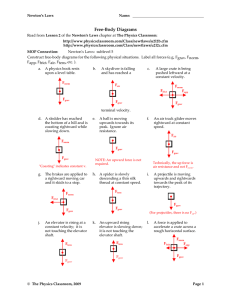
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 5. Multiply or divide as indicated using significant digits correctly. A. (9 x 105 m)(3.27 x 107 m) B. (1.48 x 10-2 km)(3.5 x 10-5 km) C. (2.76 x 104 kg) / (8.42 x 103 m) D. (6.21 x 10-1 m) / (3.52 x 102 s) 6. Add or subtract as indicated and state the answer with the correct number of significant f ...
... 5. Multiply or divide as indicated using significant digits correctly. A. (9 x 105 m)(3.27 x 107 m) B. (1.48 x 10-2 km)(3.5 x 10-5 km) C. (2.76 x 104 kg) / (8.42 x 103 m) D. (6.21 x 10-1 m) / (3.52 x 102 s) 6. Add or subtract as indicated and state the answer with the correct number of significant f ...
ACCELERATION WORD PROBLEMS
... 2. An airplane flying at a velocity of 610 m/s lands and comes to a complete stop over a 53 second period of time. a. Did this airplane speed up or slow down? b. Should your answer be positive or negative? Explain your reasoning. ...
... 2. An airplane flying at a velocity of 610 m/s lands and comes to a complete stop over a 53 second period of time. a. Did this airplane speed up or slow down? b. Should your answer be positive or negative? Explain your reasoning. ...
Ex. 1 - Mr. Schroeder
... unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s first law is called the LAW OF INERTIA. The tendency of matter to continue in its current state of motion (whether it is moving or at rest) is called inertia. When moving difficult to stop When stationary difficult to push ...
... unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s first law is called the LAW OF INERTIA. The tendency of matter to continue in its current state of motion (whether it is moving or at rest) is called inertia. When moving difficult to stop When stationary difficult to push ...
May 2008
... A particle of mass m has a velocity v relative to the Earth as it traverses the solar system at the orbital radius of the Earth around the Sun. The initial velocity v is the value far enough outside the gravitational well of Earth that the Earth’s gravitational effects need to be accounted for in wh ...
... A particle of mass m has a velocity v relative to the Earth as it traverses the solar system at the orbital radius of the Earth around the Sun. The initial velocity v is the value far enough outside the gravitational well of Earth that the Earth’s gravitational effects need to be accounted for in wh ...
Name Date
... Also, vi is the initial velocity for a time step and si is the initial position for a time step. If we let the time step be a real number t rather than a tiny infinitesimal quantity dt, then we have changed a differential equation into a finite difference equation. This is Euler’s method. It uses t ...
... Also, vi is the initial velocity for a time step and si is the initial position for a time step. If we let the time step be a real number t rather than a tiny infinitesimal quantity dt, then we have changed a differential equation into a finite difference equation. This is Euler’s method. It uses t ...
2007-08 Test 1 - Physics and Engineering Physics
... A friction force is… (A) a contact force that acts parallel to the contact surfaces. (B) a contact force that acts perpendicular to the contact surfaces. (C) a scalar quantity since it can act in any direction along a surface. (D) always proportional to the weight of an object. (E) always equal to t ...
... A friction force is… (A) a contact force that acts parallel to the contact surfaces. (B) a contact force that acts perpendicular to the contact surfaces. (C) a scalar quantity since it can act in any direction along a surface. (D) always proportional to the weight of an object. (E) always equal to t ...
Two objects are acted on by equal forces for equal times
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
... Part A-Multiple Choice. 4 points each. Choose the best answer and write it on the line to the left of the question number. ________1. Two ice hockey pucks collide on a frictionless surface. In considering conservation of momentum of the two-puck system, we would break the total momentum into x and ...
AP-1 Cutnell 00-05 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... incline. This block is connected to block 2 (m2 = 22.0 kg) by a cord that passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of each block and the tension in the ...
... incline. This block is connected to block 2 (m2 = 22.0 kg) by a cord that passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. Find the acceleration of each block and the tension in the ...