...
Numerical study of the unsteady aerodynamics of freely falling plates
... developed gas-kinetic scheme, in which the governing Navier-Stokes equations are solved on a moving grid. In the computations that follow, the grid will be fixed to the falling plate and so the motion of the grid itself will be determined by the translational and rotational motion of the plate. Simi ...
... developed gas-kinetic scheme, in which the governing Navier-Stokes equations are solved on a moving grid. In the computations that follow, the grid will be fixed to the falling plate and so the motion of the grid itself will be determined by the translational and rotational motion of the plate. Simi ...
611: Electromagnetic Theory II
... The derivation of the Lorentz transformation follows from Einstein’s two postulates: • The laws of physics are the same for all inertial observers. • The speed of light is the same for all inertial observers. To derive the Lorentz transformation, let us suppose that we have two inertial frames S and ...
... The derivation of the Lorentz transformation follows from Einstein’s two postulates: • The laws of physics are the same for all inertial observers. • The speed of light is the same for all inertial observers. To derive the Lorentz transformation, let us suppose that we have two inertial frames S and ...
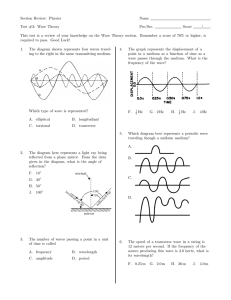
Chapter 11 Test
... A. changes direction. C. speeds up. B. is stationary. D. slows down. 2. A tug-of-war that results in one team pulling the other across the line is an example of A. action forces. C. balanced forces. B. reaction forces. D. unbalanced forces. 3. Speeding up, slowing down, and changing direction is bes ...
... A. changes direction. C. speeds up. B. is stationary. D. slows down. 2. A tug-of-war that results in one team pulling the other across the line is an example of A. action forces. C. balanced forces. B. reaction forces. D. unbalanced forces. 3. Speeding up, slowing down, and changing direction is bes ...
Lab Manual 2005
... → in the Position box that appears click on “rot” to turn it off. This measurement is not required since our object has no rotation. → We are now able to run the simulation and track the path taken. → click RUN (note: the RUN button will change to a STOP button once started) → after approximately 2. ...
... → in the Position box that appears click on “rot” to turn it off. This measurement is not required since our object has no rotation. → We are now able to run the simulation and track the path taken. → click RUN (note: the RUN button will change to a STOP button once started) → after approximately 2. ...
Document
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
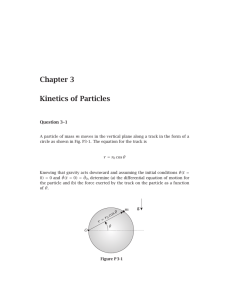
07-1 Note 07 Impulse and Momentum ∑ = ∑ =
... The second line follows if m is constant.3 T h u s the resultant force on an object (system) equals the time rate of change of linear momentum of the object (system). The definition of linear momentum enables us to put the second law into a more general powerful form. If, in addition, the system is ...
... The second line follows if m is constant.3 T h u s the resultant force on an object (system) equals the time rate of change of linear momentum of the object (system). The definition of linear momentum enables us to put the second law into a more general powerful form. If, in addition, the system is ...