Chapter 11 Clickers
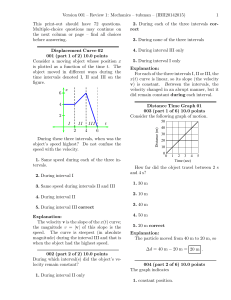
... 11.11.6. Joe has volunteered to help out in his physics class by sitting on a stool that easily rotates. Joe holds the dumbbells out as shown as the stool rotates. Then, Joe drops both dumbbells. Then, the angular momentum of Joe and the stool change, but the angular velocity does not change. Which ...
... 11.11.6. Joe has volunteered to help out in his physics class by sitting on a stool that easily rotates. Joe holds the dumbbells out as shown as the stool rotates. Then, Joe drops both dumbbells. Then, the angular momentum of Joe and the stool change, but the angular velocity does not change. Which ...
Projectile Motion
... constant speed. If not acted upon by an unbalanced force, "an object in motion will ...". This is Newton's law of inertia. ...
... constant speed. If not acted upon by an unbalanced force, "an object in motion will ...". This is Newton's law of inertia. ...
Vectors - Light and Matter
... is good for handwritten equations, but is unattractive in a printed book, so books use boldface, F, to represent vectors. After this point, I’ll use boldface for vectors throughout this book. Quantities can be classified as vectors or scalars. In a phrase like “a to the northeast,” it makes sense to ...
... is good for handwritten equations, but is unattractive in a printed book, so books use boldface, F, to represent vectors. After this point, I’ll use boldface for vectors throughout this book. Quantities can be classified as vectors or scalars. In a phrase like “a to the northeast,” it makes sense to ...
8. Rotatory Motion
... A uniform circular disc of radius R lies in the X-Y plane with its centre coinciding with the origin of the coordinate system. Its moment of inertia about an axis, lying in the X-Y plane, parallel to the X-axis and passing through a point on the Y-axis at a distance y=2R is I1. Its moment of inertia ...
... A uniform circular disc of radius R lies in the X-Y plane with its centre coinciding with the origin of the coordinate system. Its moment of inertia about an axis, lying in the X-Y plane, parallel to the X-axis and passing through a point on the Y-axis at a distance y=2R is I1. Its moment of inertia ...
Vibrating Rays Theory arXiv:1407.5001v8
... of the light. It is also important to note that measurements involving moving images produce different results than those produced by mobile sources. Therefore, to ensure the independence of the speed of light with the source, it is mandatory to have two sources with different movements. The experie ...
... of the light. It is also important to note that measurements involving moving images produce different results than those produced by mobile sources. Therefore, to ensure the independence of the speed of light with the source, it is mandatory to have two sources with different movements. The experie ...
circular motion
... (A) The resultant force on the particle must be towards the centre. (B) The resultant force may be towards the centre. (C) The direction of the angular acceleration and the angular velocity must be the same. (D) The cross product of the tangential acceleration and the angular velocity will be zero. ...
... (A) The resultant force on the particle must be towards the centre. (B) The resultant force may be towards the centre. (C) The direction of the angular acceleration and the angular velocity must be the same. (D) The cross product of the tangential acceleration and the angular velocity will be zero. ...