Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... W ithout breaking any laws (not speeding), what is the shortest time you can make it to the stop sign? Draw a velocity vs. time graph that clearly shows your motion from one stop sign to the other. 1 mile = 1609 m ...
... W ithout breaking any laws (not speeding), what is the shortest time you can make it to the stop sign? Draw a velocity vs. time graph that clearly shows your motion from one stop sign to the other. 1 mile = 1609 m ...
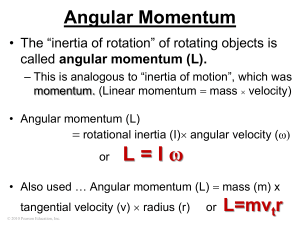
Angular Momentum
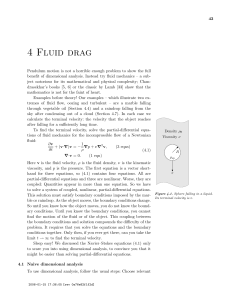
... Angular Momentum • The “inertia of rotation” of rotating objects is called angular momentum (L). – This is analogous to “inertia of motion”, which was momentum. (Linear momentum mass velocity) • Angular momentum (L) rotational inertia (I) angular velocity (ω) or ...
... Angular Momentum • The “inertia of rotation” of rotating objects is called angular momentum (L). – This is analogous to “inertia of motion”, which was momentum. (Linear momentum mass velocity) • Angular momentum (L) rotational inertia (I) angular velocity (ω) or ...
AH (Circular Motion)
... 35) A length of twine will break when a force greater than 56 N is applied to it. (a) If the twine is used to twirl a mass in a horizontal circle, what will be the maximum value of centripetal force it will withstand without snapping? (b) If the twine is used to twirl a 0.15 kg mass in a horizontal ...
... 35) A length of twine will break when a force greater than 56 N is applied to it. (a) If the twine is used to twirl a mass in a horizontal circle, what will be the maximum value of centripetal force it will withstand without snapping? (b) If the twine is used to twirl a 0.15 kg mass in a horizontal ...
Momentum
... velocity) defines momentum? • From the definition of momentum, it becomes obvious that an object has a large momentum if either its mass or its velocity is large. Both variables are of equal importance in determining the momentum of an object. Consider a Mack truck and a roller skate moving down the ...
... velocity) defines momentum? • From the definition of momentum, it becomes obvious that an object has a large momentum if either its mass or its velocity is large. Both variables are of equal importance in determining the momentum of an object. Consider a Mack truck and a roller skate moving down the ...
text - Department of Physics
... The problem isn’t that python is ignorant of basic trigonometry, but rather that these functions are hidden until you import them. In this class, we will almost exclusively be using functions that are exported by the visual module, which you can access by typing: 3 There will always be another windo ...
... The problem isn’t that python is ignorant of basic trigonometry, but rather that these functions are hidden until you import them. In this class, we will almost exclusively be using functions that are exported by the visual module, which you can access by typing: 3 There will always be another windo ...
ch08_LecturePPT
... A student sits on a stool holding a bicycle wheel with a rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What ...
... A student sits on a stool holding a bicycle wheel with a rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What ...
Momentum Momentum
... and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and teachers. These materials may not be used for any commercial purpose without the written permission of the owners. NJCTL maintains its website for the convenience of teachers who wish to make their work available to other teachers, participa ...
... and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and teachers. These materials may not be used for any commercial purpose without the written permission of the owners. NJCTL maintains its website for the convenience of teachers who wish to make their work available to other teachers, participa ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 15 Thermodynamics
... A student sits on a stool holding a bicycle wheel with a rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What ...
... A student sits on a stool holding a bicycle wheel with a rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What ...
6 ppt Momentum and Collisions
... faster than when going slower. An object that is heavier but traveling at the same speed as another, will have more momentum. Light objects traveling at great speeds can have a lot of momentum like hailstones! ...
... faster than when going slower. An object that is heavier but traveling at the same speed as another, will have more momentum. Light objects traveling at great speeds can have a lot of momentum like hailstones! ...
ch13
... and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflection of the spring velocity at the final ...
... and is held by cables so that it is initially • Apply the principle of work and energy for the rebound of the package. The compressed 120 mm. The package has a only unknown in the relation is the velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown and the maximum deflection of the spring velocity at the final ...
Physical Science - Iredell
... happening to an object in terms of velocity and acceleration. I will explain how momentum is affected if I change the mass or speed of an object. I will find everyday examples of how force and momentum are related (in sports, news, etc). I will understand the units of measure for acceleration and ve ...
... happening to an object in terms of velocity and acceleration. I will explain how momentum is affected if I change the mass or speed of an object. I will find everyday examples of how force and momentum are related (in sports, news, etc). I will understand the units of measure for acceleration and ve ...