Forces and Motion
... • Velocity is how fast an object is moving in one direction. • Velocity = • V=d/t so • T = d/v • On Earth gravity causes objects to fall at 9.8 m/s2 • Notice that an objects mass has little to do with its rate of fall in this example. • However, an objects mass has a lot to do with how quickly an ob ...
... • Velocity is how fast an object is moving in one direction. • Velocity = • V=d/t so • T = d/v • On Earth gravity causes objects to fall at 9.8 m/s2 • Notice that an objects mass has little to do with its rate of fall in this example. • However, an objects mass has a lot to do with how quickly an ob ...
Document
... resistance is _______ so he _______ downwards. 2) As his speed increases his air resistance will _______ 3) Eventually the air resistance will be big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - this is ...
... resistance is _______ so he _______ downwards. 2) As his speed increases his air resistance will _______ 3) Eventually the air resistance will be big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - this is ...
Physics Final Exam Review Packet
... If my velocity is positive and my acceleration is negative, am I speeding up or slowing down? ...
... If my velocity is positive and my acceleration is negative, am I speeding up or slowing down? ...
1 - Net Start Class
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
... representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) ...
Document
... a. This is an impulse problem where we have to drain away the momentum of the astronaut by applying an impulse. The change in momentum we need is p m v , and the working relation is F t p . Solve for t . ...
... a. This is an impulse problem where we have to drain away the momentum of the astronaut by applying an impulse. The change in momentum we need is p m v , and the working relation is F t p . Solve for t . ...
Ch. 8. Energy
... 16. What is the ground speed of a plane which is traveling at 80 km/h, if it encounters (a) tailwind of 10 km/h (b) headwind of 15 km/h (c) 60 km/h wind at right angles to it (a) 80 + 10 = 90 km/h (b) 80 – 15 = 65 km/h (c) (602 + 802)1/2 = 100 km/h 17. What are the horizontal and vertical forces act ...
... 16. What is the ground speed of a plane which is traveling at 80 km/h, if it encounters (a) tailwind of 10 km/h (b) headwind of 15 km/h (c) 60 km/h wind at right angles to it (a) 80 + 10 = 90 km/h (b) 80 – 15 = 65 km/h (c) (602 + 802)1/2 = 100 km/h 17. What are the horizontal and vertical forces act ...
Measuring Motion
... O Velocities can be added or subtracted together to give a resultant velocity. O Add velocities that are in the same direction. O Ex: Walking on a bus as the bus is moving forward. ...
... O Velocities can be added or subtracted together to give a resultant velocity. O Add velocities that are in the same direction. O Ex: Walking on a bus as the bus is moving forward. ...
Exam 1
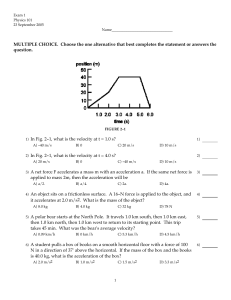
... C) The car is decelerating, and its acceleration is positive. D) A statement cannot be made using the information given. ...
... C) The car is decelerating, and its acceleration is positive. D) A statement cannot be made using the information given. ...
Motion, Forces, and Simple Machines
... States: An object at rest stays at rest unless an unbalanced force acts on it. *An object moving in a straight line at constant speed will continue doing that unless acted on by a force. This force is called friction. It is a force that resists motion between 2 surfaces that are in contact. It alway ...
... States: An object at rest stays at rest unless an unbalanced force acts on it. *An object moving in a straight line at constant speed will continue doing that unless acted on by a force. This force is called friction. It is a force that resists motion between 2 surfaces that are in contact. It alway ...
Fall Final Study Guide Define a scalar quantity. A bicycle rider
... 15. 1 millimeter is equal to how many meters? 10-3 m. 16. 86.2 cm is equal to how many kilometers? 8.62x10-4 km 17. Tim has a problem to do involving time, distance, and velocity, but he has forgotten the formula. The question asks him for a measurement in seconds, and the numbers that are given hav ...
... 15. 1 millimeter is equal to how many meters? 10-3 m. 16. 86.2 cm is equal to how many kilometers? 8.62x10-4 km 17. Tim has a problem to do involving time, distance, and velocity, but he has forgotten the formula. The question asks him for a measurement in seconds, and the numbers that are given hav ...
Force of Friction
... Friction acts to oppose motion between two surfaces in contact Ff Dependant on – Surfaces – Normal Force FF ...
... Friction acts to oppose motion between two surfaces in contact Ff Dependant on – Surfaces – Normal Force FF ...